|
Annuities
In investment, an annuity is a series of payments made at equal intervals.Kellison, Stephen G. (1970). ''The Theory of Interest''. Homewood, Illinois: Richard D. Irwin, Inc. p. 45 Examples of annuities are regular deposits to a savings account, monthly home mortgage payments, monthly insurance payments and pension payments. Annuities can be classified by the frequency of payment dates. The payments (deposits) may be made weekly, monthly, quarterly, yearly, or at any other regular interval of time. Annuities may be calculated by mathematical functions known as "annuity functions". An annuity which provides for payments for the remainder of a person's lifetime is a life annuity. Types Annuities may be classified in several ways. Timing of payments Payments of an ''annuity-immediate'' are made at the end of payment periods, so that interest accrues between the issue of the annuity and the first payment. Payments of an ''annuity-due'' are made at the beginning of payment periods, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annuities Under European Law
Under European Union law, an annuity is a financial contract which provides an income stream in return for an initial payment with specific parameters. It is the opposite of a settlement funding. A Swiss annuity is not considered a European annuity for tax reasons. Immediate annuity An immediate annuity is an annuity for which the time between the contract date and the date of the first payment is not longer than the time interval between payments. A common use for an immediate annuity is to provide a pension to a retired person or persons. It is a financial contract which makes a series of payments with certain characteristics: * either level or fluctuating periodical payments * made annually, or at more frequent intervals * in advance or arrears * duration may be: **fixed (annuity certain) **during the lifetime or one or more persons, possibly reduced after death of one person **during the lifetime but not longer than a maximum number of years **during the lifetime but not s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annuities Under American Law
In the United States, an annuity is a financial product which offers tax-deferred growth and which usually offers benefits such as an income for life. Typically these are offered as structured (insurance) products that each state approves and regulates in which case they are designed using a mortality table and mainly guaranteed by a life insurer. There are many different varieties of annuities sold by carriers. In a typical scenario, an investor (usually the annuitant) will make a single cash premium to own an annuity. After the policy is issued the owner may elect to annuitize the contract (start receiving payments) for a chosen period of time (e.g., 5, 10, 20 years, a lifetime). This process is called annuitization and can also provide a predictable, guaranteed stream of future income during retirement until the death of the annuitant (or joint annuitants). Alternatively, an investor can defer annuitizing their contract to get larger payments later, hedge long-term care cost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Annuity
A life annuity is an annuity, or series of payments at fixed intervals, paid while the purchaser (or annuitant) is alive. The majority of life annuities are insurance products sold or issued by life insurance companies however substantial case law indicates that annuity products are not necessarily insurance products. Annuities can be purchased to provide an income during retirement, or originate from a ''structured settlement'' of a personal injury lawsuit. Life annuities may be sold in exchange for the immediate payment of a lump sum (single-payment annuity) or a series of regular payments (flexible payment annuity), prior to the onset of the annuity. The payment stream from the issuer to the annuitant has an unknown duration based principally upon the date of death of the annuitant. At this point the contract will terminate and the remainder of the fund accumulated is forfeited unless there are other annuitants or beneficiaries in the contract. Thus a life annuity is a form o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Annuity
A life annuity is an annuity, or series of payments at fixed intervals, paid while the purchaser (or annuitant) is alive. The majority of life annuities are insurance products sold or issued by life insurance companies however substantial case law indicates that annuity products are not necessarily insurance products. Annuities can be purchased to provide an income during retirement, or originate from a ''structured settlement'' of a personal injury lawsuit. Life annuities may be sold in exchange for the immediate payment of a lump sum (single-payment annuity) or a series of regular payments (flexible payment annuity), prior to the onset of the annuity. The payment stream from the issuer to the annuitant has an unknown duration based principally upon the date of death of the annuitant. At this point the contract will terminate and the remainder of the fund accumulated is forfeited unless there are other annuitants or beneficiaries in the contract. Thus a life annuity is a form o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equity-indexed Annuity
An indexed annuity (the word ''equity'' previously tied to indexed annuities has been removed to help prevent the assumption of stock market investing being present in these products) in the United States is a type of tax-deferred annuity whose credited interest is linked to an equity index—typically the S&P 500 or international index. It guarantees a minimum interest rate (typically between 1% and 3%) if held to the end of the surrender term and protects against a loss of principal. An equity index annuity is a contract with an insurance or annuity company. The returns may be higher than fixed instruments such as certificates of deposit (CDs), money market accounts, and bonds but not as high as market returns. Equity Index Annuities are insured by each State's Guarantee Fund; coverage is not as strong as the insurance provided by the FDIC. For example, in California the fund will cover "80% not to exceed $250,000." The guarantees in the contract are backed by the relative s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actuarial Notation
Actuarial notation is a shorthand method to allow actuaries to record mathematical formulas that deal with interest rates and life tables. Traditional notation uses a halo system where symbols are placed as superscript or subscript before or after the main letter. Example notation using the halo system can be seen below. Various proposals have been made to adopt a linear system where all the notation would be on a single line without the use of superscripts or subscripts. Such a method would be useful for computing where representation of the halo system can be extremely difficult. However, a standard linear system has yet to emerge. Example notation Interest rates \,i is the annual effective interest rate, which is the "true" rate of interest over ''a year''. Thus if the annual interest rate is 12% then \,i = 0.12. \,i^ (pronounced "i ''upper'' m") is the nominal interest rate convertible m times a year, and is numerically equal to m times the effective rate of interest over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
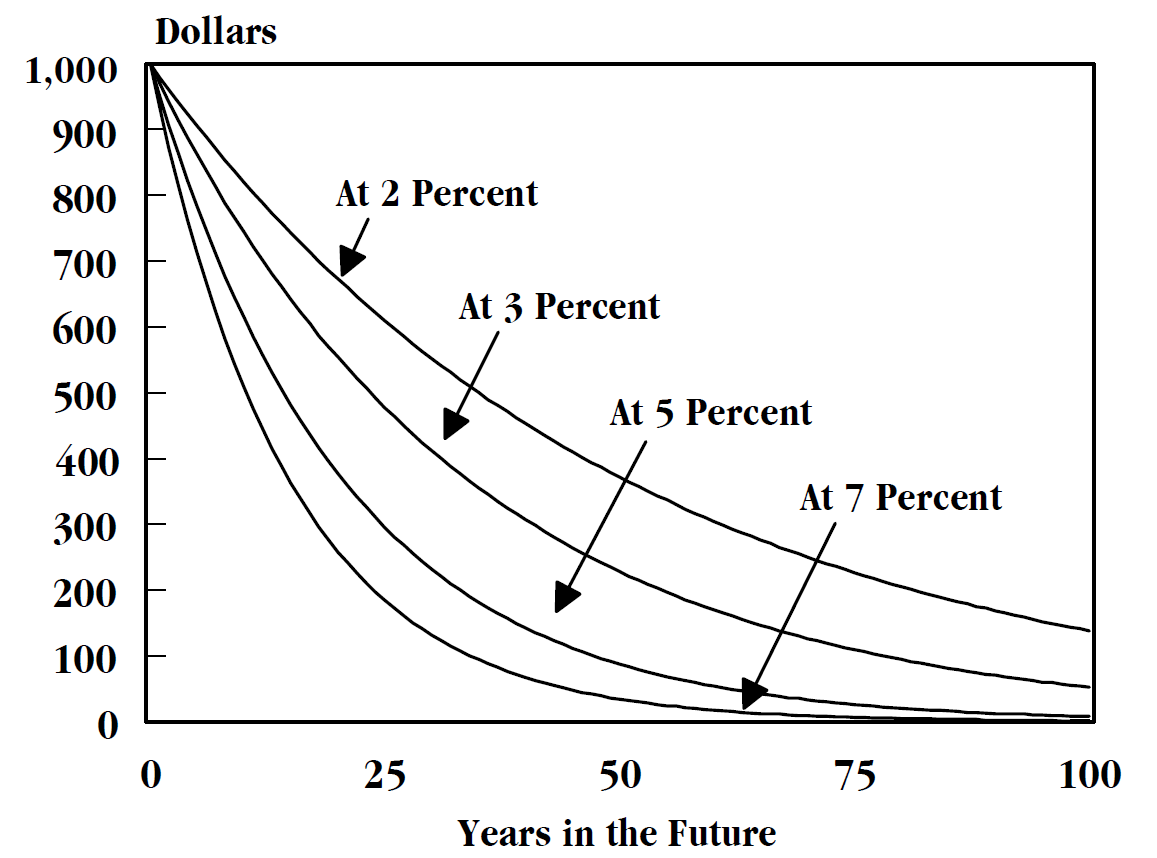
Present Value
In economics and finance, present value (PV), also known as present discounted value, is the value of an expected income stream determined as of the date of valuation. The present value is usually less than the future value because money has interest-earning potential, a characteristic referred to as the time value of money, except during times of zero- or negative interest rates, when the present value will be equal or more than the future value. Time value can be described with the simplified phrase, "A dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow". Here, 'worth more' means that its value is greater than tomorrow. A dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow because the dollar can be invested and earn a day's worth of interest, making the total accumulate to a value more than a dollar by tomorrow. Interest can be compared to rent. Just as rent is paid to a landlord by a tenant without the ownership of the asset being transferred, interest is paid to a lender by a borr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insurance
Insurance is a means of protection from financial loss in which, in exchange for a fee, a party agrees to compensate another party in the event of a certain loss, damage, or injury. It is a form of risk management, primarily used to hedge against the risk of a contingent or uncertain loss. An entity which provides insurance is known as an insurer, insurance company, insurance carrier, or underwriter. A person or entity who buys insurance is known as a policyholder, while a person or entity covered under the policy is called an insured. The insurance transaction involves the policyholder assuming a guaranteed, known, and relatively small loss in the form of a payment to the insurer (a premium) in exchange for the insurer's promise to compensate the insured in the event of a covered loss. The loss may or may not be financial, but it must be reducible to financial terms. Furthermore, it usually involves something in which the insured has an insurable interest established by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annuities Under Swiss Law
A Swiss annuity simply refers to a fixed or variable annuity marketed from Switzerland or issued by a Swiss based life insurance company but has no legal definition. Insurance brokers promoting annuity contracts issued by insurance companies domiciled in jurisdictions outside of Switzerland, such as Liechtenstein, also market such contracts as Swiss annuities. The hallmarks of a Swiss annuity generally include the ability to invest in multiple currencies, the custody of assets within Switzerland, and the flexibility of withdrawals. Often touted benefits of a Swiss annuity include the safety of Switzerland plus some degree of asset protection. U.S. Tax Considerations For U.S. taxpayers owning a fixed annuity issued by a non-U.S. insurance company, including a Swiss annuity, the interest credited within the policy is subject to U.S. income tax on an annual basis under the original issue discount rules. Variable annuities issued by non-U.S. insurance companies may permit tax deferr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Value Of Money
The time value of money is the widely accepted conjecture that there is greater benefit to receiving a sum of money now rather than an identical sum later. It may be seen as an implication of the later-developed concept of time preference. The time value of money is among the factors considered when weighing the opportunity costs of spending rather than saving or investing money. As such, it is among the reasons why interest is paid or earned: interest, whether it is on a bank deposit or debt, compensates the depositor or lender for the loss of their use of their money. Investors are willing to forgo spending their money now only if they expect a favorable net return on their investment in the future, such that the increased value to be available later is sufficiently high to offset both the preference to spending money now and inflation (if present); see required rate of return. History The Talmud (~500 CE) recognizes the time value of money. In Tractate Makkos page 3a the Ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actuarial Present Value
The actuarial present value (APV) is the expected value of the present value of a contingent cash flow stream (i.e. a series of payments which may or may not be made). Actuarial present values are typically calculated for the benefit-payment or series of payments associated with life insurance and life annuities. The probability of a future payment is based on assumptions about the person's future mortality which is typically estimated using a life table. Life insurance Whole life insurance pays a pre-determined benefit either at or soon after the insured's death. The symbol ''(x)'' is used to denote "a life aged ''x''" where ''x'' is a non-random parameter that is assumed to be greater than zero. The actuarial present value of one unit of whole life insurance issued to ''(x)'' is denoted by the symbol \,A_x or \,\overline_x in actuarial notation. Let ''G>0'' (the "age at death") be the random variable that models the age at which an individual, such as ''(x)'', will die. And let ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Value Of Money
The time value of money is the widely accepted conjecture that there is greater benefit to receiving a sum of money now rather than an identical sum later. It may be seen as an implication of the later-developed concept of time preference. The time value of money is among the factors considered when weighing the opportunity costs of spending rather than saving or investing money. As such, it is among the reasons why interest is paid or earned: interest, whether it is on a bank deposit or debt, compensates the depositor or lender for the loss of their use of their money. Investors are willing to forgo spending their money now only if they expect a favorable net return on their investment in the future, such that the increased value to be available later is sufficiently high to offset both the preference to spending money now and inflation (if present); see required rate of return. History The Talmud (~500 CE) recognizes the time value of money. In Tractate Makkos page 3a the Ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |