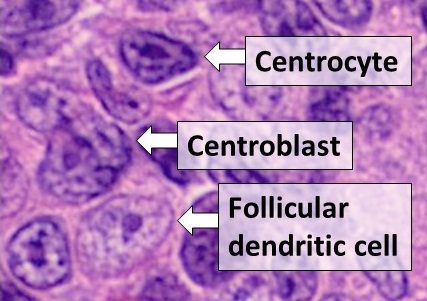
|
CCl4
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligands 4 (also CCL4) previously known as macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP-1β), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''CCL4'' gene. ''CCL4'' belongs to a cluster of genes located on 17q11-q21 of the chromosomal region. Identification and localization of the gene on the chromosome 17 was in 1990 although the discovery of MIP-1 was initiated in 1988 with the purification of a protein doublet corresponding to inflammatory activity from supernatant of endotoxinstimulated murine macrophages. At that time, it was also named as "macrophage inflammatory protein-1" (MIP-1) due to its inflammatory properties. CCL4 is a small cytokine that belongs to the CC chemokine subfamily. CCL4 is being secreted under mitogenic signals and antigens and hereby acts as a chemoattractant for natural killer cells, monocytes and various other immune cells in the site of inflamed or damaged tissue. Genomics In the human genome, CCL4 and many other CC chemokines is enc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage Inflammatory Protein
Macrophage Inflammatory Proteins (MIP) belong to the family of chemotactic cytokines known as chemokines. In humans, there are two major forms, MIP-1α and MIP-1β that are now (according to the new nomenclature) officially named CCL3 and CCL4, respectively. However, other names can sometimes be encountered, especially in older literature, as LD78α, AT 464.1 and GOS19-1 for human CCL3 and AT 744, Act-2, LAG-1, HC21 and G-26 for human CCL4. Other macrophage inflammatory proteins include MIP-2, MIP-3 and MIP-5. MIP-1 MIP-1α and MIP-1β are major factors produced by macrophages and monocytes after they are stimulated with bacterial endotoxin or proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β. But it appears that they can be expressed by all hematopoietic cells and some tissue cells such as fibroblasts, epithelial cells, vascular smooth muscle cells or platelets upon activation. They are crucial for immune responses towards infection and inflammation. CCL3 and CCL4 can bind to extracellu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
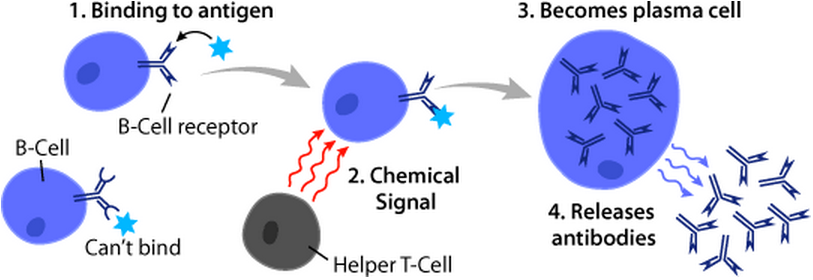
B Cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. Additionally, B cells present antigens (they are also classified as professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs)) and secrete cytokines. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the 'B' stands for bursa and not bone marrow as commonly believed. B cells, unlike the other two classes of lymphocytes, T cells and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
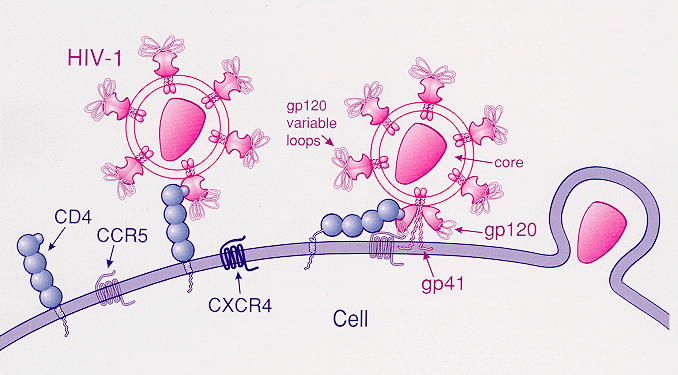
CCR5
C-C chemokine receptor type 5, also known as CCR5 or CD195, is a protein on the surface of white blood cells that is involved in the immune system as it acts as a receptor for chemokines. In humans, the ''CCR5'' gene that encodes the CCR5 protein is located on the short (p) arm at position 21 on chromosome 3. Certain populations have inherited the ''Delta 32'' mutation, resulting in the genetic deletion of a portion of the CCR5 gene. Homozygous carriers of this mutation are resistant to M-tropic strains of HIV-1 infection. Function The CCR5 protein belongs to the beta chemokine receptors family of integral membrane proteins. It is a G protein–coupled receptor which functions as a chemokine receptor in the CC chemokine group. CCR5's cognate ligands include CCL3, CCL4 (also known as MIP 1''α'' and 1''β'', respectively), and CCL3L1. CCR5 furthermore interacts with CCL5 (a chemotactic cytokine protein also known as RANTES). CCR5 is predominantly expressed on T cells, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CCL3
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3 (CCL3) also known as macrophage inflammatory protein 1-alpha (MIP-1-alpha) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CCL3'' gene. Function CCL3 is a cytokine belonging to the CC chemokine family that is involved in the acute inflammatory state in the recruitment and activation of polymorphonuclear leukocytes through binding to the receptors CCR1, CCR4 and CCR5. Sherry et al. (1988) demonstrated 2 protein components of MIP1, called by them alpha (CCL3, this protein) and beta (CCL4). CCL3 produces a monophasic fever of rapid onset whose magnitude is equal to or greater than that of fevers produced with either recombinant human tumor necrosis factor or recombinant human interleukin-1. However, in contrast to these two endogenous pyrogens, the fever induced by MIP-1 is not inhibited by the cyclooxygenase inhibitor ibuprofen and CCL3 may participate in the febrile response that is not mediated through prostaglandin synthesis and clinically ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perforin
Perforin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PRF1'' gene and the ''Prf1'' gene in mice. Function Perforin is a pore forming cytolytic protein found in the granules of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and natural killer cells (NK cells). Upon degranulation, perforin molecules translocate to the target cell with the help of calreticulin, which works as a chaperone protein to prevent perforin from degrading. Perforin then binds to the target cell's plasma membrane via membrane phospholipids while phosphatidylcholine binds calcium ions to increase perforin's affinity to the membrane. Perforin oligomerises in a Ca2+ dependent manner to form pores on the target cell. The pore formed allows for the passive diffusion of a family of pro-apoptotic proteases, known as the granzymes, into the target cell. The lytic membrane-inserting part of perforin is the MACPF domain. This region shares homology with cholesterol-dependent cytolysins from Gram-positive bacteria. Perforin has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microglia
Microglia are a type of neuroglia (glial cell) located throughout the brain and spinal cord. Microglia account for about 7% of cells found within the brain. As the resident macrophage cells, they act as the first and main form of active immune defense in the central nervous system (CNS). Microglia (and other neuroglia including astrocytes) are distributed in large non-overlapping regions throughout the CNS. Microglia are key cells in overall brain maintenance—they are constantly scavenging the CNS for plaques, damaged or unnecessary neurons and synapses, and infectious agents. Since these processes must be efficient to prevent potentially fatal damage, microglia are extremely sensitive to even small pathological changes in the CNS. This sensitivity is achieved in part by the presence of unique potassium channels that respond to even small changes in extracellular potassium. Recent evidence shows that microglia are also key players in the sustainment of normal brain functions und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endothelium
The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vessel wall. Endothelial cells form the barrier between vessels and tissue and control the flow of substances and fluid into and out of a tissue. Endothelial cells in direct contact with blood are called vascular endothelial cells whereas those in direct contact with lymph are known as lymphatic endothelial cells. Vascular endothelial cells line the entire circulatory system, from the heart to the smallest capillaries. These cells have unique functions that include fluid filtration, such as in the glomerulus of the kidney, blood vessel tone, hemostasis, neutrophil recruitment, and hormone trafficking. Endothelium of the interior surfaces of the heart chambers is called endocardium. An impaired function can lead to serious health issues throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibroblast
A fibroblast is a type of cell (biology), biological cell that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework (Stroma (tissue), stroma) for animal Tissue (biology), tissues, and plays a critical role in wound healing. Fibroblasts are the most common cells of connective tissue in animals. Structure Fibroblasts have a branched cytoplasm surrounding an elliptical, speckled cell nucleus, nucleus having two or more nucleoli. Active fibroblasts can be recognized by their abundant Endoplasmic reticulum#Rough endoplasmic reticulum, rough endoplasmic reticulum. Inactive fibroblasts (called fibrocytes) are smaller, spindle-shaped, and have a reduced amount of rough endoplasmic reticulum. Although disjointed and scattered when they have to cover a large space, fibroblasts, when crowded, often locally align in parallel clusters. Unlike the epithelial cells lining the body structures, fibroblasts do not form flat monolayers and are not restricted by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrophil
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in different animals. They are formed from stem cells in the bone marrow and Cellular differentiation, differentiated into #Subpopulations, subpopulations of neutrophil-killers and neutrophil-cagers. They are short-lived and highly mobile, as they can enter parts of tissue where other cells/molecules cannot. Neutrophils may be subdivided into segmented neutrophils and banded neutrophils (or Band cell, bands). They form part of the polymorphonuclear cells family (PMNs) together with basophils and eosinophils. The name ''neutrophil'' derives from staining characteristics on hematoxylin and eosin (H&E stain, H&E) histology, histological or cell biology, cytological preparations. Whereas basophilic white blood cells stain dark blue and eosinoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendritic Cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and the adaptive immune systems. Dendritic cells are present in those tissues that are in contact with the external environment, such as the skin (where there is a specialized dendritic cell type called the Langerhans cell) and the inner lining of the nose, lungs, stomach and intestines. They can also be found in an immature state in the blood. Once activated, they migrate to the lymph nodes where they interact with T cells and B cells to initiate and shape the adaptive immune response. At certain development stages they grow branched projections, the ''dendrites'' that give the cell its name (δένδρον or déndron being Greek for 'tree'). While similar in appearance, these are structures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Killer Cell
Natural killer cells, also known as NK cells or large granular lymphocytes (LGL), are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte critical to the innate immune system that belong to the rapidly expanding family of known innate lymphoid cells (ILC) and represent 5–20% of all circulating lymphocytes in humans. The role of NK cells is analogous to that of cytotoxic T cells in the vertebrate adaptive immune response. NK cells provide rapid responses to virus-infected cell and other intracellular pathogens acting at around 3 days after infection, and respond to tumor formation. Typically, immune cells detect the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) presented on infected cell surfaces, triggering cytokine release, causing the death of the infected cell by lysis or apoptosis. NK cells are unique, however, as they have the ability to recognize and kill stressed cells in the absence of antibodies and MHC, allowing for a much faster immune reaction. They were named "natural killers" because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)