|
CNK Operating System
Compute Node Kernel (CNK) is the node level operating system for the IBM Blue Gene series of supercomputers.''Euro-Par 2004 Parallel Processing: 10th International Euro-Par Conference'' 2004, by Marco Danelutto, Marco Vanneschi and Domenico Laforenza pages 835''Euro-Par 2006 Parallel Processing: 12th International Euro-Par Conference'', 2006, by Wolfgang E. Nagel, Wolfgang V. Walter and Wolfgang Lehner page The compute nodes of the Blue Gene family of supercomputers run ''Compute Node Kernel'' (CNK), a lightweight kernel that runs on each node and supports one application running for one user on that node. To maximize operating efficiency, the design of CNK was kept simple and minimal. It was implemented in about 5,000 lines of C++ code. Physical memory is statically mapped and the CNK neither needs nor provides scheduling or context switching, given that at each point it runs one application for one user. By not allowing virtual memory or multi-tasking, the design of CNK aim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LLNL BGL Diagram
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) is a federal research facility in Livermore, California, United States. The lab was originally established as the University of California Radiation Laboratory, Livermore Branch in 1952 in response to the detonation of the first atomic bomb by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. It later became autonomous in 1971 and was designated a national laboratory in 1981. A federally funded research and development center, Lawrence Livermore Lab is primarily funded by the U.S. Department of Energy and it is managed privately and operated by Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC (a partnership of the University of California), Bechtel, BWX Technologies, AECOM, and Battelle Memorial Institute in affiliation with the Texas A&M University System. In 2012, the laboratory had the synthetic chemical element livermorium (element 116) named after it. Overview LLNL is self-described as a "premier research and development institution for sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating System
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs. Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation of Scheduling (computing), processor time, mass storage, printing, and other resources. For hardware functions such as input and output and memory allocation, the operating system acts as an intermediary between programs and the computer hardware, although the application code is usually executed directly by the hardware and frequently makes system calls to an OS function or is interrupted by it. Operating systems are found on many devices that contain a computer from cellular phones and video game consoles to web servers and supercomputers. The dominant general-purpose personal computer operating system is Microsoft Windows with a market share of aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
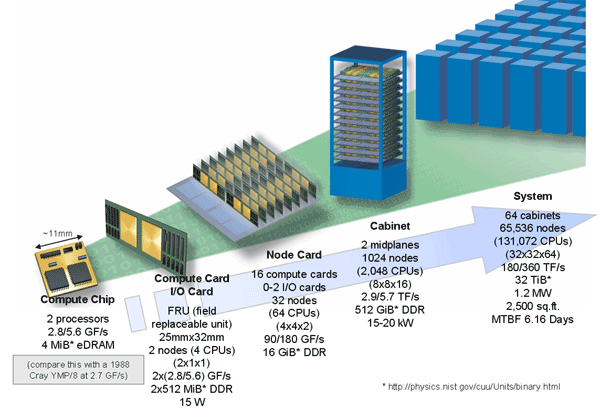
Blue Gene
Blue Gene is an IBM project aimed at designing supercomputers that can reach operating speeds in the petaFLOPS (PFLOPS) range, with low power consumption. The project created three generations of supercomputers, Blue Gene/L, Blue Gene/P, and Blue Gene/Q. During their deployment, Blue Gene systems often led the TOP500 and Green500 rankings of the most powerful and most power-efficient supercomputers, respectively. Blue Gene systems have also consistently scored top positions in the Graph500 list. The project was awarded the 2009 National Medal of Technology and Innovation. As of 2015, IBM seems to have ended the development of the Blue Gene family though no public announcement has been made. IBM's continuing efforts of the supercomputer scene seems to be concentrated around OpenPower, using accelerators such as FPGAs and GPUs to battle the end of Moore's law. History In December 1999, IBM announced a US$100 million research initiative for a five-year effort to build a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercomputer
A supercomputer is a computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) instead of million instructions per second (MIPS). Since 2017, there have existed supercomputers which can perform over 1017 FLOPS (a hundred quadrillion FLOPS, 100 petaFLOPS or 100 PFLOPS). For comparison, a desktop computer has performance in the range of hundreds of gigaFLOPS (1011) to tens of teraFLOPS (1013). Since November 2017, all of the world's fastest 500 supercomputers run on Linux-based operating systems. Additional research is being conducted in the United States, the European Union, Taiwan, Japan, and China to build faster, more powerful and technologically superior exascale supercomputers. Supercomputers play an important role in the field of computational science, and are used for a wide range of computationally intensive tasks in v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lightweight Kernel Operating System
A lightweight kernel (LWK) operating system is one used in a large computer with many processor cores, termed a parallel computer. A massively parallel high-performance computing (HPC) system is particularly sensitive to operating system overhead. Traditional multi-purpose operating systems are designed to support a wide range of usage models and requirements. To support the range of needs, a large number of system processes are provided and are often inter-dependent on each other. The computing overhead of these processes leads to an unpredictable amount of processor time available to a parallel application. A very common parallel programming model is referred to as the bulk synchronous parallel model which often employs Message Passing Interface (MPI) for communication. The synchronization events are made at specific points in the application code. If one processor takes longer to reach that point than all the other processors, everyone must wait. The overall finish time is incre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Input/output
In computing, input/output (I/O, or informally io or IO) is the communication between an information processing system, such as a computer, and the outside world, possibly a human or another information processing system. Inputs are the signals or data received by the system and outputs are the signals or data sent from it. The term can also be used as part of an action; to "perform I/O" is to perform an input or output operation. are the pieces of hardware used by a human (or other system) to communicate with a computer. For instance, a keyboard or computer mouse is an input device for a computer, while monitors and printers are output devices. Devices for communication between computers, such as modems and network cards, typically perform both input and output operations. Any interaction with the system by a interactor is an input and the reaction the system responds is called the output. The designation of a device as either input or output depends on perspective. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
INK (operating System)
INK (for I/O Node Kernel) is the operating system that runs on the input output nodes of the IBM Blue Gene supercomputer.''Euro-Par 2004 Parallel Processing: 10th International Euro-Par Conference'' 2004, by Marco Danelutto, Marco Vanneschi and Domenico Laforenza pages 835''Euro-Par 2006 Parallel Processing: 12th International Euro-Par Conference'', 2006, by Wolfgang E. Nagel, Wolfgang V. Walter and Wolfgang Lehner page INK is a Linux-derivative. See also * Compute Node Linux * Timeline of operating systems * Rocks Cluster Distribution * Cray Linux Environment UNICOS is a range of Unix and after it Linux operating system (OS) variants developed by Cray for its supercomputers. UNICOS is the successor of the Cray Operating System (COS). It provides network clustering and source code compatibility layers ... References Linux kernel variant Supercomputer operating systems {{super-compu-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux Kernel
The Linux kernel is a free and open-source, monolithic, modular, multitasking, Unix-like operating system kernel. It was originally authored in 1991 by Linus Torvalds for his i386-based PC, and it was soon adopted as the kernel for the GNU operating system, which was written to be a free (libre) replacement for Unix. Linux is provided under the GNU General Public License version 2 only, but it contains files under other compatible licenses. Since the late 1990s, it has been included as part of a large number of operating system distributions, many of which are commonly also called Linux. Linux is deployed on a wide variety of computing systems, such as embedded devices, mobile devices (including its use in the Android operating system), personal computers, servers, mainframes, and supercomputers. It can be tailored for specific architectures and for several usage scenarios using a family of simple commands (that is, without the need of manually editing its source c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catamount (operating System)
Catamount is an operating system for supercomputers. Catamount is a lightweight kernel that provides basic functionality and aims for efficiency. The roots of Catamount go back to 1991 when SUNMOS was developed by Sandia National Laboratories and the University of New Mexico as a lightweight operating system. The Cray XT3 uses Catamount on compute nodes and Linux on server nodes.''An Evaluation of the Oak Ridge National Laboratory Cray XT3'' by Sadaf R. Alam etal ''International Journal of High Performance Computing Applications'' February 2008 vol. 22 no. 1 52-80 A case study by the IEEE assessed the performance of a particle transport code on AWE's Cray XT3 8,000-core supercomputer while running images of the Catamount and the Cray Linux Environment (CLE) operating systems. This work demonstrated that by running a number of small benchmarks on a test machine it is possible to speculate as to the performance impact of upgrading from one operating system to another on the sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compute Node Linux
Compute Node Linux (CNL) is a runtime environment based on the Linux kernel for the Cray XT3, Cray XT4, Cray XT5, Cray XT6, Cray XE6 and Cray XK6 supercomputer systems based on SUSE Linux Enterprise Server. CNL forms part of the Cray Linux Environment UNICOS is a range of Unix and after it Linux operating system (OS) variants developed by Cray for its supercomputers. UNICOS is the successor of the Cray Operating System (COS). It provides network clustering and source code compatibility layers .... systems running CNL were ranked 3rd, 6th and 8th among the fastest supercomputers in the world. See also * INK (operating system) References External links SUSE Linux Enterprise Server Cray software Linux kernel variant {{super-compu-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocks Cluster Distribution
Rocks Cluster Distribution (originally NPACI Rocks) is a Linux distribution intended for high-performance computing (HPC) clusters. It was started by National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure and the San Diego Supercomputer Center (SDSC) in 2000. It was initially funded in part by an NSF grant (2000–07), but was funded by the follow-up NSF grant through 2011. Distribution Rocks was initially based on the Red Hat Linux (RHL) distribution, however modern versions of Rocks were based on CentOS, with a modified Anaconda installer that simplifies mass installation onto many computers. Rocks includes many tools (such as Message Passing Interface (MPI)) which are not part of CentOS but are integral components that make a group of computers into a cluster. Installations can be customized with additional software packages at install-time by using special user-supplied CDs (called "Roll CDs"). The "Rolls" extend the system by integrating seamlessly and auto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timeline Of Operating Systems
This article presents a timeline of events in the history of computer operating systems from 1951 to the current day. For a narrative explaining the overall developments, see the History of operating systems. 1950s * 1951 ** LEO I 'Lyons Electronic Office' was the commercial development of EDSAC computing platform, supported by British firm J. Lyons and Co. * 1955 ** MIT's Tape Director operating system made for UNIVAC 1103 * 1955 ** General Motors Operating System made for IBM 701 * 1956 ** GM-NAA I/O for IBM 704, based on General Motors Operating System * 1957 ** Atlas Supervisor (Manchester University) (''Atlas computer project start'') ** BESYS (Bell Labs), for IBM 704, later IBM 7090 and IBM 7094 * 1958 ** University of Michigan Executive System (UMES), for IBM 704, 709, and 7090 * 1959 ** SHARE Operating System (SOS), based on GM-NAA I/O 1960s * 1960 ** IBSYS ( IBM for its 7090 and 7094) * 1961 ** CTSS demonstration ( MIT's Compatible Time-Sharing Syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |