|
Admiralty Islands Languages
The Admiralty Islands languages are a group of some thirty Oceanic languages spoken on the Admiralty Islands. They may include Yapese, which has proven difficult to classify. Languages According to Lynch, Ross, & Crowley (2002), the structure of the family is: *Eastern **Manus Manus may refer to: * Manus (anatomy), the zoological term for the distal portion of the forelimb of an animal (including the human hand) * ''Manus'' marriage, a type of marriage during Roman times Relating to locations around New Guinea * Man ... **Southeast: Baluan-Pam, Lenkau, Lou, Nauna, Penchal *Western ** Northern Kaniet and Southern Kaniet (†) ** Seimat ** Wuvulu-Aua (as two languages) As noted, Yapese and Nguluwan may be part of the Admiralty Islands languages as well. References * Blust, Robert (2007). The prenasalised trills of Manus. In ''Language description, history, and development: Linguistic indulgence in memory of Terry Crowley,'' ed. by Jeff Siegel, John Lynch, and Dian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
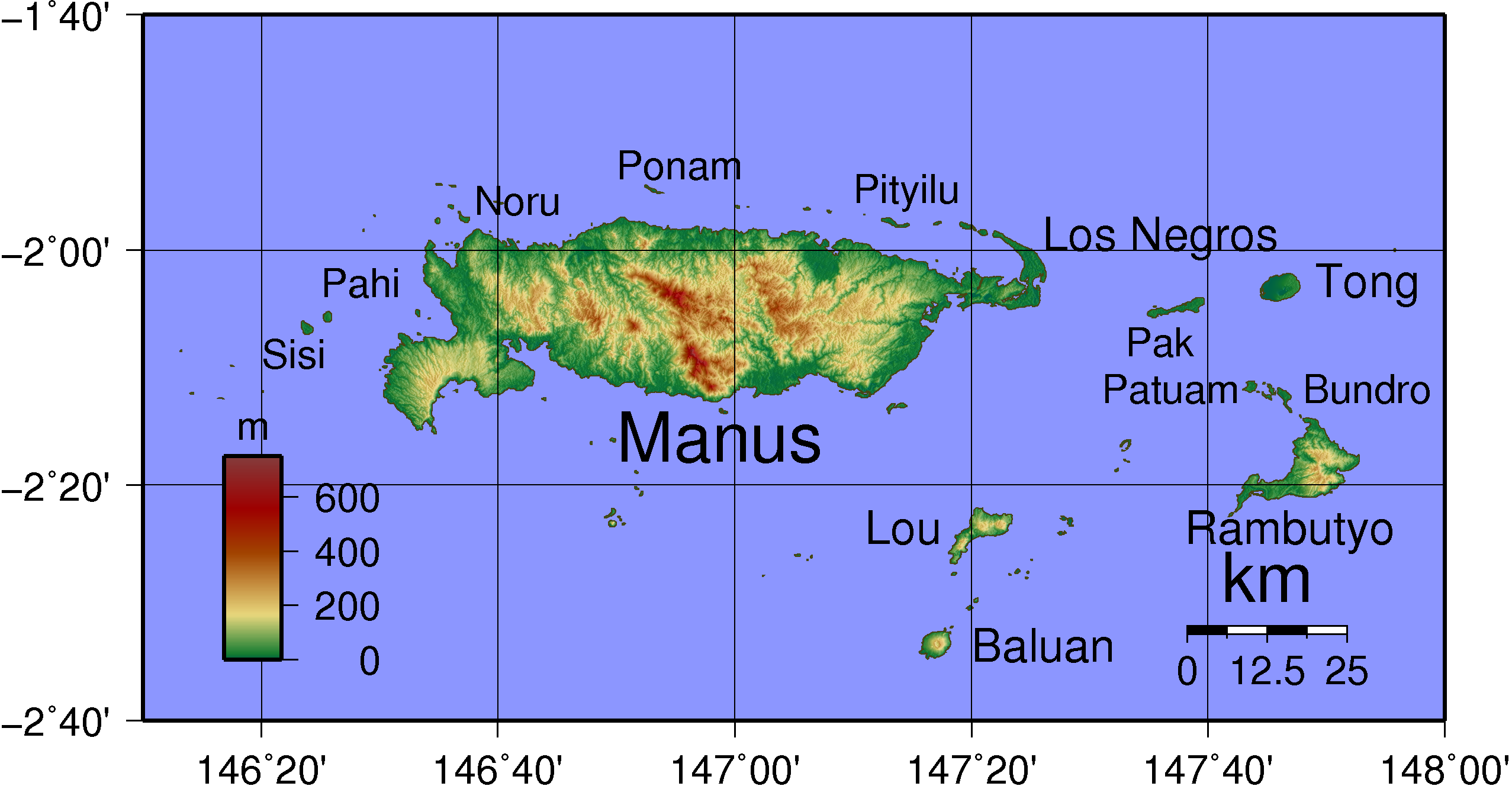
Admiralty Islands
The Admiralty Islands are an archipelago group of 18 islands in the Bismarck Archipelago, to the north of New Guinea in the South Pacific Ocean. These are also sometimes called the Manus Islands, after the largest island. These rainforest-covered islands form part of Manus Province, the smallest and least-populous province of Papua New Guinea, in its Islands Region. The total area is . Many of the Admiralty Islands are atolls and uninhabited. Islands The larger islands in the center of the group are Manus Island and Los Negros Island. The other larger islands are Tong Island, Pak Island, Rambutyo Island, Lou Island, and Baluan Island to the east, Mbuke Island to the south and Bipi Island to the west of Manus Island. Other islands that have been noted as significant places in the history of Manus include Ndrova Island, Pitylu Island and Ponam Island. Geography The temperature of the Admiralty Islands varies little throughout the year, reaching daily highs of and at ni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nauna Language
Nauna is an Oceanic language spoken in the single village of Nauna () on Nauna Island in Rapatona Rural LLG, Manus Province, Papua New Guinea. References External links Audio recordingsanwritten materialson Nauna are available through Kaipuleohone Kaipuleohone is a digital ethnographic archive that houses audio and visual files, photographs, as well as hundreds of textual material such as notes, dictionaries, and transcriptions relating to small and endangered languages. The archive is stored ... Admiralty Islands languages Languages of Manus Province Vulnerable languages {{admiralty-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admiralty Islands Languages
The Admiralty Islands languages are a group of some thirty Oceanic languages spoken on the Admiralty Islands. They may include Yapese, which has proven difficult to classify. Languages According to Lynch, Ross, & Crowley (2002), the structure of the family is: *Eastern **Manus Manus may refer to: * Manus (anatomy), the zoological term for the distal portion of the forelimb of an animal (including the human hand) * ''Manus'' marriage, a type of marriage during Roman times Relating to locations around New Guinea * Man ... **Southeast: Baluan-Pam, Lenkau, Lou, Nauna, Penchal *Western ** Northern Kaniet and Southern Kaniet (†) ** Seimat ** Wuvulu-Aua (as two languages) As noted, Yapese and Nguluwan may be part of the Admiralty Islands languages as well. References * Blust, Robert (2007). The prenasalised trills of Manus. In ''Language description, history, and development: Linguistic indulgence in memory of Terry Crowley,'' ed. by Jeff Siegel, John Lynch, and Dian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nguluwan Language
Nguluwan is a mixed language A mixed language is a language that arises among a bilingual group combining aspects of two or more languages but not clearly deriving primarily from any single language. It differs from a creole language, creole or pidgin, pidgin language in that ... spoken on an atoll of that name between Yap and Palau. The grammar and lexicon are Yapese, but the phonology has been affected by Ulithian, and speakers are shifting to that language. References Oceanic languages Languages of the Federated States of Micronesia Admiralty Islands languages Mixed languages {{austronesian-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuvulu-Aua Language
The Wuvulu-Aua language is spoken on Wuvulu and Aua Islands by speakers scattered around the Manus Province of Papua New Guinea. Although the Wuvulu-Aua language has a similar grammatical structure, word order, and tense to other Oceanic languages, it has an unusually complex morphology. Wuvulu Island is located in the Papua New Guinea Manus Province and reaches about 10 feet above sea level. As a member of the Admiralty Islands, the Wuvulu and Aua islands are a part of the Bismarck Archipelago that includes other provinces such as the New Ireland province, the East New Britain province, the Morobe province and much more. Wuvulu is spoken by an estimated 1,600 people in the Manus Province. There are approximately 1,000 speakers of the language on Wuvulu and 400 on Aua. The remaining speakers of Wuvulu inhabit either the other islands located in the Papua New Guinea territory. Wuvulu is most similar to Austronesian, Malayo-Paolynesian, and other Oceanic languages scattered aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seimat Language
The Seimat language is one of three Western Admiralty Islands languages, the other two being Wuvulu-Aua and the extinct Kaniet. The language is spoken by approximately 1000 people on the Ninigo and the Anchorite Islands in western Manus Province of Papua New Guinea. It has SVO word order. References Further reading * External links * Kaipuleohone Kaipuleohone is a digital ethnographic archive that houses audio and visual files, photographs, as well as hundreds of textual material such as notes, dictionaries, and transcriptions relating to small and endangered languages. The archive is stored ... has recordings and written materials for Seimat Admiralty Islands languages Languages of Manus Province Subject–verb–object languages {{admiralty-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Kaniet Language
The Kaniet languages were two of four Western Admiralty Islands languages, a subgroup of the Admiralty Islands languages, the other two being Wuvulu-Aua and Seimat. The languages were spoken on the Kaniet Islands (Anchorite Islands) in western Manus Province of Papua New Guinea Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country i ... until the 1950s. Two languages were spoken on the islands, one reported by Thilenius and one by Dempwolff. References Admiralty Islands languages Languages of Manus Province Extinct languages of Oceania Languages extinct in the 1950s {{admiralty-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Kaniet Language
The Kaniet languages were two of four Western Admiralty Islands languages, a subgroup of the Admiralty Islands languages, the other two being Wuvulu-Aua and Seimat. The languages were spoken on the Kaniet Islands The Kaniet Islands are the easternmost group islands within the Western Islands of the Bismarck Archipelago, Papua New Guinea. It consists four islands and one islet. Their coordinates are , located north-east of the Hermit Islands. Sae Island is ... (Anchorite Islands) in western Manus Province of Papua New Guinea until the 1950s. Two languages were spoken on the islands, one reported by Thilenius and one by Dempwolff. References Admiralty Islands languages Languages of Manus Province Extinct languages of Oceania Languages extinct in the 1950s {{admiralty-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penchal Language
Penchal is an Oceanic language of Manus Province, Papua New Guinea. References External links * Kaipuleohone has archived audio recordings Sound recording and reproduction is the electrical, Mechanical system, mechanical, electronic, or digital inscription and re-creation of sound waves, such as spoken voice, singing, instrumental music, or sound effects. The two main classes of ... and written materials on Penchal Admiralty Islands languages Languages of Manus Province {{admiralty-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lou Language (Austronesian)
Lou is a Southeast Admiralty Islands language spoken on Lou Island of Manus Province, Papua New Guinea by 1,000 people. Dialects There are three dialects. The main dialect is Rei. Grammar Lou has thirteen consonants and seven vowels. It is a nominative–accusative language and has SVO word order. References External links A Lou dictionary* Kaipuleohone archive of Robert Blust's materials include written Writing is a medium of human communication which involves the representation of a language through a system of physically inscribed, mechanically transferred, or digitally represented symbols. Writing systems do not themselves constitute h ... and audio recorded materials Admiralty Islands languages Languages of Manus Province {{admiralty-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayo-Polynesian Languages
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast Asia (Indonesian and Philippine Archipelago) and the Pacific Ocean, with a smaller number in continental Asia in the areas near the Malay Peninsula. Cambodia, Vietnam and the Chinese island Hainan serve as the northwest geographic outlier. Malagasy, spoken in the island of Madagascar off the eastern coast of Africa in the Indian Ocean, is the furthest western outlier. The languages spoken south-westward from central Micronesia until Easter Island are sometimes referred to as the Polynesian languages. Many languages of the Malayo-Polynesian family show the strong influence of Sanskrit and Arabic, as the western part of the region has been a stronghold of Hinduism, Buddhism, and, later, Islam. Two morphological characteristics of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lenkau Language
Lenkau is an Oceanic language spoken in a single village on Rambutyo Island in Manus Province, Papua New Guinea. It is spoken in Lenkau village (), Rapatona Rural LLG. References External links * Kaipuleohone's Robert Blust Robert A. Blust (; ; May 9, 1940 – January 5, 2022) was an American linguist who worked in several areas, including historical linguistics, lexicography and ethnology. He was Professor of Linguistics at the University of Hawaii at Mānoa. Blus ... collection includes written materials from Lenkau Admiralty Islands languages Languages of Manus Province {{admiralty-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |