|
Calcium Concentration Microdomains
Calcium concentration microdomains (CCMs) are sites in a cell's cytoplasm with a localised high calcium ion (Ca2+) concentration. They are found immediately around the intracellular opening of calcium channels; when a calcium channel opens, the Ca2+ concentration in the adjacent CCM increases up to several hundred micromolar (μM). These microdomains take part in calcium signaling, which has a diverse range of potential outcomes. Calcium concentration microdomains can be visualised with fluorescence microscopy by using aequorin as a reporter protein. Ion Channel Process The actions of the Na-K-ATPase enzyme relate with the creation of calcium-signaling microdomains. Na-K-ATPase is a protein that pumps Na+ and K+ across the cell membrane. Na-K-ATPase helps to keep the body at equilibrium by the movement of those ions through the plasma membrane. This ion pump helps to reset the movement of ions during an action potential by sending K+ into the cell and sending Na+ out of the cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are cytosol (a gel-like substance), the organelles (the cell's internal sub-structures), and various cytoplasmic inclusions. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance or cytoplasmic matrix which remains after exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, the plant plastids, lipid droplets, and vacuoles. Most cellular activities take place within the cytoplasm, such as many metabolic pathways including glycolysis, and proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Ion
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossilised remnants of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name derives from Latin ''calx'' " lime", which was obtained from heating limestone. Some calcium compounds were known to the ancients, though their chemistry was unknown until the seventeenth century. Pure calcium was isolated in 1808 via electrolysis of its oxide by Humphry Davy, who named the element. Calcium compounds are widely used in many industries: in foods and pharmace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
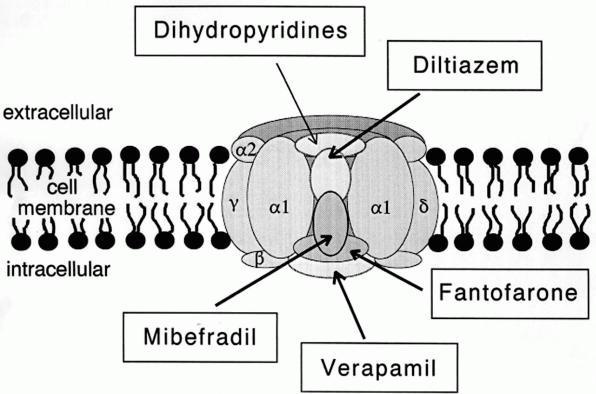
Calcium Channel
A calcium channel is an ion channel which shows selective permeability to calcium ions. It is sometimes synonymous with voltage-gated calcium channel, although there are also ligand-gated calcium channels. Comparison tables The following tables explain gating, gene, location and function of different types of calcium channels, both voltage and ligand-gated. Voltage-gated Ligand-gated *the ''receptor-operated calcium channels'' (in vasoconstriction) ** P2X receptors Page 479 Pharmacology L-type calcium channel blockers are used to treat hypertension. In most areas of the body, depolarization is mediated by sodium influx into a cell; changing the calcium permeability has little effect on action potentials. However, in many smooth muscle tissues, depolarization is mediated primarily by calcium influx into the cell. L-type calcium channel blockers selectively inhibit these action potentials in smooth muscle which leads to dilation of blood vessels; this in turn corrects hype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molar Concentration
Molar concentration (also called molarity, amount concentration or substance concentration) is a measure of the concentration of a chemical species, in particular of a solute in a solution, in terms of amount of substance per unit volume of solution. In chemistry, the most commonly used unit for molarity is the number of moles per liter, having the unit symbol mol/L or mol/ dm3 in SI unit. A solution with a concentration of 1 mol/L is said to be 1 molar, commonly designated as 1 M. Definition Molar concentration or molarity is most commonly expressed in units of moles of solute per litre of solution. For use in broader applications, it is defined as amount of substance of solute per unit volume of solution, or per unit volume available to the species, represented by lowercase c: :c = \frac = \frac = \frac. Here, n is the amount of the solute in moles, N is the number of constituent particles present in volume V (in litres) of the solution, and N_\text is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Signaling
Calcium signaling is the use of calcium ions (Ca2+) to communicate and drive intracellular processes often as a step in signal transduction. Ca2+ is important for cellular signalling, for once it enters the cytosol of the cytoplasm it exerts allosteric regulatory effects on many enzymes and proteins. Ca2+ can act in signal transduction resulting from activation of ion channels or as a second messenger caused by indirect signal transduction pathways such as G protein-coupled receptors. Concentration regulation The resting concentration of Ca2+ in the cytoplasm is normally maintained around 100 nM. This is 20,000- to 100,000-fold lower than typical extracellular concentration. To maintain this low concentration, Ca2+ is actively pumped from the cytosol to the extracellular space, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), and sometimes into the mitochondria. Certain proteins of the cytoplasm and organelles act as buffers by binding Ca2+. Signaling occurs when the cell is stimulated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescence Microscopy
A fluorescence microscope is an optical microscope that uses fluorescence instead of, or in addition to, scattering, reflection, and attenuation or absorption, to study the properties of organic or inorganic substances. "Fluorescence microscope" refers to any microscope that uses fluorescence to generate an image, whether it is a simple set up like an epifluorescence microscope or a more complicated design such as a confocal microscope, which uses optical sectioning to get better resolution of the fluorescence image. Principle The specimen is illuminated with light of a specific wavelength (or wavelengths) which is absorbed by the fluorophores, causing them to emit light of longer wavelengths (i.e., of a different color than the absorbed light). The illumination light is separated from the much weaker emitted fluorescence through the use of a spectral emission filter. Typical components of a fluorescence microscope are a light source ( xenon arc lamp or mercury-vapor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aequorin
Aequorin is a calcium-activated photoprotein isolated from the hydrozoan ''Aequorea victoria''. Its bioluminescence was studied decades before the protein was isolated from the animal by Osamu Shimomura in 1962. In the animal, the protein occurs together with the green fluorescent protein to produce green light by resonant energy transfer, while aequorin by itself generates blue light. Discussions of "jellyfish DNA" that can make "glowing" animals often refer to transgenic animals that express the green fluorescent protein, not aequorin, although both originally derive from the same animal. Apoaequorin, the protein portion of aequorin, is an ingredient in the dietary supplement Prevagen. The US Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has charged the maker with false advertising for its memory improvement claims. Discovery Work on aequorin began with E. Newton Harvey in 1921. Though Harvey was unable to demonstrate a classical luciferase-luciferin reaction, he showed that water could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Ion
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. The free metal does not occur in nature, and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl). Many salts of sodium are highly water-soluble: sodium ions have been leached by the action of water from the Earth's minerals over eons, and thus sodium and chlorine are the most common dissolved elements by weight in the oceans. Sodium was first isolated by Humphry Davy in 1807 by the electrolysis of sodium hydroxide. Among many other useful sodium compounds, sodium hydroxide ( lye) is used in soap manufacture, and sodium chloride (edible salt) is a de-icing agent and a nutrient for animals including hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Ion
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin '' kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to form flaky white potassium peroxide in only seconds of exposure. It was first isolated from potash, the ashes of plants, from which its name derives. In the periodic table, potassium is one of the alkali metals, all of which have a single valence electron in the outer electron shell, that is easily removed to create an ion with a positive charge – a cation, that combines with anions to form salts. Potassium in nature occurs only in ionic salts. Elemental potassium reacts vigorously with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite hydrogen emitted in the reaction, and burning with a lilac- colored flame. It is found dissolved in sea water (which is 0.04% potassium by weight), and occurs in many minerals such as orthoclas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action Potential
An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells, called excitable cells, which include neurons, muscle cells, and in some plant cells. Certain endocrine cells such as pancreatic beta cells, and certain cells of the anterior pituitary gland are also excitable cells. In neurons, action potentials play a central role in cell-cell communication by providing for—or with regard to saltatory conduction, assisting—the propagation of signals along the neuron's axon toward synaptic boutons situated at the ends of an axon; these signals can then connect with other neurons at synapses, or to motor cells or glands. In other types of cells, their main function is to activate intracellular processes. In muscle cells, for example, an action potential is the first step in the chain of event ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. The human body recycles its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day. It is also a precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base ( adenine), the sugar ribose, and the triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of an adenine attached by the 9-nitrogen atom to the 1′ carbon atom of a sugar ( ribose), which in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |