|
CORE (research Service)
CORE (Connecting Repositories) is a service provided by the based at The Open University, United Kingdom. The goal of the project is to aggregate all open access content distributed across different systems, such as repositories and open access journals, enrich this content using text mining and data mining, and provide free access to it through a set of services. The CORE project also aims to promote open access to scholarly outputs. CORE works closely with digital libraries and institutional repositories. Service description There are existing commercial academic search systems, such as Google Scholar, which provide search and access level services, but do not support programmable machine access to the content. This is seen with the use of an API or data dumps, and limits the further reuse of the open access content (e.g., text and data mining). There are three access levels to content: * access at the granularity of papers * analytical access and granularity of colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open University
The Open University (OU) is a Public university, public research university and the largest university in the United Kingdom by List of universities in the United Kingdom by enrolment, number of students. The majority of the OU's undergraduate students are based in the United Kingdom and principally study off-campus; many of its courses (both undergraduate and postgraduate education, postgraduate) can also be studied anywhere in the world. There are also a number of full-time postgraduate research students based on the university campus at Walton Hall, Milton Keynes, Walton Hall, Milton Keynes, Buckinghamshire, where they use the staff facilities for research, as well as more than 1,000 members of academic and research staff and over 2,500 administrative, operational and support staff. The OU was established in 1969 and was initially based at Alexandra Palace, north London, using the television studios and editing facilities which had been vacated by the BBC. The first students ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the primary Executive (government), executive arm of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with a number of European Commissioner, members of the Commission (directorial system, informally known as "commissioners") corresponding to two thirds of the number of Member state of the European Union, member states, unless the European Council, acting unanimously, decides to alter this number. The current number of commissioners is 27, including the president. It includes an administrative body of about 32,000 European civil servants. The commission is divided into departments known as Directorate-General, Directorates-General (DGs) that can be likened to departments or Ministry (government department), ministries each headed by a director-general who is responsible to a commissioner. Currently, there is one member per European Union member state, member state, but members are bound by their oath of office to represent the genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directory Of Open Access Journals
The Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ) is a website that hosts a community-curated list of open access journals, maintained by Infrastructure Services for Open Access (IS4OA). It was launched in 2003 with 300 open access journals. The mission of DOAJ is to "increase the visibility, accessibility, reputation, usage and impact of quality, peer-reviewed, open access scholarly research journals globally, regardless of discipline, geography or language." In 2015, DOAJ launched a reapplication process based on updated and expanded inclusion criteria. At the end of the process (December 2017), close to 5,000 journals, out of the 11,600 indexed in May 2016, had been removed from their database, in majority for failure to reapply. Notwithstanding the substantial cleanup, the number of journals included in DOAJ has continued to grow, to reach 14,299 as of 3 March 2020. the independent database contains more than 21,480 open access journals and 11,045,921 articles covering all area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BASE (search Engine)
BASE (Bielefeld Academic Search Engine) is a multi-disciplinary search engine to scholarly internet resources, created by Bielefeld University Library in Bielefeld, Germany. It is based on free and open-source software such as Apache Solr and VuFind. It harvests OAI metadata from institutional repositories and other academic digital libraries that implement the Open Archives Initiative Protocol for Metadata Harvesting (OAI-PMH), and then normalizes and indexes the data for searching. In addition to OAI metadata, the library indexes selected web sites and local data collections, all of which can be searched via a single search interface. History BASE was developed at the German university of Bielefeld beginning in 2002. The project's initial goal was to develop a search engine that would provide users access to the university's research resources. Yet as the initiative advanced, the creators came to see the need for a more thorough search engine that might provide users acce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Academic Databases And Search Engines
This page contains a representative list of major databases and search engines useful in an academic setting for finding and accessing articles in academic journals, institutional repository, institutional repositories, archives, or other collections of scientific journal, scientific and academic journal, other articles. As the distinction between a database and a search engine is unclear for these complex document retrieval systems, see: * the general list of search engines for all-purpose search engines that can be used for academic purposes * the article about bibliographic databases for information about databases giving bibliographic information about finding books and journal articles. Note that "free" or "subscription" can refer both to the availability of the database or of the journal articles included. This has been indicated as precisely as possible in the list: List See also * Academic publishing * Google Scholar * List of digital library projects * List of edu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybrid Open Access Journal
A hybrid open-access journal is a subscription journal in which some of the articles are open access. This status typically requires the payment of a publication fee (also called an article processing charge or APC) to the publisher in order to publish an article open access, in addition to the continued payment of subscriptions to access all other content. Strictly speaking, the term "hybrid open-access journal" is incorrect, possibly misleading, as using the same logic such journals could also be called "hybrid subscription journals". Simply using the term "hybrid access journal" is accurate. Publishers that offer a hybrid open access option often use different names for it. The SHERPA/RoMEO site provides a list of publishers and the names of their options. The Open Access Directory provides a list of funds that support open access journals, and provides information about which funds will pay fees of hybrid open access journals. Origins The concept was first proposed in 1998 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Registry Of Open Access Repositories
The Registry of Open Access Repositories (ROAR) is a searchable international database indexing the creation, location and growth of open access institutional repositories and their contents. ROAR was created by EPrints at University of Southampton, UK, in 2003. It began as the ''Institutional Archives Registry'' and was renamed '' Registry of Open Access Repositories'' in 2006. To date, over 3,000 institutional and cross-institutional repositories have been registered. As of 2015, ROAR and the UK-based Directory of Open Access Repositories (OpenDOAR) "are considered the two leading open access directories worldwide. ROAR is the larger directory and allows direct submissions to the directory. OpenDOAR controls submission of materials and is dependent on the discretion of its staff. OpenDOAR requires open access of scholarly publications; whereas ROAR allows other types of materials to be included. ROAR allows filtering by country, type of repository, and sorting by repository ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
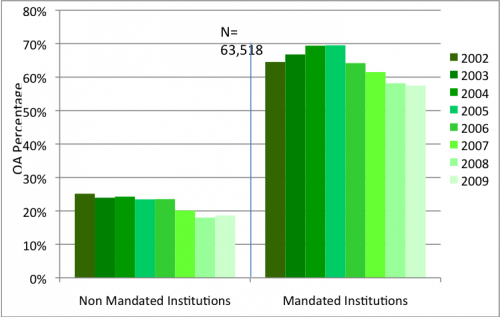
Open Access Mandate
An open-access mandate is a policy adopted by a research institution, research funder, or government which requires or recommends researchers—usually university faculty or research staff and/or research grant recipients—to make their published, peer-reviewed journal articles and conference papers open access (1) by self-archiving their final, peer-reviewed drafts in a freely accessible institutional repository or disciplinary repository ("Green OA") or (2) by publishing them in an open-access journal ("Gold OA") or both. Characteristics Among the universities that have adopted open-access mandates for faculty are Harvard University, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, University College London, Queensland University of Technology, University of Minho (Portugal), University of Liège and ETH Zürich. Among the funding organizations that have adopted open-access mandates for grant recipients are National Institutes of Health (with the NIH Public Access Policy), Research Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faceted Search
Faceted search augments lexical search with a faceted navigation system, allowing users to narrow results by applying filters based on a faceted classification of the items. It is a parametric search technique. A faceted classification system classifies each information element along multiple explicit dimensions, facets, enabling the classifications to be accessed and ordered in multiple ways rather than in a single, predetermined, taxonomic order. Facets correspond to properties of the information elements. They are often derived by analysis of the text of an item using entity extraction techniques or from pre-existing fields in a database such as author, descriptor, language, and format. Thus, existing web-pages, product descriptions or online collections of articles can be augmented with navigational facets. Faceted search interfaces were first developed in the academic world by Ben Shneiderman, Steven Pollitt, Marti Hearst, and Gary Marchionini in the 1990s and 2000s. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Archive Scholar ...
The Internet Archive Scholar is a scholarly search engine created by the Internet Archive in 2020. , it contained over 35 million research articles with full text access. The materials available come from three different forms: content identified by the Wayback Machine, by digitized print material and sources such as uploads from users and collections from partnerships. References External linksInternet Archive Scholar{{Internet Archive navbox Scholar A scholar is a person who is a researcher or has expertise in an academic discipline. A scholar can also be an academic, who works as a professor, teacher, or researcher at a university. An academic usually holds an advanced degree or a termina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Budapest Open Access Initiative
The Budapest Open Access Initiative (BOAI) is a public statement of principles relating to open access to the Scientific literature, research literature, which was released to the public on February 14, 2002. It arose from a convening in Budapest organized by the Open Society Institute on December 1–2 2001 to promote open access, which at that time was also known as ''Free Online Scholarship''. This small gathering of individuals is recognized as one of the major defining events of the open access movement. As of 2021, the text of the initiative had been translated to 13 languages. On the 10th anniversary of the initiative in 2012, the original initiative was reaffirmed and supplemented with a set of recommendations for achieving open access in the next 10 years. Content The opening sentence of the BOAI encapsulated the purpose and potential of an open access movement: Definition The document contains one of the first and most widely used definitions of open access, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenDOAR
OpenDOAR: Directory of Open Access Repositories is a UK-based website that lists open access repositories (including academic ones). It is searchable by locale, content, and other measures. The service does not require complete repository details and does not search repositories' metadata. OpenDOAR is maintained by the University of Nottingham under the SHERPA umbrella of services and was developed in collaboration with Lund University. The project is funded by the Open Science Institute, Jisc, the Consortium of Research Libraries (CURL) and SPARC Europe. As of 2015, OpenDOAR and the UK-based Registry of Open Access Repositories (ROAR) "are considered the Two leading open access directories worldwide. ROAR is the larger directory and allows direct submissions to the directory. OpenDOAR controls submission of materials and is dependent on the discretion of its staff. OpenDOAR requires open access of scholarly publications; whereas ROAR allows other types of materials to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |