|
Biosphere Reserves Of Poland
UNESCO Biosphere Reserves are environment-protected scientific-research institutions of international status that are created with the intent for conservation in a natural state the most typical natural complexes of biosphere, conducting background ecological monitoring, studying of the surrounding natural environment, its changes under the activity of anthropogenic factors. Biosphere Preserves are created on the base of nature preserves or national parks including to their composition territories and objects of other categories of nature-preserving fund and other lands as well as including in the established order the World Network of Biosphere Reserves in the UNESCO framework "Man and the Biosphere Programme". The focal point in Poland for the Biosphere Reserves is the Polish Academy of Sciences (PAS), Institute of Geography and Spatial Organisation. Reserves There are currently ten such reserves in Poland, including trans-boundary reserves shared between Poland and neighbori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
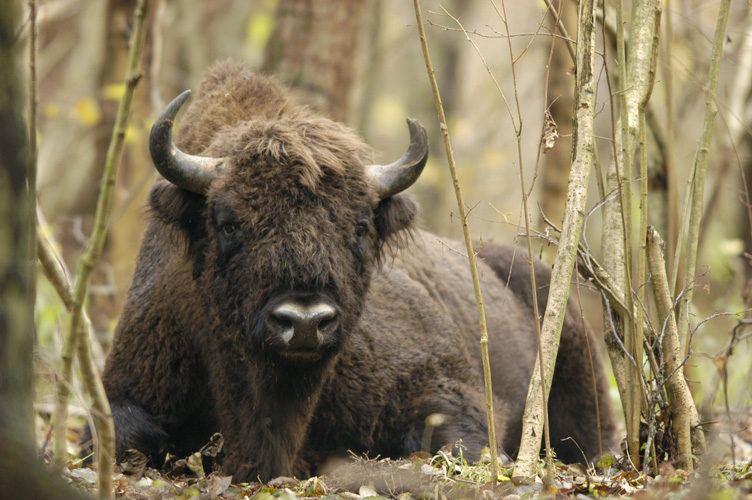
Białowieża Forest
Białowieża Forest; lt, Baltvyžių giria; pl, Puszcza Białowieska ; russian: Беловежская пуща, Belovezhskaya Pushcha is a forest on the border between Belarus and Poland. It is one of the last and largest remaining parts of the immense primeval forest that once stretched across the European Plain. The forest is home to 800 European bison, Europe's heaviest land animal. UNESCO's Man and the Biosphere Programme designated the Polish Biosphere Reserve ' in 1976 and the Belarusian Biosphere Reserve ' in 1993. In 2015, the Belarusian Biosphere Reserve occupied the area of , subdivided into transition, buffer and core zones. The forest has been designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site and an EU Natura 2000 Special Area of Conservation. The World Heritage Committee by its decision of June 2014 approved the extension of the UNESCO World Heritage site "Belovezhskaya Pushcha/Białowieża Forest, Belarus, Poland", which became "Białowieża Forest, Belarus, Pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Man And The Biosphere Programme
Man and the Biosphere Programme (MAB) is an intergovernmental scientific program, launched in 1971 by UNESCO, that aims to establish a scientific basis for the improvement of relationships between people and their environments. MAB's work engages fully with the international development agenda—specially with the Sustainable Development Goals and the Post 2015 Development Agenda—and addresses challenges linked to scientific, environmental, societal and development issues in diverse ecosystems; from mountain regions to marine, coastal and island areas; from tropical forests to dry lands and urban areas. MAB combines the natural and social sciences, economics and education to improve human livelihoods and the equitable sharing of benefits, and to safeguard natural and managed ecosystems, thus promoting innovative approaches to economic development that are socially and culturally appropriate, and environmentally sustainable. The MAB program provides a unique platform for co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
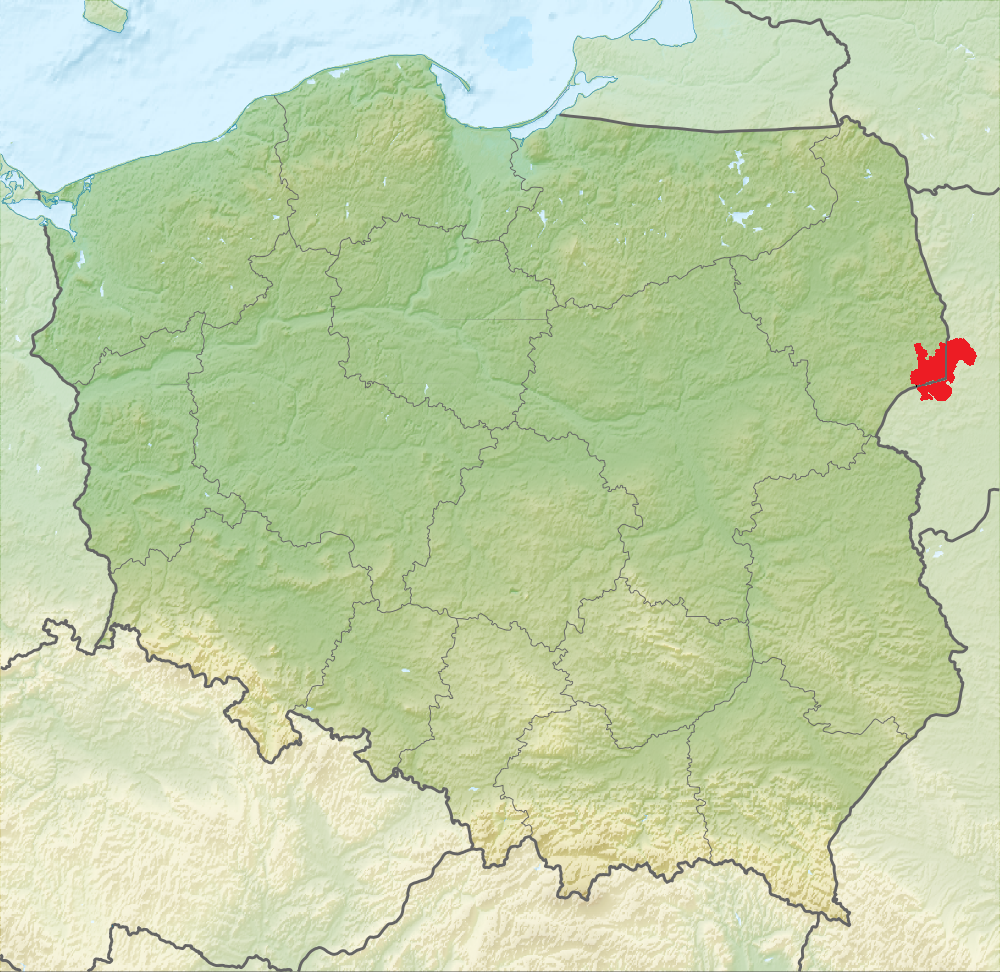
Podlaskie Voivodeship
Podlaskie Voivodeship or Podlasie Province ( pl, Województwo podlaskie, ) is a voivodeship (province) in northeastern Poland. The name of the province and its territory correspond to the historic region of Podlachia. The capital and largest city is Białystok. It borders on Masovian Voivodeship to the west, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship to the northwest, Lublin Voivodeship to the south, the Belarusian oblasts of Grodno and Brest to the east, the Lithuanian Counties of Alytus and Marijampolė to the northeast, and the Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia to the north. The province was created on 1 January 1999, pursuant to the Polish local government reforms adopted in 1998, from the former Białystok and Łomża Voivodeships and the eastern half of the former Suwałki Voivodeship. Etymology The voivodeship takes its name from the historic region of Poland called ''Podlasie'', or in Latin known as Podlachia. There are two opinions regarding the origin of the region's name. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in many colors, sizes, and forms and are sometimes plant-like, but are not plants. They may have tiny, leafless branches ( fruticose); flat leaf-like structures ( foliose); grow crust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaccinium Myrtillus
''Vaccinium myrtillus'' or European blueberry is a holarctic species of shrub with edible fruit of blue color, known by the common names bilberry, blaeberry, wimberry, and whortleberry. It is more precisely called common bilberry or blue whortleberry to distinguish it from other '' Vaccinium'' relatives. Description ''Vaccinium myrtillus'' is a small deciduous shrub that grows tall. It has light green leaves that turn red in autumn and are simple and alternate in arrangement. Leaves are long and ovate to lanceolate or broadly elliptic in shape. Common names Regional names include blaeberry (Scotland), urts or hurts (Cornwall and Devon), hurtleberry, citing Wiersema, J. H. & B. León (1999), ''World economic plants: a standard reference'', and Huxley, A., ed. (1992), ''The new Royal Horticultural Society dictionary of gardening'' myrtleberry, wimberry, whinberry, winberry,Henley, JonBilberries: the true taste of northern England The Guardian, Monday 9 June 2008 and fraug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Pine
''Pinus mugo'', known as bog pine, creeping pine, dwarf mountain pine, mugo pine, mountain pine, scrub mountain pine, or Swiss mountain pine, is a species of conifer, native to high elevation habitats from southwestern to Central Europe and Southeast Europe. Description The tree has dark green leaves ("needles") in pairs, long. The cones are nut-brown, long. Custura Bucurei.jpg, ''Pinus mugo'' subsp. ''mugo'', Romania Pinus mugo uncinata trees.jpg, ''Pinus mugo'' subsp. ''uncinata'' Swiss National Park 007.JPG, ''Pinus mugo'' subsp. ''rotundata'', Swiss National Park Бор кривул 01.JPG, On Jakupica mountain, Republic of North Macedonia Taxonomy There are three subspecies: *''Pinus mugo'' subsp. ''mugo'' — in the east and south of the range (southern & eastern Alps, Balkan Peninsula), a low, shrubby, often multi-stemmed plant to tall with matte-textured symmetrical cones, which are thin-scaled. *''Pinus mugo'' subsp. ''uncinata'' — in the west and no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abies Alba
''Abies alba'', the European silver fir or silver fir, is a fir native to the mountains of Europe, from the Pyrenees north to Normandy, east to the Alps and the Carpathians, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Serbia, and south to Italy, Bulgaria, Kosovo, Albania and northern Greece; it is also commonly grown on Christmas tree plantations in the North East region of North America spanning New England in the US to the Maritime provinces of Canada. Description ''Abies alba'' is a large evergreen coniferous tree growing to tall and with a trunk diameter up to . The largest measured tree was tall and had a trunk diameter of . It occurs at altitudes of (mainly over ), on mountains with rainfall over per year. The leaves are needle-like, flattened, long and wide by thick, glossy dark green above, and with two greenish-white bands of stomata below. The leaf is usually slightly notched at the tip. The cones are long and broad, with about 150-200 scale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beech
Beech (''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to temperate Europe, Asia, and North America. Recent classifications recognize 10 to 13 species in two distinct subgenera, ''Engleriana'' and ''Fagus''. The ''Engleriana'' subgenus is found only in East Asia, distinctive for its low branches, often made up of several major trunks with yellowish bark. The better known ''Fagus'' subgenus beeches are high-branching with tall, stout trunks and smooth silver-grey bark. The European beech ('' Fagus sylvatica'') is the most commonly cultivated. Beeches are monoecious, bearing both male and female flowers on the same plant. The small flowers are unisexual, the female flowers borne in pairs, the male flowers wind-pollinating catkins. They are produced in spring shortly after the new leaves appear. The fruit of the beech tree, known as beechnuts or mast, is found in small burrs that drop from the tree in autumn. They are small, roughly triangular, and edib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Romania, Russia, Turkey, and Ukraine. The Black Sea is supplied by major rivers, principally the Danube, Dnieper, and Don. Consequently, while six countries have a coastline on the sea, its drainage basin includes parts of 24 countries in Europe. The Black Sea covers (not including the Sea of Azov), has a maximum depth of , and a volume of . Most of its coasts ascend rapidly. These rises are the Pontic Mountains to the south, bar the southwest-facing peninsulas, the Caucasus Mountains to the east, and the Crimean Mountains to the mid-north. In the west, the coast is generally small floodplains below foothills such as the Strandzha; Cape Emine, a dwindling of the east end of the Balkan Mountains; and the Dobruja Plateau considerably ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain. The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 10°E to 30°E longitude. A marginal sea of the Atlantic, with limited water exchange between the two water bodies, the Baltic Sea drains through the Danish Straits into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, Great Belt and Little Belt. It includes the Gulf of Bothnia, the Bay of Bothnia, the Gulf of Finland, the Gulf of Riga and the Bay of Gdańsk. The "Baltic Proper" is bordered on its northern edge, at latitude 60°N, by Åland and the Gulf of Bothnia, on its northeastern edge by the Gulf of Finland, on its eastern edge by the Gulf of Riga, and in the west by the Swedish part of the southern Scandinavian Peninsula. The Baltic Sea is connected by artificial waterways to the White Sea via the White Sea–Baltic Canal and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massif
In geology, a massif ( or ) is a section of a planet's crust that is demarcated by faults or flexures. In the movement of the crust, a massif tends to retain its internal structure while being displaced as a whole. The term also refers to a group of mountains formed by such a structure. In mountaineering and climbing literature, a massif is frequently used to denote the main mass of an individual mountain. The massif is a smaller structural unit of the crust than a tectonic plate, and is considered the fourth-largest driving force in geomorphology. The word is taken from French (in which the word also means "massive"), where it is used to refer a large mountain mass or compact group of connected mountains forming an independent portion of a range. One of the most notable European examples of a massif is the Massif Central of the Auvergne region of France. The Face on Mars is an example of an extraterrestrial massif. Massifs may also form underwater, as with the Atlantis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beskidy Mountains
The Beskids or Beskid Mountains ( pl, Beskidy, cs, Beskydy, sk, Beskydy, rue, Бескиды (''Beskydŷ''), ua, Бескиди (''Beskydy'')) are a series of mountain ranges in the Carpathians, stretching from the Czech Republic in the west along the border of Poland with Slovakia up to Ukraine in the east. The highest mountain in the Beskids is Hoverla, at 2,061 m metres (6,762 ft). Etymology The origin of the name ''beskydy'' has not been conclusively established. A Thracian or Illyrian origin has been suggested, however, as yet, no theory has majority support among linguists. The word appears in numerous mountain names throughout the Carpathians and the adjacent Balkan regions, like in Albanian ''bjeshkë''. According to linguists Çabej and Orel, it is possibly derived from Proto-Albanian "''*beškāi tāi''" (meaning the mountain pastures).The Slovak name ''Beskydy'' refers to the Polish Bieszczady Mountains, which is not a synonym for the entire Beskids but one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


%2C_Italy.jpg)



