|
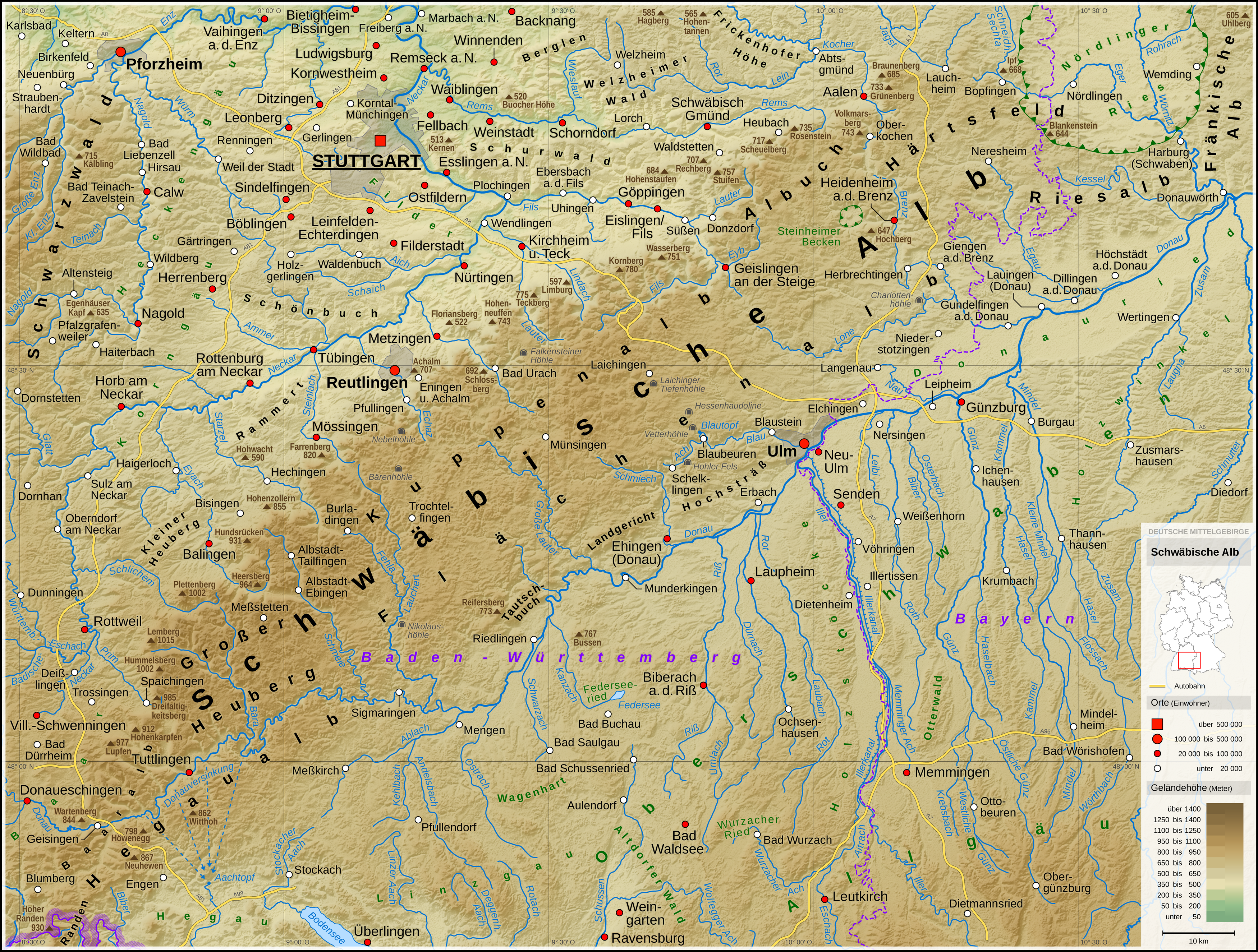
Burladingen
Burladingen is a town in the Zollernalbkreis district of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. History In 1849, Burladingen and the villages of and came under the dominion of the Kingdom of Prussia. They were assigned in 1850 to , one of the of Province of Hohenzollern. The Oberamt was dissolved in 1925 the three towns were joined in the new by Melchingen, , and , former possessions of the Kingdom of Württemberg ceded to Prussia in 1807. In 1973, as part of the , Hechingen's district was merged into the Zollernalb district. Hörschwag, was assigned to Reutlingen's district on 1 January 1973, but on 30 June 1974 was merged into Burladingen with the other townships. Burladingen was made an independent municipality in July 1978. 2008 flood In the evening of 2 June 2008, three women drowned in the Starzel, near Burladingen, following heavy rainfalls and flooding across south-western Baden-Württemberg. Geography The township ('' Stadt'') of Burladingen is located in the Swabian Jur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burladingen
Burladingen is a town in the Zollernalbkreis district of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. History In 1849, Burladingen and the villages of and came under the dominion of the Kingdom of Prussia. They were assigned in 1850 to , one of the of Province of Hohenzollern. The Oberamt was dissolved in 1925 the three towns were joined in the new by Melchingen, , and , former possessions of the Kingdom of Württemberg ceded to Prussia in 1807. In 1973, as part of the , Hechingen's district was merged into the Zollernalb district. Hörschwag, was assigned to Reutlingen's district on 1 January 1973, but on 30 June 1974 was merged into Burladingen with the other townships. Burladingen was made an independent municipality in July 1978. 2008 flood In the evening of 2 June 2008, three women drowned in the Starzel, near Burladingen, following heavy rainfalls and flooding across south-western Baden-Württemberg. Geography The township ('' Stadt'') of Burladingen is located in the Swabian Jur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kornbühl
Kornbühl is a mountain of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It belongs to the Swabian Jura and is located in Zollernalbkreis near Burladingen Burladingen is a town in the Zollernalbkreis district of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. History In 1849, Burladingen and the villages of and came under the dominion of the Kingdom of Prussia. They were assigned in 1850 to , one of the of Prov .... On its top the "Salmendinger Kapelle" is located. Mountains and hills of the Swabian Jura Burladingen {{BadenWürttemberg-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zollernalbkreis
The Zollernalbkreis is a ''Landkreis'' (district) in the middle of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The district is located in the Swabian Alb, and contains the second highest elevation of this range, the high '' Oberhohenberg''. In the south-east the district nearly reaches to the river Danube. The district was created on January 1, 1973, when the two previous districts Balingen and Hechingen were merged. Neighboring districts are (from north clockwise) Tübingen, Reutlingen, Sigmaringen, Tuttlingen, Rottweil and Freudenstadt. Coat of arms The coat of arms show the black-and-white checkered symbol of the Hohenzollern in the left half, and the triple black deer antler on yellow ground as the symbol of Württemberg. Almost all of the district's area belonged to these two states historically. Towns (''Städte'') and municipalities (''Gemeinden'') Language In the area of Zollernalbkreis, Swabian German is spoken. In former times, Yiddish, Pleißne and Romani was also s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swabian Jura
The Swabian Jura (german: Schwäbische Alb , more rarely ), sometimes also named Swabian Alps in English, is a mountain range in Baden-Württemberg, Germany, extending from southwest to northeast and in width. It is named after the region of Swabia. The Swabian Jura occupies the region bounded by the Danube in the southeast and the upper Neckar in the northwest. In the southwest it rises to the higher mountains of the Black Forest. The highest mountain of the region is the Lemberg (). The area's profile resembles a high plateau, which slowly falls away to the southeast. The northwestern edge is a steep escarpment (called the Albtrauf or Albanstieg, rising up , covered with forests), while the top is flat or gently rolling. In economic and cultural terms, the Swabian Jura includes regions just around the mountain range. It is a popular recreation area. Geology The geology of the Swabian Jura is mostly limestone, which formed the seabed during the Jurassic period. The se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melchingen
Melchingen is a Swabian village in the district of Zollernalbkreis, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is 730 m above sea level and has 895 inhabitants (as of December 31, 2019). Melchingen is known for its annual pottery and handicraft market, and the Theater Lindenhof, founded in 1981. Melchingen was first mentioned in 772 on the occasion of a donation to Lorsch Abbey in a document of the Lorsch Codex. In 1588 and 1598, the town held witch trials, all of which ended in executions. On January 1, 1973, Melchingen was incorporated into the city of Burladingen Burladingen is a town in the Zollernalbkreis district of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. History In 1849, Burladingen and the villages of and came under the dominion of the Kingdom of Prussia. They were assigned in 1850 to , one of the of Prov .... References Villages in Baden-Württemberg {{Zollernalbkreis-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a total area of nearly , it is the third-largest German state by both area (behind Bavaria and Lower Saxony) and population (behind North Rhine-Westphalia and Bavaria). As a federated state, Baden-Württemberg is a partly-sovereign parliamentary republic. The largest city in Baden-Württemberg is the state capital of Stuttgart, followed by Mannheim and Karlsruhe. Other major cities are Freiburg im Breisgau, Heidelberg, Heilbronn, Pforzheim, Reutlingen, Tübingen, and Ulm. What is now Baden-Württemberg was formerly the historical territories of Baden, Prussian Hohenzollern, and Württemberg. Baden-Württemberg became a state of West Germany in April 1952 by the merger of Württemberg-Baden, South Baden, and Württemberg-Hohe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It was the driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1871 and was the leading state of the German Empire until its dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin. The kings of Prussia were from the House of Hohenzollern. Brandenburg-Prussia, predecessor of the kingdom, became a military power under Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg, known as "The Great Elector". As a kingdom, Prussia continued its rise to power, especially during the reign of Frederick II, more commonly known as Frederick the Great, who was the third son of Frederick William I.Horn, D. B. "The Youth of Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argent
In heraldry, argent () is the tincture of silver, and belongs to the class of light tinctures called "metals". It is very frequently depicted as white and usually considered interchangeable with it. In engravings and line drawings, regions to be tinctured ''argent'' are either left blank, or indicated with the abbreviation ''ar''. The name derives from Latin ''argentum'', translated as " silver" or "white metal". The word ''argent'' had the same meaning in Old French ''blazon'', whence it passed into the English language. In some historical depictions of coats of arms, a kind of silver leaf was applied to those parts of the device that were argent. Over time, the silver content of these depictions has tarnished and darkened. As a result, it can sometimes be difficult to distinguish regions that were intended as "argent" from those that were " sable". This leaves a false impression that the rule of tincture has been violated in cases where, when applied next to a dark colou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schwarzwälder Bote
''Schwarzwälder Bote'', also known as ''Schwabo'', is a German regional daily newspaper for the Black Forest and Upper Neckar region. ''Schwabo'' operates a network of 15 branches, three service points, and 18 local editorial offices. The main circulation area, including the partner newspapers ''Oberbadische Zeitung'' and ''Lahrer Zeitung'', extends from Calw and Bad Herrenalb in the north to Lörrach in the south, from Lahr in the west to Balingen and Albstadt Albstadt () is the largest city in the district of Zollernalbkreis in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is located on the Swabian Jura mountains, about halfway between Stuttgart and Lake Constance. Geography Albstadt is spread across a variety of ... in the East. The sold circulation is 105,265 copies, a decrease of 23.9 percent since 1998. Since 2001 the "''Schwabo''" has received the national part of its content from the '' Stuttgarter Nachrichten''. Ownership structure ''Schwabo'' is published by the Schwarzwä ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Ministry Of The Interior, Building And Community
The Federal Ministry of the Interior and for Community (german: Bundesministerium des Innern und für Heimat, ; ''Heimat'' also translates to "homeland"), abbreviated , is a cabinet-level ministry of the Federal Republic of Germany. Its main office is in Berlin, with a secondary seat in Bonn. The current minister of the Interior and Community is Nancy Faeser. It is comparable to the British Home Office or a combination of the US Department of Homeland Security and the US Department of Justice, because both manage several law enforcement agencies. The BMI is tasked with the internal security of Germany. To fulfill this responsibility it maintains, among other agencies, the two biggest federal law enforcement agencies in Germany, the Federal Police and the Federal Criminal Police Office. It is also responsible for the federal domestic intelligence agency, the Federal Office for the Protection of the Constitution. History The ''Reichsamt des Innern'' (Imperial Office of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tincture (heraldry)
Tincture is the limited palette of colours and patterns used in heraldry. The need to define, depict, and correctly blazon the various tinctures is one of the most important aspects of heraldic art and design. Development and history The use of tinctures dates back to the formative period of European heraldry in the twelfth and thirteenth centuries. The range of tinctures and the manner of depicting and describing them has evolved over time, as new variations and practices have developed. The basic scheme and rules of applying the heraldic tinctures dates back to the 12th century. The earliest surviving coloured heraldic illustrations, from the mid-thirteenth century, show the standardized usage of two metals, five colours, and two furs. Since that time, the great majority of heraldic art has employed these nine tinctures. Over time, variations on these basic tinctures were developed, particularly with respect to the furs. Authorities differ as to whether these variations shou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hohenzollern-Hechingen
Hohenzollern-Hechingen was a small principality in southwestern Germany. Its rulers belonged to the Swabian branch of the Hohenzollern dynasty. History The County of Hohenzollern-Hechingen was created in 1576, upon the partition of the County of Hohenzollern, a fief of the Holy Roman Empire. When the last count of Hohenzollern, Charles I of Hohenzollern (1512–1579) died, the territory was to be divided up between his three sons: * Eitel Frederick IV of Hohenzollern-Hechingen (1545–1605) * Charles II of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen (1547–1606) * Christopher of Hohenzollern-Haigerloch (1552–1592) Unlike the Hohenzollerns of Brandenburg and Prussia, the Hohenzollerns of southwest Germany remained Roman Catholic. The county was raised to a principality in 1623. The principality joined the Confederation of the Rhine in 1806 and was a member state of the German Confederation between 1815 and 1850. The democratic Revolution of 1848 was relatively successful in Hohenzoll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |