|
Candelaria Of San José
Candelaria de San José (11 August 1863 - 31 January 1940) was a Venezuelan religious sister and the founder of the Carmelite Sisters of Venezuela - also known as the Carmelites of Mother Candelaria. The death of her parents in 1870 and 1887 prompted her to assume household responsibilities though in 1900 set her heart on aiding others in her area; this started in 1903 when she served as the director of a new hospital though she also tended to ill people during epidemics and conflicts that broke out over time. Her beatification was celebrated on 27 April 2008 and was the first to be celebrated on her home soil; Cardinal José Saraiva Martins presided over the celebration on the behalf of Pope Benedict XVI. Life Susana Paz-Castillo Ramírez was born on 11 August 1863 in Guárico in Venezuela to Francisco de Paula Paz-Castillo and María del Rosario Ramírez. Her father died on 23 November 1870 when she was seven and her mother died on 24 December 1887; it was upon her mother's de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beatification
Beatification (from Latin ''beatus'', "blessed" and ''facere'', "to make”) is a recognition accorded by the Catholic Church of a deceased person's entrance into Heaven and capacity to intercede on behalf of individuals who pray in their name. ''Beati'' is the plural form, referring to those who have undergone the process of beatification; they possess the title of "Blessed" (abbreviation "Bl.") before their names and are often referred to in English as "a Blessed" or, plurally, "Blesseds". History Local bishops had the power of beatifying until 1634, when Pope Urban VIII, in the apostolic constitution ''Cœlestis Jerusalem'' of 6 July, reserved the power of beatifying to the Holy See. Since the reforms of 1983, as a rule, one miracle must be confirmed to have taken place through the intercession of the person to be beatified. Miracles are almost always unexplainable medical healings, and are scientifically investigated by commissions comprising physicians and theologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Anthony's Hospital
St. Anthony's Hospital is a private 393-bed hospital in St. Petersburg, Florida. It was founded by the Franciscan Sisters of Allegany in 1931 and is part of BayCare Health System. History The hospital opened in 1920 as Faith Hospital. The hospital faced financial troubles due to the Great Depression and closed in 1930. In June 1931, the Franciscan Sisters of Allegany bought Faith Hospital for $40,000 (). They renamed the hospital after the Franciscan saint, St. Anthony of Padua Anthony of Padua ( it, Antonio di Padova) or Anthony of Lisbon ( pt, António/Antônio de Lisboa; born Fernando Martins de Bulhões; 15 August 1195 – 13 June 1231) was a Portuguese Catholic priest and friar of the Franciscan Order. He was bor ..., because of his selfless dedication to God. References External links * Hospitals in Florida Buildings and structures in St. Petersburg, Florida Hospital buildings completed in 1920 1920 establishments in Florida Hospitals established in 1920< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nihil Obstat
''Nihil obstat'' (Latin for "nothing hinders" or "nothing stands in the way") is a declaration of no objection that warrants censoring of a book, e.g., Catholic published books, to an initiative, or an appointment. Publishing The phrase ''nihil obstat'' is used by a cleric, of the Catholic Church, known as a ''Censor Librorum'', to indicate that a book contains nothing contrary to Catholic doctrines, faith, or morals. Canon law requires this approval for the publication of books by faithful Catholics if they "touch upon matters of faith and morals", and requires that pastors enforce this rule. The ''Censor librorum'' (Latin for "censor of books") is delegated by a bishop of the Catholic Church. The ''Censor Librorum'' reviews the text in question, a process that in the modern era is roughly two months long. If an author is a member of a religious institute (such as a monastery), and if the book concerns religion or morals, then canon law requires obtaining the '' imprimi pote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congregation For The Causes Of Saints
In the Catholic Church, the Dicastery for the Causes of Saints, previously named the Congregation for the Causes of Saints (), is the dicastery of the Roman Curia that oversees the complex process that leads to the canonization of saints, passing through the steps of a declaration of "heroic virtues" and beatification. After preparing a case, including the approval of miracles, the case is presented to the pope, who decides whether or not to proceed with beatification or canonization. History The predecessor of the congregation was the Sacred Congregation for Rites, founded by Pope Sixtus V on 22 January 1588 in the bull '' Immensa Aeterni Dei''. The congregation dealt both with regulating divine worship and the causes of saints. On 8 May 1969, Pope Paul VI issued the Apostolic Constitution ''Sacra Rituum Congregatio'', dividing it into two congregations, the Congregation for the Divine Worship and one for the causes of saints. The latter was given three offices, those o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesus Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious leader; he is the central figure of Christianity, the world's largest religion. Most Christians believe he is the incarnation of God the Son and the awaited Messiah (the Christ) prophesied in the Hebrew Bible. Virtually all modern scholars of antiquity agree that Jesus existed historically. Research into the historical Jesus has yielded some uncertainty on the historical reliability of the Gospels and on how closely the Jesus portrayed in the New Testament reflects the historical Jesus, as the only detailed records of Jesus' life are contained in the Gospels. Jesus was a Galilean Jew who was circumcised, was baptized by John the Baptist, began his own ministry and was often referred to as "rabbi". Jesus debated with fellow Jews on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) certified the global eradication of the disease in 1980, making it the only human disease to be eradicated. The initial symptoms of the disease included fever and vomiting. This was followed by formation of ulcers in the mouth and a skin rash. Over a number of days, the skin rash turned into the characteristic fluid-filled blisters with a dent in the center. The bumps then scabbed over and fell off, leaving scars. The disease was spread between people or via contaminated objects. Prevention was achieved mainly through the smallpox vaccine. Once the disease had developed, certain antiviral medication may have helped. The risk of death was about 30%, with higher rates among babies. Often, those who survived had extensive scarring of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1929 Cumaná Earthquake
The 1929 Cumaná earthquake occurred on January 17 at 07:45:44 local time, affecting Venezuela. Measuring 6.9 on the surface wave magnitude scale () at a depth of 10 km, the earthquake severely damaged the city of Cumaná in Sucre state. The earthquake had an epicenter located offshore in the Caribbean Sea, but had a maximum Modified Mercalli intensity scale rating of IX (''Violent'') or XI (''Extreme'') lasting 30 seconds, causing major damage and a tsunami. More than 200 people were killed although the finalized death toll is unknown; possibly 1,600. Earthquake The earthquake was associated with strike-slip faulting at a shallow depth; a common characteristic for earthquakes of this depth in the region of northern Venezuela. The El Pilar Fault System, a right-lateral strike-slip fault extending 350 km from the Cariaco Basin to the Paria Peninsula is thought to be the source of the event. The earthquake in 1929 is thought to have ruptured approximately 30 to 40 km of the fault. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mistress Of Novices
In the Roman Catholic Church, a novice master or master of novices, lat. ''Magister noviciorum'', is a member of a religious institute who is responsible for the training and government of the novitiate in that institute. In religious institutes for women, the novice mistress, lat. ''Magistra noviciorum'', is the equivalent. The direction of the novices is reserved solely to the master of novices, under the authority of the major superiors. The master of novices must be a member of the institute; he must have taken perpetual vows and be legally appointed. The novice master is often assisted by a zelator (second or deputy novice master). The novice master's duty is to see that the time devoted to the period of the novitiate be passed in prayer, meditation, and the development of character through a study of the life of Jesus Christ and the saints, church history, the vows and the constitution of the institute. Within the time of this probation, he must make reports about each novi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scapular
The scapular (from Latin ''scapulae'', "shoulders") is a Western Christian garment suspended from the shoulders. There are two types of scapulars, the monastic and devotional scapular, although both forms may simply be referred to as "scapular". As an object of popular piety, it serves to remind the wearers of their commitment to live a Christian life. The "monastic scapular" appeared first, perhaps as early as the 7th century in the Order of Saint Benedict. It is a length of cloth suspended both front and back from the shoulders of the wearer, often reaching to the knees. It may vary in shape, color, size and style. Monastic scapulars originated as aprons worn by medieval monks, and were later extended to habits for members of religious organizations, orders or confraternities. Monastic scapulars now form part of the habit of monks and nuns in many Christian orders. The "devotional scapular" is a much smaller item and evolved from the monastic scapular. These may also be worn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Chapter
A chapter ( la, capitulum or ') is one of several bodies of clergy in Roman Catholic, Old Catholic, Anglican, and Nordic Lutheran churches or their gatherings. Name The name derives from the habit of convening monks or canons for the reading of a chapter of the Bible or a heading of the order's rule. The 6th-century St Benedict directed that his monks begin their daily assemblies with such readings and over time expressions such as "coming together for the chapter" (') found their meaning transferred from the text to the meeting itself and then to the body gathering for it. The place of such meetings similarly became known as the "chapter house" or "room". Cathedral chapter A cathedral chapter is the body ("college") of advisors assisting the bishop of a diocese at the cathedral church. These were a development of the presbyteries (') made up of the priests and other church officials of cathedral cities in the early church. In the Catholic Church, they are now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
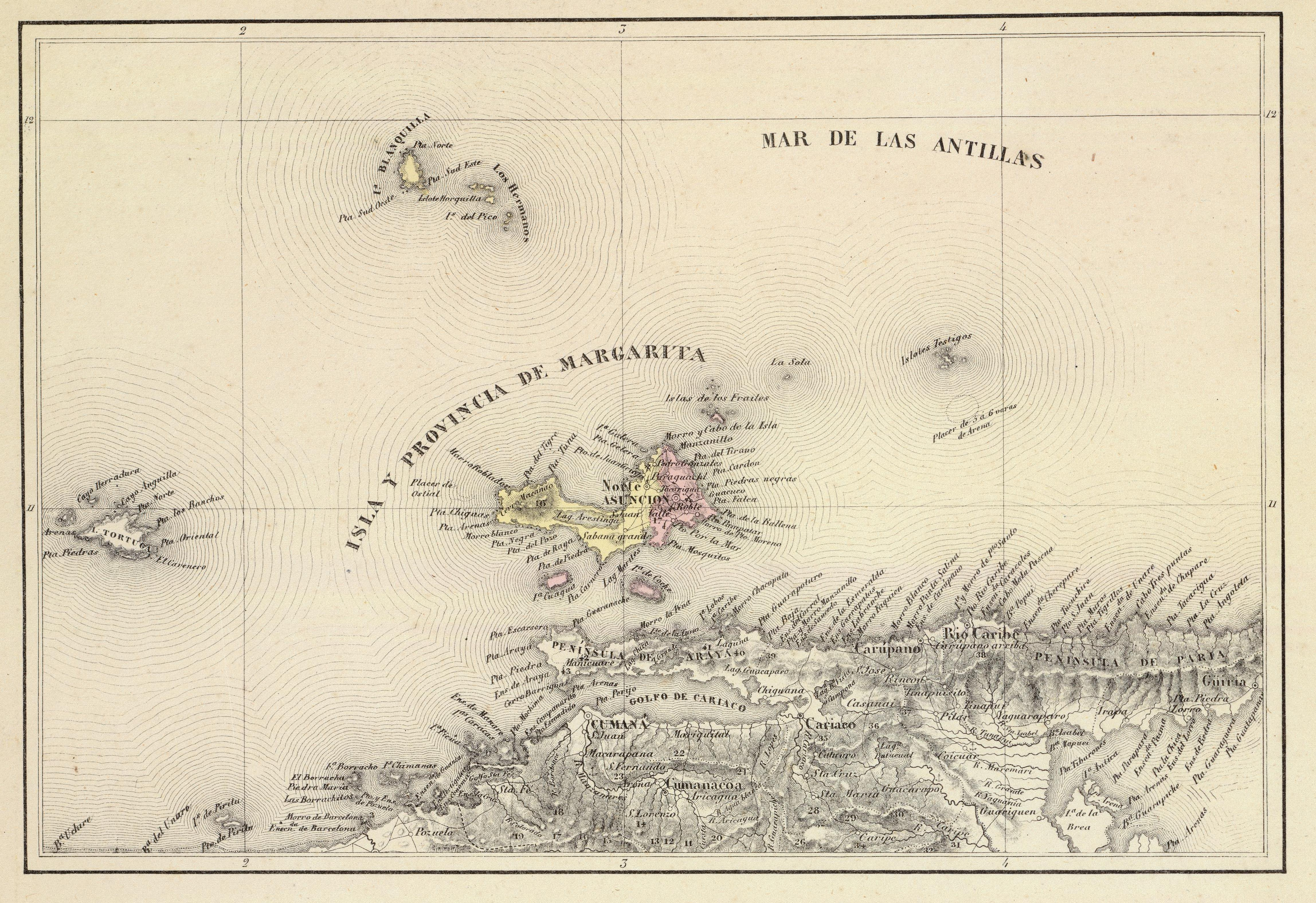
Isla Margarita
Margarita Island (, ) is the largest island in the Venezuelan state of Nueva Esparta, situated off the northeastern coast of the country, in the Caribbean Sea. The capital city of Nueva Esparta, La Asunción, is located on the island. History Age of Exploration Christopher Columbus was the first European to arrive on Margarita Island in 1498. The local natives were the Guaiqueries people. The coast of the island was abundant in pearls, which represented almost a third of all New World tribute to the Spanish Crown. Margarita Island was fortified against the increasing threat of pirate attacks, and some fortifications remain today. It was the center of Spanish colonial Margarita Province, established in 1525. In 1561, the island was seized by Lope de Aguirre, a notoriously violent and rebellious conquistador. Around 1675, the island was captured again, this time by Red Legs Greaves, a pirate known for his humanity and morality. He captured a fleet of Spanish ships off po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carmelites
, image = , caption = Coat of arms of the Carmelites , abbreviation = OCarm , formation = Late 12th century , founder = Early hermits of Mount Carmel , founding_location = Mount Carmel , type = Mendicant order of pontifical right , status = Institute of Consecrated Life , membership = 1,979 (1,294 priests) as of 2017 , leader_title = Motto , leader_name = la, Zelo zelatus sum pro Domino Deo exercituumEnglish: ''With zeal have I been zealous for the Lord God of hosts'' , leader_title2 = General Headquarters , leader_name2 = Curia Generalizia dei CarmelitaniVia Giovanni Lanza, 138, 00184 Roma, Italia , leader_title3 = Prior General , leader_name3 = Mícéal O'Neill, OCarm , leader_title4 = Patron saints , leader_name4 = Our Lady of Mt. Carmel, Elijah , parent_organization = Catholic Church , website = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |