|
Cahuapanan Languages
The Cahuapanan languages are a language family spoken in the Amazon basin of northern Peru. They include two languages, Chayahuita and Jebero, which are spoken by more than 11,300 people. Chayahuita is spoken by most of that number, but Jebero is almost extinct. Language contact Jolkesky (2016) notes that there are lexical similarities with the Kechua, Arawak, Kandoshi, Pukina, and Karib language families due to contact. Varieties * Chayahuita or Chawi (also known or rendered as Balsapuertino, Cahuapa, Chayabita, Chayawita, Chayhuita, Tshaahui, Paranapura, Shayabit) ** Chayahuita dialect ** Cahuapana dialect * Jebero (also known or rendered as Chebero, Xebero, Xihuila) ''Glottolog'' classifies the extinct language Maynas as close to Chawi. Other Cahuapanan varieties that are listed by Loukotka (1968): *Yamorai - spoken on the Sillai River in Loreto Department *Ataguate - extinct language of the same region, once spoken on the Aipena River and around Lake Atagua (unattest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macro-Jibaro
The Macro-Jibaro proposal, also known as ''(Macro-)Andean'', is a language proposal of Morris Swadesh and other historical linguists. The two families, Jivaroan and Cahuapanan are most frequently linked, the isolates less often. Documentation of Urarina is underway as of 2006, but Puelche and Huarpe are extinct. Kaufman (1994) linked Huarpe instead to the Muran languages and Matanawi (see Macro-Warpean), but as of 1990 found the Jibaro–Cahuapanan connection plausible. It forms one part of his expanded 2007 suggestion for Macro-Andean.Kaufman, Terrence. 2007. South America. In: R. E. Asher and Christopher Moseley (eds.), ''Atlas of the World’s Languages (2nd edition)'', 59–94. London: Routledge. David Payne (1981) proposes that Candoshi Candoshi-Shapra (also known as Candoshi, Candoxi, Kandoshi, and Murato) is an indigenous American language isolate, spoken by several thousand people in western South America along the Chapuli, Huitoyacu, Pastaza, and Morona river va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freshwater Crab
Around 1,300 species of freshwater crabs are distributed throughout the tropics and subtropics, divided among eight families. They show direct development and maternal care of a small number of offspring, in contrast to marine crabs, which release thousands of planktonic larvae. This limits the dispersal abilities of freshwater crabs, so they tend to be endemic to small areas. As a result, a large proportion are threatened with extinction. Systematics More than 1,300 described species of freshwater crabs are known, out of a total of 6,700 species of crabs across all environments. The total number of species of freshwater crabs, including undescribed species, is thought to be up to 65% higher, potentially up to 2,155 species, although most of the additional species are currently unknown to science. They belong to eight families, each with a limited distribution, although various crabs from other families are also able to tolerate freshwater conditions ( euryhaline) or are secon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepidocaryum
''Lepidocaryum'' is a monotypic genus of flowering plant in the palm family from South America where the lone species, ''Lepidocaryum tenue'', is commonly called poktamui. Nine species names have been published, but palm taxonomists currently agree that just one variable species includes them all.Riffle, Robert L. and Craft, Paul (2003) ''An Encyclopedia of Cultivated Palms''. Portland: Timber Press. / The most reduced member of the Lepidocaryeae, it is similar in appearance to three closely related genera, ''Mauritia'', ''Mauritiella'', and ''Lytocaryum''.Uhl, Natalie W. and Dransfield, John (1987) ''Genera Palmarum - A classification of palms based on the work of Harold E. Moore''. Lawrence, Kansas: Allen Press. / The genus name combines the Greek words for "scale" and "nut" and the species epithet is Latin for "thin". Description At just 2.5 cm in width, the clustering trunks reach no higher than 3.5 m and are covered at the top by old, adherent leaf bases. The small, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huito
''Genipa americana'' () is a species of trees in the family Rubiaceae. It is native to the tropical forests of North and South America, as well as the Caribbean. Description ''Genipa americana'' trees are up to 30 m tall and up to 60 cm dbh. Their bark is smooth with little fissures. The leaves are opposite, obovate, or obovate oblong, 10–35 cm long, 6–13 cm wide, and glossy dark green, with entire margin, acute or acuminate apex, and attenuated base. The inflorescences are cymes up to 10 cm long. The flowers are white to yellowish, slightly fragrant, calyx bell-shaped, corolla at 2–4.5 cm long, trumpet-shaped, and five- or six-lobed. The five short stamens are inserted on top of the corolla tube. The fruit is a thick-skinned edible greyish berry 10–12 cm long, 5–9 cm in diameter. Distribution and habitat ''Genipa americana'' is native to the tropical forests of the Americas, from tropical Florida south to Argentina. It is present ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traira
The Erythrinidae are a family of fishes found in rivers and other freshwater habitats from Costa Rica south as far as Argentina. They are common and are caught with hooks by fishermen, partially because of their voracious behaviour. They are sometimes called ''trahiras'' (also spelled trairas) or ''tarariras''. The Erythrinidae include cylindrical fish with blunt heads, and prey on other fish. They can reach lengths up to . Some species can breathe air, enabling them to survive in water low in oxygen, and even to move over land between ponds. Species The 16 species are contained in three genera: *''Erythrinus'' *''Hoplerythrinus'' *''Hoplias'' - giant trahiras References * Nelson, Joseph S. (2006). ''Fishes of the World ''Fishes of the World'' by the American ichthyologist Joseph S. Nelson (1937–2011) is a standard reference for fish systematics. Now in its fifth edition (2016), the work is a comprehensive overview of the diversity and classification of the ...''. John ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
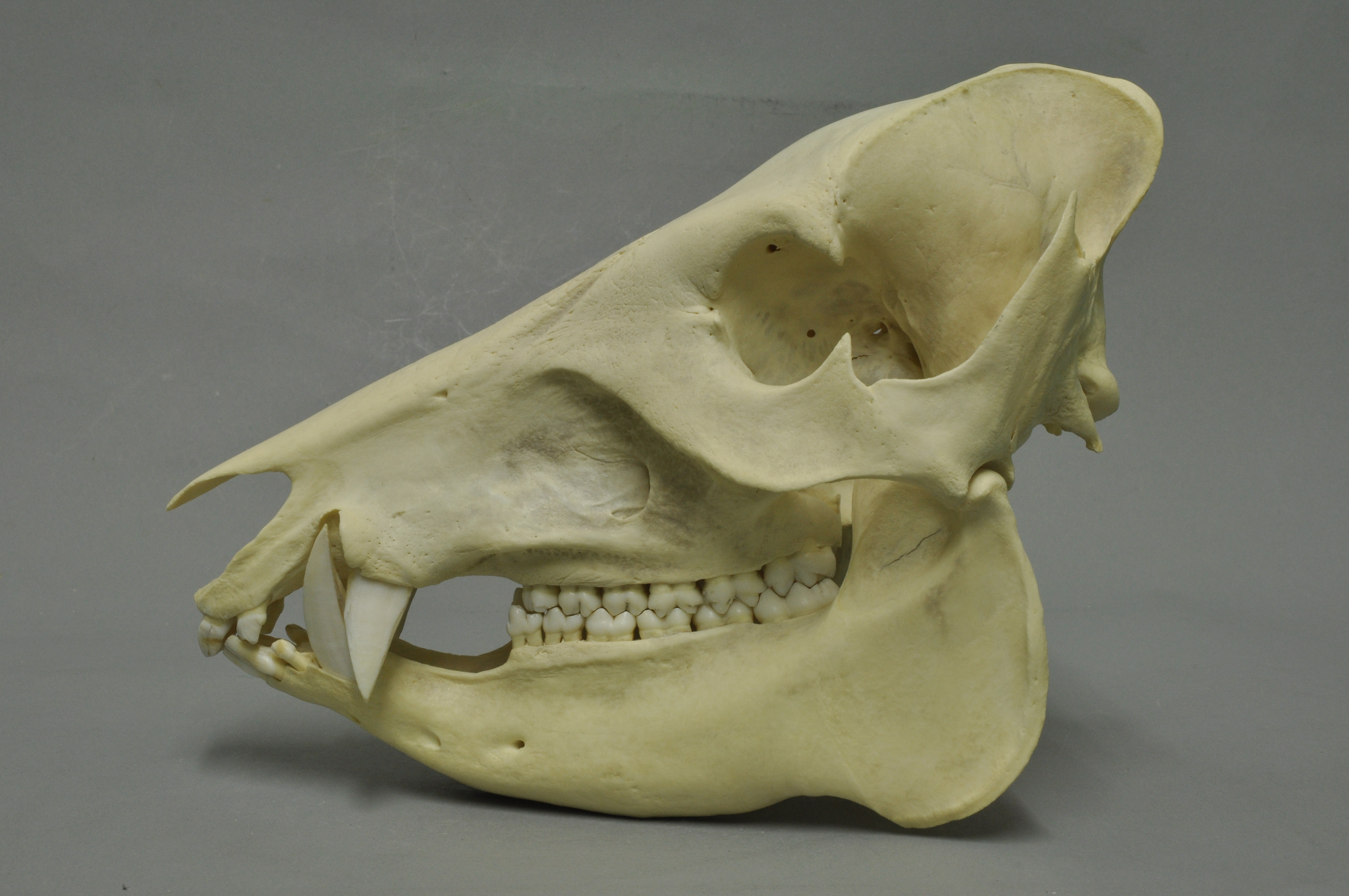
Huangana
The white-lipped peccary (''Tayassu pecari'') is a species of peccary found in Central and South America and the only member of the genus ''Tayassu''. Multiple subspecies have been identified. White-lipped peccaries are similar in appearance to pigs, but covered in dark hair (except on certain regions, such as the throat, where it is cream). The range of ''T. pecari'', which extends from Mexico to Argentina, has become fragmented, and the species's population is declining overall (especially in Mexico and Central America). They can be found in a variety of habitats. Social animals, white-lipped peccaries typically forage in large groups, which can have as many as 300 peccaries. They are an important part of their ecosystem and multiple efforts are being made to preserve them in the wild. Not all disappearances are explained, but human activities play a role, with two major threats being deforestation and hunting; the latter is very common in rural areas, although it can be dange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dictyoloma .
''Dictyoloma'' is a genus of flowering plants that belongs to the family Rutaceae The Rutaceae is a family, commonly known as the rueRUTACEAE in BoDD – Botanical Derm ... References Cneoroideae Rutaceae genera {{Rutaceae-stub ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
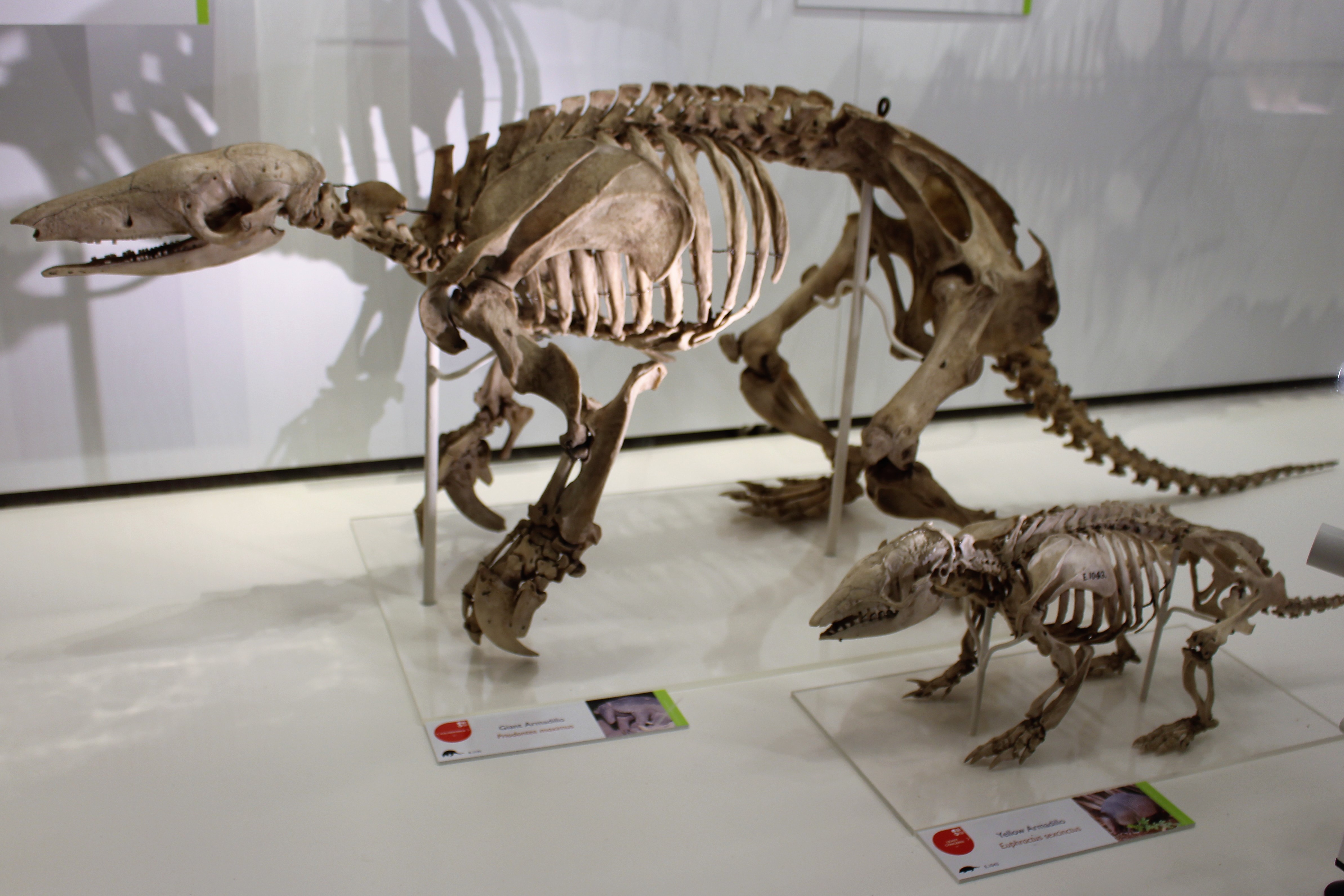
Giant Armadillo
The giant armadillo (''Priodontes maximus''), colloquially ''tatu-canastra'', ''tatou'', ''ocarro'' or ''tatú carreta'', is the largest living species of armadillo (although their extinct relatives, the Glyptodontidae, glyptodonts, were much larger). It lives in South America, ranging throughout as far south as northern Argentina. This species is considered vulnerable to extinction. The giant armadillo prefers termites and some ants as prey, and often consumes the entire population of a termite mound. It also has been known to prey upon worms, larvae and larger creatures, such as spiders and snakes, and plants. Some giant armadillos have been reported to have eaten bees by digging into beehives. At least one zoo park, in Villavicencio, Colombia – ''Los Ocarros'' – is dedicated to this animal. Description The giant armadillo is the largest living species of armadillo, with 11 to 13 hinged bands protecting the body and a further three or four on the neck. Its body is dark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genipa
''Genipa'' is a genus of trees in the family Rubiaceae. This genus is native to the American tropical forests. Description Tall trees, without any spines, prickles or thorns; with large opposite leaves of almost leathery texture, smooth or hairy. Presence of interpetiolar stipules, triangle-shaped. The large flowers are arranged in terminal cymes; the calyx is tubular, while the corolla can be trumpet-shaped or short-cylindrical, with 5-6 lobes. The stamens are located at the top of the corolla. The fruit is an almost globose or ovoid berry, smooth, fleshy, with a thick rind. The seeds are large and flat. Taxonomy The species from Madagascar, originally described by Drake, do not belong to the Rubiaceae tribe Gardenieae like the New World ''Genipa'' species, but in the tribe Octotropideae. Those species were transferred to the genus '' Hyperacanthus''. ''Genipa spruceana'' is considered doubtfully distinct from ''Genipa americana''. Species currently recognized in ''Genipa' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
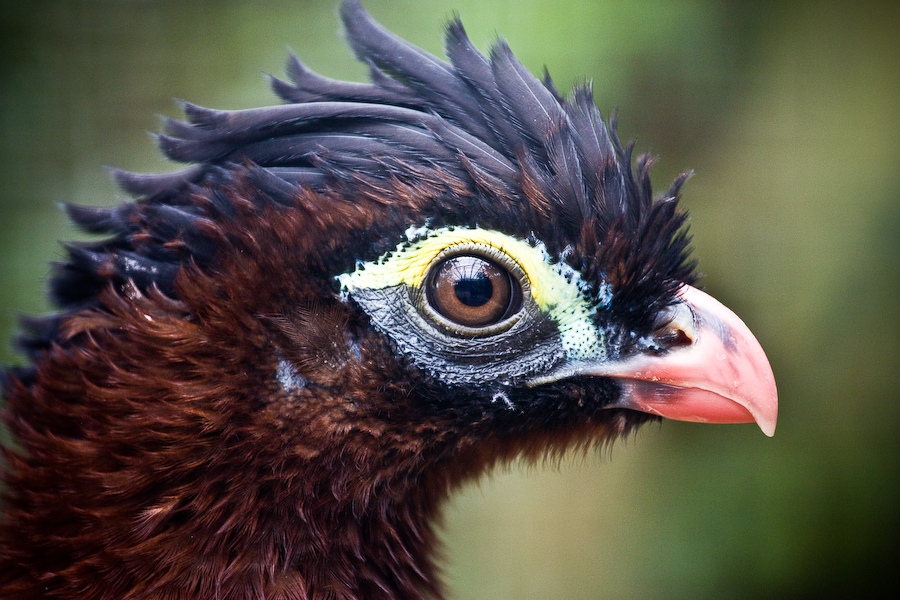
Curassow
Curassows are one of the three major groups of cracid birds. They comprise the largest-bodied species of the cracid family. Three of the four genera are restricted to tropical South America; a single species of ''Crax'' ranges north to Mexico. They form a distinct clade which is usually classified as the subfamily Cracinae. Evolution In line with the other 3 main lineages of cracids (chachalacas, true guans, and the horned guan), mt and nDNA sequence data indicates that the curassows diverged from their closest living relatives (probably the guans) at some time during the Oligocene, or c.35–20 mya (Pereira ''et al.'' 2002). This data must be considered preliminary until corroborated by material (e.g. fossil) evidence however. What appears certain from analysis of the molecular data, calibrated against geological events that would have induced speciation is that there are 2 major lineages of curassows: one containing only ''Crax'', and another made up of ''Mitu'' and ''Paux ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilded Catfish
The gilded catfish or ''jau'' (''Zungaro zungaro'') is a South American catfish (order Siluriformes) of the family Pimelodidae. It is also known as ''manguruyu'' or black manguruyu. Taxonomy By some sources, it is the only species of the monotypic genus ''Zungaro''. However, some sources list other species as valid, such as ''Zungaro jahu''. This species may be referred to by one of its synonyms, ''Brachyplatystoma flavicans''. This species contains two subspecies, ''Z. z. mangurus'' and ''Z. z. zungaro''. Distribution and habitat They are sexually mature upon reaching weight. This fish native to the Orinoco and Amazon basins; in the Amazon, this fish is found quite upstream, in the main bed of the big tributaries with muddy bottoms. Description This fish reaches in total length, and specimens measuring and weighing are not rare. These fish are mainly piscivorous, hunt at night, and sometimes go into flood-prone areas of rivers. Some migrations in pursuit of migrating ''Tripo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colombian Red Howler
The Colombian red howler or Venezuelan red howler (''Alouatta seniculus'') is a South American species of howler monkey, a type of New World monkey, found in the western Amazon Basin in Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru and Brazil. The population in the Santa Cruz Department in Bolivia was split off as a separate species, the Bolivian red howler, in 1986, and more recently, splitting off the population in northeastern South America and Trinidad as the Guyanan red howler has occurred. All howler monkeys belong to the family Atelidae and the infraorder Platyrrhini (New World monkeys). Description Sexual dimorphism in this species is small; males range from 49 to 72 cm and females from 46 to 57 cm long. The males weigh 5.4-9 kg, while females weigh 4.2–7 kg. It has a long prehensile tail of 49–75 cm. The tail is covered with fur except for the last third of the underside, which allows it to grab branches. The color of both males and females is a deep reddi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |