|
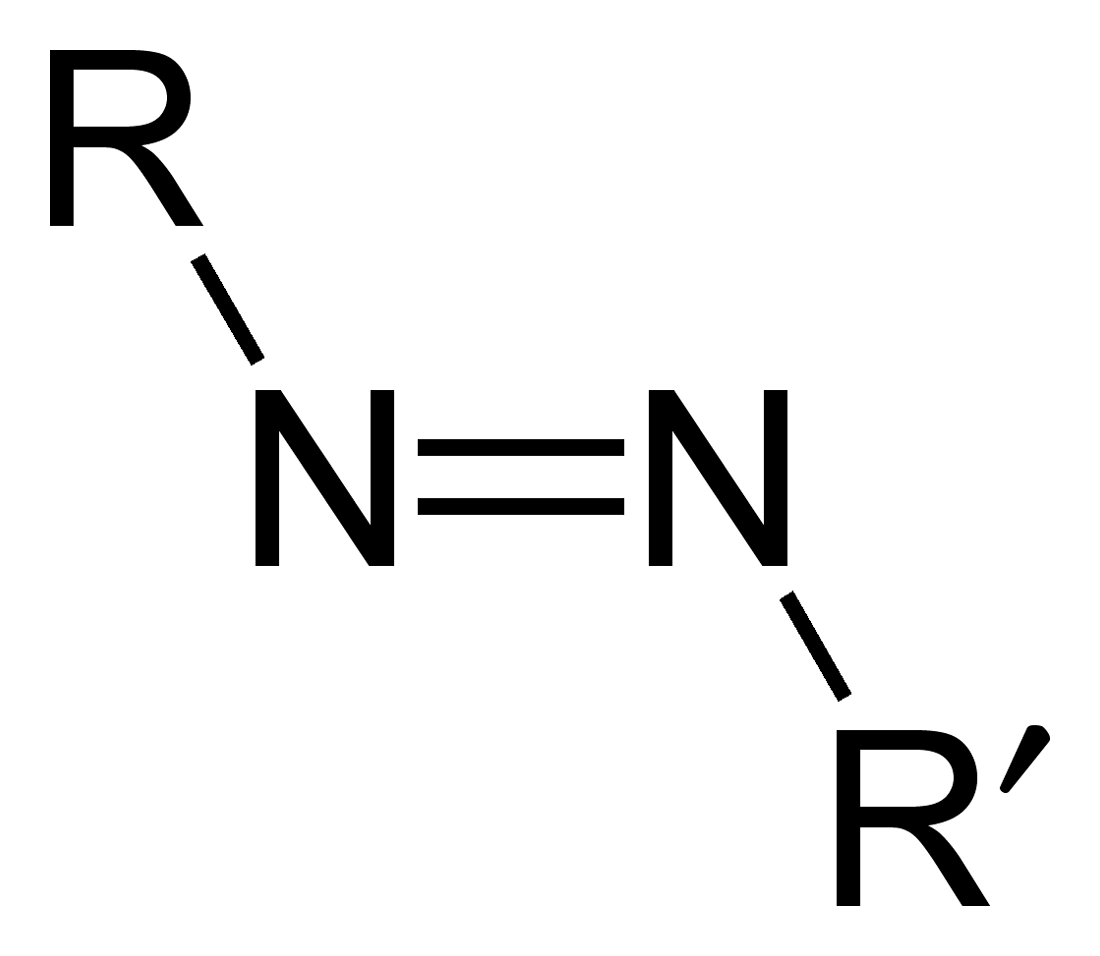
Azo Compounds
Azo compounds are organic compounds bearing the functional group diazenyl (, in which R and R′ can be either aryl or alkyl groups). IUPAC defines azo compounds as: "Derivatives of diazene (diimide), , wherein both hydrogens are substituted by hydrocarbyl groups, e.g. azobenzene or diphenyldiazene.", where Ph stands for phenyl group. The more stable derivatives contain two aryl groups. The group is called an ''azo group'' (, ). Many textile and leather articles are dyed with azo dyes and pigments. Aryl azo compounds urinary tract infections">Phenazopyridine, an aryl azo compound, is used to treat urinary tract infections">150px Aryl azo compounds are usually stable, crystalline species. Azobenzene is the prototypical aromatic azo compound. It exists mainly as the Cis-trans isomerism, ''trans'' isomer, but upon illumination, converts to the Cis-trans isomerism, ''cis'' isomer. Aromatic azo compounds can be synthesized by azo coupling, which entails an electrophilic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aryl
In organic chemistry, an aryl is any functional group or substituent derived from an aromatic ring, usually an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as phenyl and naphthyl. "Aryl" is used for the sake of abbreviation or generalization, and "Ar" is used as a placeholder for the aryl group in chemical structure diagrams, analogous to “R” used for any organic substituent. “Ar” is not to be confused with the elemental symbol for argon. A simple aryl group is phenyl (), a group derived from benzene. Examples of other aryl groups consist of: * The tolyl group () which is derived from toluene (methylbenzene) * The xylyl group (), which is derived from xylene (dimethylbenzene) * The naphthyl group (), which is derived from naphthalene Arylation is the process in which an aryl group is attached to a substituent. It is typically achieved by cross-coupling reactions. Nomenclature The simplest aryl group is phenyl, which is made up of a benzene ring with one of its hydrogen atom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aniline
Aniline (From , meaning ' indigo shrub', and ''-ine'' indicating a derived substance) is an organic compound with the formula . Consisting of a phenyl group () attached to an amino group (), aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an industrially significant commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starting material for fine chemical synthesis. Its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane, dyes, and other industrial chemicals. Like most volatile amines, it has the odor of rotten fish. It ignites readily, burning with a smoky flame characteristic of aromatic compounds. It is toxic to humans. Relative to benzene, aniline is "electron-rich". It thus participates more rapidly in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Likewise, it is also prone to oxidation: while freshly purified aniline is an almost colorless oil, exposure to air results in gradual darkening to yellow or red, due to the formation of strongly colored, oxidized impurities. Ani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitro Compound
In organic chemistry, nitro compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more nitro functional groups (). The nitro group is one of the most common explosophores (functional group that makes a compound explosive) used globally. The nitro group is also strongly electron-withdrawing. Because of this property, bonds alpha (adjacent) to the nitro group can be acidic. For similar reasons, the presence of nitro groups in aromatic compounds retards electrophilic aromatic substitution but facilitates nucleophilic aromatic substitution. Nitro groups are rarely found in nature. They are almost invariably produced by nitration reactions starting with nitric acid. Synthesis Preparation of aromatic nitro compounds Aromatic nitro compounds are typically synthesized by nitration. Nitration is achieved using a mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid, which produce the nitronium ion (), which is the electrophile: + The nitration product produced on the largest scale, by f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensation Reaction
In organic chemistry, a condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, usually with the loss of a small molecule such as water. If water is lost, the reaction is also known as a dehydration synthesis. However other molecules can also be lost, such as ammonia, ethanol, acetic acid and hydrogen sulfide. The addition of the two molecules typically proceeds in a step-wise fashion to the addition product, usually in equilibrium, and with loss of a water molecule (hence the name condensation). The reaction may otherwise involve the functional groups of the molecule, and is a versatile class of reactions that can occur in acidic or basic conditions or in the presence of a catalyst. This class of reactions is a vital part of life as it is essential to the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids and to the biosynthesis of fatty acids. Many variations of condensation reactions exist. Common examples include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrazines
Hydrazines (R2N−NR2) are a class of chemical compounds with two nitrogen atoms linked via a covalent bond and which carry from one up to four alkyl or aryl substituents. Hydrazines can be considered as derivatives of the inorganic hydrazine (H2N−NH2), in which one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by hydrocarbon groups. Production * 1,1-dimethylhydrazine, 1,1-Dimethylhydrazine is produced by the reduction of N-Nitrosodimethylamine, ''N''-nitrosodimethylamine.Siegfried Hauptmann: ''Organische Chemie'', 2. durchgesehene Auflage, VEB Deutscher Verlag für Grundstoffindustrie, Leipzig, 1985, S. 522–523, . * The reduction of benzenediazonium chloride with tin(II) chloride and hydrochloric acid provides phenylhydrazine. * 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine is produced by the reaction of 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene with hydrazine. * Tetraphenylhydrazine is formed by the oxidation of diphenylamine with potassium permanganate in acetone. Classification Hydrazines can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidation
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. The oxidation and reduction processes occur simultaneously in the chemical reaction. There are two classes of redox reactions: * Electron-transfer – Only one (usually) electron flows from the atom, ion, or molecule being oxidized to the atom, ion, or molecule that is reduced. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * Atom transfer – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously, the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron-donating Group
Electron-rich is jargon that is used in multiple related meanings with either or both kinetic and thermodynamic implications: * with regards to electron-transfer, electron-rich species have low ionization energy and/or are reducing agents. Tetrakis(dimethylamino)ethylene is an electron-rich alkene because, unlike ethylene, it forms isolable radical cation. In contrast, electron-poor alkene tetracyanoethylene is an electron acceptor, forming isolable anions. * with regards to acid-base reactions, electron-rich species have high pKa's and react with weak Lewis acids. * with regards to nucleophilic substitution reactions, electron-rich species are relatively strong nucleophiles, as judged by rates of attack by electrophiles. For example, compared to benzene, pyrrole is more rapidly attacked by electrophiles. Pyrrole is therefore considered to be an electron-rich aromatic ring. Similarly, benzene derivatives with electron-donating groups (EDGs) are attacked by electrophile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diazonium Salt
Diazonium compounds or diazonium salts are a group of organic compounds sharing a common functional group where R can be any organic group, such as an alkyl or an aryl, and X is an inorganic or organic anion, such as a halide. The parent, compound where R is hydrogen, is diazenylium. Structure and general properties Arene derivatives According to X-ray crystallography the linkage is linear in typical diazonium salts. The bond distance in benzenediazonium tetrafluoroborate is 1.083(3) Å, which is almost identical to that for dinitrogen molecule (N≡N). The linear free energy constants σm and σp indicate that the diazonium group is strongly electron-withdrawing. Thus, the diazonio-substituted phenols and benzoic acids have greatly reduced p''K''a values compared to their unsubstituted counterparts. The p''K''a of phenolic proton of 4-hydroxybenzenediazonium is 3.4, versus 9.9 for phenol itself. In other words, the diazonium group raises the ionization constant ''K'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrophilic Substitution Reaction
Electrophilic substitution reactions are chemical reactions in which an electrophile displaces a functional group in a compound, which is typically, but not always, aromatic. Aromatic substitution reactions are characteristic of aromatic compounds and are common ways of introducing functional groups into benzene rings. Some aliphatic compounds can undergo electrophilic substitution as well. Electrophilic aromatic substitution In electrophilic substitution in aromatic compounds, an atom appended to the aromatic ring, usually hydrogen, is replaced by an electrophile. The most important reactions of this type that take place are aromatic nitration, aromatic halogenation, aromatic sulfonation and acylation and alkylating Friedel-Crafts reactions. It further consists of alkylation and acylation. Electrophilic aliphatic substitution In electrophilic substitution in aliphatic compounds, an electrophile displaces a functional group. This reaction is similar to nucleophili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azo Coupling
In organic chemistry, an azo coupling is an organic reaction, reaction between a diazonium compound () and another aromatic compound that produces an azo compound (). In this electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the aryldiazonium cation is the electrophile, and the activating group, activated carbon (usually from an arene, which is called coupling agent), serves as a nucleophile. Classical coupling agents are phenols and naphthols. Usually the diazonium reagent attacks at the para position of the coupling agent. When the para position is occupied, coupling occurs at a ortho position, albeit at a slower rate. Uses of the reaction Aromatic azo compounds tend to be brightly colored due to their extended Conjugated system, conjugated systems. Many are useful dyes (see azo dye). Important azo dyes include methyl red and pigment red 170. Azo printing exploits this reaction as well. In this case, the diazonium ion is degraded by light, leaving a latent image in undegrade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isomer
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formula – that is, the same number of atoms of each element (chemistry), element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. ''Isomerism'' refers to the existence or possibility of isomers. Isomers do not necessarily share similar chemical property, chemical or physical property, physical properties. Two main forms of isomerism are structural isomerism, structural (or constitutional) isomerism, in which ''chemical bond, bonds'' between the atoms differ; and stereoisomerism (or spatial isomerism), in which the bonds are the same but the ''relative positions'' of the atoms differ. Isomeric relationships form a hierarchy. Two chemicals might be the same constitutional isomer, but upon deeper analysis be stereoisomers of each other. Two molecules that are the same stereoisomer as each other might be in different conformational forms or be different Isotopologue, isotopologues. The depth of analy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |