|
California Unions For Reliable Energy
California Unions for Reliable Energy (CURE) is a coalition of labor unions, mainly affiliated with the State Building & Construction Trades Council of California, that uses California Environmental Quality Act lawsuits (or threats thereof) to force developers of power plants, including new solar and other clean energy projects, to sign "project labor agreements", which require construction be done by union workers. This practice has been described as "greenmailing". Using union construction workers has been estimated to increase the cost of renewable energy projects by about 20%. References {{reflist, refs= {{ cite news , url=https://www.latimes.com/business/la-xpm-2011-feb-05-la-fi-solar-unions-20110205-story.html , title=Labor coalition's tactics on renewable energy projects are criticized - Three California unions criticize CURE for challenging construction projects on environmental grounds, then dropping objections after CURE's affiliate wins contracts to supply worke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Environmental Quality Act
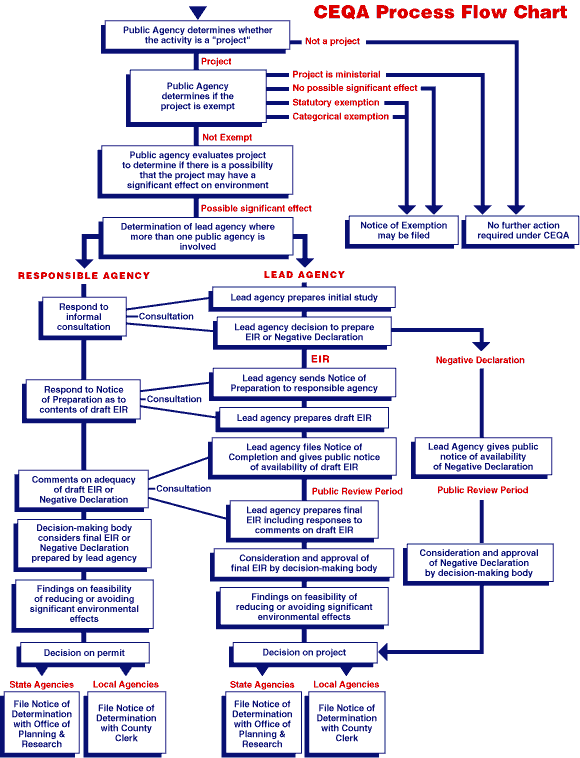
The California Environmental Quality Act (CEQA) is a California statute passed in 1970 and signed in to law by then-Governor Ronald Reagan, shortly after the United States federal government passed the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA), to institute a statewide policy of environmental protection. CEQA does not directly regulate land uses, but instead requires state and local agencies within California to follow a protocol of analysis and public disclosure of environmental impacts of proposed projects and, in a departure from NEPA, adopt all feasible measures to mitigate those impacts. CEQA makes environmental protection a mandatory part of every California state and local (public) agency's decision making process. It has also become the basis for numerous lawsuits concerning public and private projects. CEQA has been criticized for being "abused" (used for reasons than environmental ones) to block, downsize, delay, or gain other concessions from new development. CEQA has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monterey County Weekly
The ''Monterey County Weekly'' (sometimes called the "Weekly," formerly the ''Coast Weekly.'') is a locally owned and independent newsmedia company founded in 1988. As per the publication's name, it publishes in print weekly, and since 2020 online daily as ''Monterey County NOW''. The company is based in the city of Seaside, in Monterey County, California. The Weekly has been a member of the Association of Alternative Newsmedia since 1989. History Monterey County Weekly was launched in 1988 by Bradley Zeve, its founding Editor & Publisher, and current CEO. Zeve served as the Free Speech chair for the Association of Alternative Newsmedia (2004-2019), is the former president of the Sea Studios Foundation and co-founded The Sun newspaper in Santa Cruz, CA. Erik Cushman serves as Publisher and currently sits on the California Newspaper Publisher's Association Board of Directors. Cushman was the co-founder of the Missoula Independent. The Weekly established the Monterey Count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Los Angeles Times
The ''Los Angeles Times'' (abbreviated as ''LA Times'') is a daily newspaper that started publishing in Los Angeles in 1881. Based in the LA-adjacent suburb of El Segundo since 2018, it is the sixth-largest newspaper by circulation in the United States. The publication has won more than 40 Pulitzer Prizes. It is owned by Patrick Soon-Shiong and published by the Times Mirror Company. The newspaper’s coverage emphasizes California and especially Southern California stories. In the 19th century, the paper developed a reputation for civic boosterism and opposition to labor unions, the latter of which led to the bombing of its headquarters in 1910. The paper's profile grew substantially in the 1960s under publisher Otis Chandler, who adopted a more national focus. In recent decades the paper's readership has declined, and it has been beset by a series of ownership changes, staff reductions, and other controversies. In January 2018, the paper's staff voted to unionize and final ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as '' The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national " newspaper of record". For print it is ranked 18th in the world by circulation and 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 1896, through a dual-class share structure after its shares became publicly traded. A. G. Sulzberger, the paper's publisher and the company's chairman, is the fifth generation of the family to head the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environment Of California
The environment of California describes results of human habitation of the American State of California. History of environmental action California's Mediterranean climate makes vegetation susceptible to wildfires through the dry summers. Aboriginal Californians used fire to control brush, promote growth of seed-producing plants important to subsistence, and perhaps as an aid to hunting wildlife. These periodic fires kept woodland areas relatively open until 20th century laws curtailed burning in an effort to protect structures. European crops and livestock were introduced with missions along the coast from San Diego to San Francisco Bay through the late 18th and early 19th century. The California Gold Rush caused explosive population growth making San Francisco the only 19th century city west of St. Louis, Missouri.Donley, Allan, Caro, and Patton ''Atlas of California'' (1979) pp.9-19 Water soon became the limiting factor for population growth, and early laws establish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)