|
Campbell's Theorem (probability)
In probability theory and statistics, Campbell's theorem or the Campbell–Hardy theorem is either a particular equation or set of results relating to the Expected value, expectation of a Function (mathematics), function summed over a point process to an integral involving the Moment measure#First moment measure, mean measure of the point process, which allows for the calculation of expected value and variance of the random summation, sum. One version of the theorem,D. Stoyan, W. S. Kendall, J. Mecke. ''Stochastic geometry and its applications'', volume 2. Wiley Chichester, 1995. also known as Campbell's formula, entails an integral equation for the aforementioned sum over a general point process, and not necessarily a Poisson point process. There also exist equations involving moment measures and factorial moment measures that are considered versions of Campbell's formula. All these results are employed in probability and statistics with a particular importance in the theory of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Theory
Probability theory or probability calculus is the branch of mathematics concerned with probability. Although there are several different probability interpretations, probability theory treats the concept in a rigorous mathematical manner by expressing it through a set of axioms of probability, axioms. Typically these axioms formalise probability in terms of a probability space, which assigns a measure (mathematics), measure taking values between 0 and 1, termed the probability measure, to a set of outcomes called the sample space. Any specified subset of the sample space is called an event (probability theory), event. Central subjects in probability theory include discrete and continuous random variables, probability distributions, and stochastic processes (which provide mathematical abstractions of determinism, non-deterministic or uncertain processes or measured Quantity, quantities that may either be single occurrences or evolve over time in a random fashion). Although it is no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Statistics ...
Spatial statistics is a field of applied statistics dealing with spatial data. It involves stochastic processes (random fields, point processes), sampling, smoothing and interpolation, regional ( areal unit) and lattice ( gridded) data, point patterns, as well as image analysis and stereology. See also *Geostatistics *Modifiable areal unit problem *Spatial analysis *Spatial econometrics * Statistical geography *Spatial epidemiology * Spatial network * Statistical shape analysis References {{Statistics-stub Applied statistics Statistics Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moment-generating Function
In probability theory and statistics, the moment-generating function of a real-valued random variable is an alternative specification of its probability distribution. Thus, it provides the basis of an alternative route to analytical results compared with working directly with probability density functions or cumulative distribution functions. There are particularly simple results for the moment-generating functions of distributions defined by the weighted sums of random variables. However, not all random variables have moment-generating functions. As its name implies, the moment-generating function can be used to compute a distribution’s moments: the -th moment about 0 is the -th derivative of the moment-generating function, evaluated at 0. In addition to univariate real-valued distributions, moment-generating functions can also be defined for vector- or matrix-valued random variables, and can even be extended to more general cases. The moment-generating function of a real-valu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry Bateman
Harry Bateman FRS (29 May 1882 – 21 January 1946) was an English mathematician with a specialty in differential equations of mathematical physics. With Ebenezer Cunningham, he expanded the views of spacetime symmetry of Lorentz and Poincare to a more expansive conformal group of spacetime leaving Maxwell's equations invariant. Moving to the US, he obtained a Ph.D. in geometry with Frank Morley and became a professor of mathematics at California Institute of Technology. There he taught fluid dynamics to students going into aerodynamics with Theodore von Karman. Bateman made a broad survey of applied differential equations in his Gibbs Lecture in 1943 titled, "The control of an elastic fluid". Biography Bateman was born in Manchester, England, on 29 May 1882. He first gained an interest in mathematics during his time at Manchester Grammar School. In his final year, he won a scholarship to Trinity College, Cambridge. Bateman studied with coach Robert Alfred Herman to prepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Particle
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay but may also be produced in different ways. Alpha particles are named after the first letter in the Greek alphabet, α. The symbol for the alpha particle is α or α2+. Because they are identical to helium nuclei, they are also sometimes written as He2+ or 2+ indicating a helium ion with a +2 charge (missing its two electrons). Once the ion gains electrons from its environment, the alpha particle becomes a normal (electrically neutral) helium atom . Alpha particles have a net spin of zero. When produced in standard alpha radioactive decay, alpha particles generally have a kinetic energy of about 5 MeV and a velocity in the vicinity of 4% of the speed of light. They are a highly ionizing form of particle radiation, with low penetration depth (stopped b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Geiger
Johannes Wilhelm Geiger ( , ; ; 30 September 1882 – 24 September 1945) was a German nuclear physicist. He is known as the inventor of the Geiger counter, a device used to detect ionizing radiation, and for carrying out the Rutherford scattering experiments, which led to the discovery of the atomic nucleus. He also performed the Bothe–Geiger coincidence experiment, which confirmed the conservation of energy in light-particle interactions. He was the brother of meteorologist and climatologist Rudolf Geiger. Biography Geiger was born in 1882 in Neustadt an der Haardt. He was one of five children born to the Indologist Wilhelm Ludwig Geiger, who was a professor at the University of Erlangen. In 1902, Geiger started studying physics and mathematics at Erlangen and was awarded a doctorate in 1906. His thesis was on electrical discharges through gases. He received a fellowship to the University of Manchester and worked as an assistant to Arthur Schuster. In 1907, after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest Rutherford
Ernest Rutherford, 1st Baron Rutherford of Nelson (30 August 1871 – 19 October 1937) was a New Zealand physicist who was a pioneering researcher in both Atomic physics, atomic and nuclear physics. He has been described as "the father of nuclear physics", and "the greatest experimental physics, experimentalist since Michael Faraday". In 1908, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry "for his investigations into the disintegration of the elements, and the chemistry of radioactive substances." He was the first Oceanian Nobel laureate, and the first to perform the awarded work in Canada. Rutherford's discoveries include the concept of radioactive half-life, the radioactive element radon, and the differentiation and naming of Alpha decay, alpha and Beta particle, beta radiation. Together with Thomas Royds, Rutherford is credited with proving that alpha radiation is composed of helium nuclei. In 1911, he theorized that atoms have their charge concentrated in a very small atomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
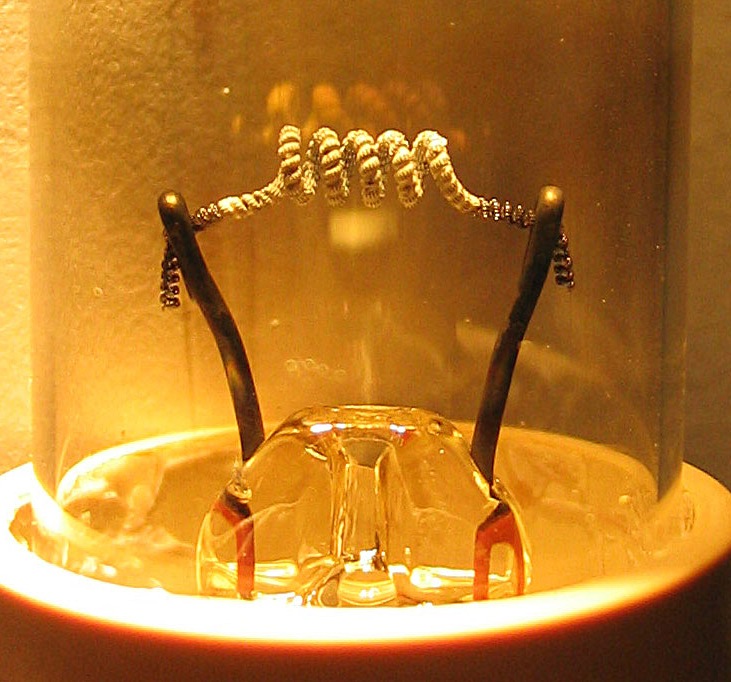
Vacuum Tubes
A vacuum tube, electron tube, thermionic valve (British usage), or tube (North America) is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. It takes the form of an evacuated tubular envelope of glass or sometimes metal containing electrodes connected to external connection pins. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental Electronics, electronic functions such as signal amplifier, amplification and current Rectifier, rectification. Non-thermionic types such as vacuum phototubes achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light and measurement of its intensity. In both types the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The first, and simplest, vacuum tube, the diode or Flem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shot Noise
Shot noise or Poisson noise is a type of noise which can be modeled by a Poisson process. In electronics shot noise originates from the discrete nature of electric charge. Shot noise also occurs in photon counting in optical devices, where shot noise is associated with the particle nature of light. Origin In a statistical experiment such as tossing a fair coin and counting the occurrences of heads and tails, the numbers of heads and tails after many throws will differ by only a tiny percentage, while after only a few throws outcomes with a significant excess of heads over tails or vice versa are common; if an experiment with a few throws is repeated over and over, the outcomes will fluctuate a lot. From the law of large numbers, one can show that the relative fluctuations reduce as the reciprocal square root of the number of throws, a result valid for all statistical fluctuations, including shot noise. Shot noise exists because phenomena such as light and electric curren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermionic Emission
Thermionic emission is the liberation of charged particles from a hot electrode whose thermal energy gives some particles enough kinetic energy to escape the material's surface. The particles, sometimes called ''thermions'' in early literature, are now known to be ions or electrons. Thermal electron emission specifically refers to emission of electrons and occurs when thermal energy overcomes the material's work function. After emission, an opposite charge of equal magnitude to the emitted charge is initially left behind in the emitting region. But if the emitter is connected to a battery, that remaining charge is neutralized by charge supplied by the battery as particles are emitted, so the emitter will have the same charge it had before emission. This facilitates additional emission to sustain an electric current. Thomas Edison in 1880 while inventing his light bulb noticed this current, so subsequent scientists referred to the current as the Edison effect, though it wasn't un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Robert Campbell
Norman Robert Campbell (1880–1949) was an English physicist and philosopher of science. Early life Norman Robert Campbell was born in 1880. He was the son of William Middleton Campbell, Governor of the Bank of England, and his wife Edith Agneta Bevan. He was educated at Eton College and at Trinity College, Cambridge, graduating B.A. in 1902. Career Campbell became a fellow at Trinity College, Cambridge in 1902. He was also a research assistant at the Cavendish Laboratory under the direction of J. J. Thomson. He became an honorary fellow in physics research at Leeds University in 1913. During World War I Campbell was at the National Physical Laboratory, working under Clifford Paterson. They investigated spark discharge in internal combustion engines. He then worked from 1919 to 1944 as a member of the research staff at the Hirst Research Centre of the General Electric Company England, set up in Wembley Middlesex in 1919. While at Hirst Research he encouraged unqua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proceedings Of The Cambridge Philosophical Society
''Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society'' is a mathematical journal published by Cambridge University Press for the Cambridge Philosophical Society. It aims to publish original research papers from a wide range of pure and applied mathematics. The journal, titled ''Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society'' before 1975, has been published since 1843. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in *MathSciNet *Science Citation Index Expanded *Scopus *ZbMATH Open See also *Cambridge Philosophical Society The Cambridge Philosophical Society (CPS) is a scientific society at the University of Cambridge. It was founded in 1819. The name derives from the medieval use of the word philosophy to denote any research undertaken outside the fields of law ... External linksofficial website References Academic journals associated with learned and professional societies Cambridge University Press academic journals Mathematics e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |