|
Ahmose I
Ahmose I ( egy, jꜥḥ ms(j .w), reconstructed /ʔaʕaħ'maːsjə/ ( MK), Egyptological pronunciation ''Ahmose'', sometimes written as ''Amosis'' or ''Aahmes'', meaning "Iah (the Moon) is born") was a pharaoh Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: ''pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the an ... and founder of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, classified as the first dynasty of the New Kingdom of Egypt, the era in which ancient Egypt achieved the peak of its power. He was a member of the Thebes, Egypt, Theban royal house, the son of pharaoh Seqenenre Tao and brother of the last pharaoh of the Seventeenth Dynasty of Egypt, Seventeenth dynasty, Kamose. During the reign of his father or grandfather, Thebes rebelled against the Hyksos, the rulers of Lower Egypt. When he was seven years old, his father was killed,#Shaw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manetho
Manetho (; grc-koi, Μανέθων ''Manéthōn'', ''gen''.: Μανέθωνος) is believed to have been an Egyptian priest from Sebennytos ( cop, Ϫⲉⲙⲛⲟⲩϯ, translit=Čemnouti) who lived in the Ptolemaic Kingdom in the early third century BC, during the Hellenistic period. He authored the ''Aegyptiaca'' (''History of Egypt'') in Greek, a major chronological source for the reigns of the kings of ancient Egypt. It is unclear if he wrote his history and king list during the reign of Ptolemy I Soter or Ptolemy II Philadelphos, but it was completed no later than that of Ptolemy III Euergetes. Name The original Egyptian version of Manetho's name is lost, but some speculate it means "Truth of Thoth", "Gift of Thoth", "Beloved of Thoth", "Beloved of Neith", or "Lover of Neith". Less accepted proposals are ''Myinyu-heter'' ("Horseherd" or "Groom") and ''Ma'ani-Djehuti'' ("I have seen Thoth"). In the Greek language, the earliest fragments (the inscription of uncertain date ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmose-Henuttamehu
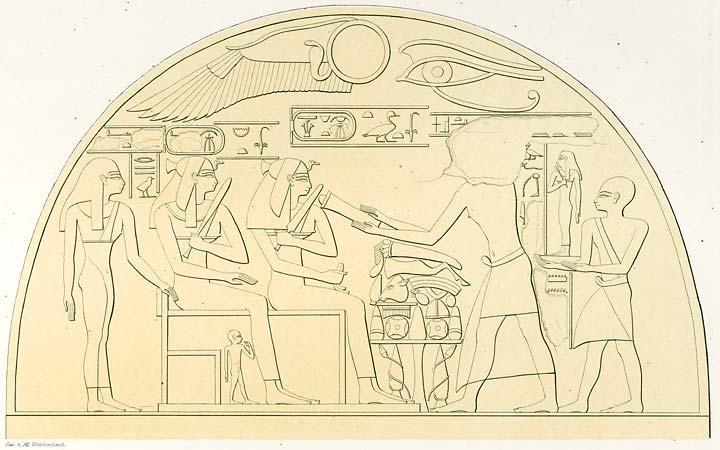
Ahmose-Henuttamehu (“Child of the Moon; Mistress of Lower Egypt”) was a princess and queen of the late 17th-early 18th dynasties of Egypt. Family Ahmose-Henuttamehu was a daughter of Pharaoh Seqenenre Tao by his sister-wife Ahmose Inhapy. She was probably married to her half-brother Pharaoh Ahmose I, since her titles include King's Wife (''hmt-nisw''), Great King's Wife (''hmt-niswt-wrt''), King's Daughter (''s3t-niswt'') and King's Sister (''snt-niswt''). Ahmose-Henuttamehu was a half-sister to the Great Royal Wife and God's Wife of Amun Ahmose-Nefertari. Life and burial Not much is known about the life of Ahmose-Henuttamehu. The Queen is mentioned on a stela as depicted in Lepsius' Denkmahler. Ahmose-Henuttamehu's mummy was discovered in 1881 in her own coffin in the tomb DB320 and is now in the Egyptian Museum in Cairo. It was examined by Gaston Maspero in December 1882. Henuttamehu was an old woman when she died, with worn teeth. Quotes from the ''Book of the Dead'' w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amun
Amun (; also ''Amon'', ''Ammon'', ''Amen''; egy, jmn, reconstructed as (Old Egyptian and early Middle Egyptian) → (later Middle Egyptian) → (Late Egyptian), cop, Ⲁⲙⲟⲩⲛ, Amoun) romanized: ʾmn) was a major ancient Egyptian deity who appears as a member of the Hermopolitan Ogdoad. Amun was attested from the Old Kingdom together with his wife Amunet. With the 11th Dynasty ( 21st century BC), Amun rose to the position of patron deity of Thebes by replacing Montu. After the rebellion of Thebes against the Hyksos and with the rule of Ahmose I (16th century BC), Amun acquired national importance, expressed in his fusion with the Sun god, Ra, as Amun-Ra (alternatively spelled Amon-Ra or Amun-Re). Amun-Ra retained chief importance in the Egyptian pantheon throughout the New Kingdom (with the exception of the " Atenist heresy" under Akhenaten). Amun-Ra in this period (16th to 11th centuries BC) held the position of transcendental, self-created creator dei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avaris
Avaris (; Egyptian: ḥw.t wꜥr.t, sometimes ''hut-waret''; grc, Αὔαρις, Auaris; el, Άβαρις, Ávaris; ar, حوّارة, Hawwara) was the Hyksos capital of Egypt located at the modern site of Tell el-Dab'a in the northeastern region of the Nile Delta. As the main course of the Nile migrated eastward, its position at the hub of Egypt's delta emporia made it a major capital suitable for trade. It was occupied from about the 18th century BC until its capture by Ahmose I. Etymology The name in the Egyptian language of the 2nd millennium BC was probably pronounced *Ḥaʔət-Waʕrəʔ “House of the Region” and denotes the capital of an administrative division of the land (''wʕr.t''). Today, the name ''Hawara'' survives, referring to the site at the entrance to Faiyum. Alternatively, Clement of Alexandria referred to the name of this city as "Athyria". Excavations In 1885, the Swiss Édouard Naville started the first excavations in the area around Tell-el-Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abydos, Egypt
Abydos ( ar, أبيدوس, Abīdūs or ; Sahidic cop, Ⲉⲃⲱⲧ ') is one of the oldest cities of ancient Egypt, and also of the eighth nome in Upper Egypt. It is located about west of the Nile at latitude 26° 10' N, near the modern Egyptian towns of El Araba El Madfuna and El Balyana. In the ancient Egyptian language, the city was called Abdju (''ꜣbḏw'' or ''AbDw''). The English name ''Abydos'' comes from the Greek , a name borrowed by Greek geographers from the unrelated city of Abydos on the Hellespont. Considered one of the most important archaeological sites in Egypt, the sacred city of Abydos was the site of many ancient temples, including Umm el-Qa'ab, a royal necropolis where early pharaohs were entombed. These tombs began to be seen as extremely significant burials and in later times it became desirable to be buried in the area, leading to the growth of the town's importance as a cult site. Today, Abydos is notable for the memorial temple of Seti I, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deir El-Bahri
Deir el-Bahari or Dayr al-Bahri ( ar, الدير البحري, al-Dayr al-Baḥrī, the Monastery of the North) is a complex of mortuary temples and tombs located on the west bank of the Nile, opposite the city of Luxor, Egypt. This is a part of the Theban Necropolis. The first monument built at the site was the mortuary temple of Mentuhotep II of the Eleventh Dynasty. It was constructed during the 21st century BC. During the Eighteenth Dynasty, Amenhotep I and Hatshepsut also built extensively at the site. Mortuary temple of Nebhepetre Mentuhotep Mentuhotep II, the Eleventh Dynasty king who reunited Egypt at the beginning of the Middle Kingdom, built a very unusual funerary complex. His mortuary temple was built on several levels in the great bay at Deir el-Bahari. It was approached by a 16-metre-wide (50-ft) causeway leading from a valley temple which no longer exists. The mortuary temple itself consists of a forecourt and entrance gate, enclosed by walls on three sides, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahhotep I
Ahhotep I ( egy, jꜥḥ-ḥtp (.w), alternatively Anglicized ''Ahhotpe'' or ''Aahhotep'', "Iah (the Moon) is satisfied") was an ancient Egyptian queen who lived circa 1560– 1530 BC, during the end of the Seventeenth Dynasty of Egypt. She was the daughter of Queen Tetisheri (known as Teti the Small) and Senakhtenre Ahmose, and was probably the sister, as well as the queen consort, of Pharaoh Seqenenre Tao ll. Ahhotep I had a long and influential life. She ruled as regent for her son Ahmose I for a time. Her titles include Great Royal Wife and "Associate of the White Crown Bearer" ( egy, label=none, ẖnmt nfr-ḥḏt). The title "King's Mother" ( egy, label=none, mwt nswt) was found on the Deir el-Bahari coffin. Different Ahhoteps The naming and numbering of the queens named Ahhotep has changed during the years. Outlining the different naming and numbering conventions over the years: Late 19th century: Ahhotep I was thought to be the wife of Seqenenre Tao. The coffins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seqenenre Tao
Seqenenre Tao (also Seqenera Djehuty-aa or Sekenenra Taa, called 'the Brave') ruled over the last of the local kingdoms of the Theban region of Egypt in the Seventeenth Dynasty during the Second Intermediate Period. He probably was the son and successor to Senakhtenre Ahmose and Queen Tetisheri. The dates of his reign are uncertain, but he may have risen to power in the decade ending in 1560 BC or in 1558 BC (based on the probable accession date of his son, Ahmose I, the first ruler of the Eighteenth Dynasty, see Egyptian chronology). With his queen, Ahhotep I, Seqenenre Tao fathered two pharaohs, Kamose, his immediate successor who was the last pharaoh of the Seventeenth Dynasty, and Ahmose I who, following a regency by his mother, was the first pharaoh of the Eighteenth. Seqenenre Tao is credited with starting the opening moves in a war of revanchism against Hyksos incursions into Egypt, which saw the country completely liberated during the reign of his son Ahmose I. Reign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutnofret
Mutnofret (“Mut is Beautiful”), also rendered as Mutneferet or Mutnefert, was a queen during the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. She was a secondary wife of Thutmose I—Queen Ahmose was the chief wife—and the mother of Thutmose II. Based on her titles of ''King's Daughter'' and ''King's Sister'', she is likely to have been a daughter of Ahmose I and a sister of Amenhotep I. It is likely that she was also the mother of Thutmose I's other sons, Amenmose, Wadjmose and Ramose. She was depicted in the Deir el-Bahri temple built by her grandson Thutmose III; on a stela found at the Ramesseum The Ramesseum is the memorial temple (or mortuary temple) of Pharaoh Ramesses II ("Ramesses the Great", also spelled "Ramses" and "Rameses"). It is located in the Theban Necropolis in Upper Egypt, on the west of the River Nile, across from the m ...; on the colossus of her son; and a statue of her bearing a dedication by Thutmose II was found in Wadjmose's chapel. This suggests that Mutnofr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramose (prince)
Ramose was an ancient Egyptian prince of the Eighteenth Dynasty; probably the son of Pharaoh Ahmose I. He is depicted in the 20th Dynasty tomb of Inherkhau (TT359) among the "Lords of the West" with several of his family members and a few important pharaohs (among the depicted are (Amenhotep I, Ahmose I, Ahhotep, Ahmose Meritamon, Ahmose Sitamun, Siamun, Ahmose Henuttamehu, Ahmose Tumerisy, Ahmose Nebetta, Ahmose Sipair, Ahmose Nefertari, Ramesses I, Mentuhotep II, Amenhotep II, Seqenenre Tao II, Ramesses IV, Thutmose I Thutmose I (sometimes read as Thutmosis or Tuthmosis I, Thothmes in older history works in Latinized Greek; Ancient Egyptian: '' ḏḥwtj- ms'', ''Tʼaḥawtī-mīsaw'', , meaning "Thoth is born") was the third pharaoh of the 18th Dynasty of E ...). A statue of his is owned by the University of Liverpool.Dodson–Hilton, p.129 Sources {{reflist Princes of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt Children of Ahmose I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmose-ankh
Ahmose-ankh was a prince during the early Eighteenth dynasty of Egypt. He was the son of Pharaoh Ahmose I and Queen Ahmose Nefertari. He was the crown prince but pre-deceased his father, thus the next pharaoh was his younger brother Amenhotep I. His sister was Ahmose-Meritamun. A stela which depicts him with his parents is now in the Luxor Museum. Sources *Aidan Dodson & Dyan Hilton: The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt. Thames & Hudson Thames & Hudson (sometimes T&H for brevity) is a publisher of illustrated books in all visually creative categories: art, architecture, design, photography, fashion, film, and the performing arts. It also publishes books on archaeology, history, ..., 2004, , p. 129 {{DEFAULTSORT:Ahmose-ankh Princes of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt Heirs to the ancient Egyptian throne 16th-century BC Egyptian people Children of Ahmose I Heirs apparent who never acceded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(2865505031).jpg)
.jpg)
