|
1984 In Israel
Events in the year 1984 in Israel. Incumbents * President of Israel – Chaim Herzog * Prime Minister of Israel – Yitzhak Shamir (Likud) until 13 September, Shimon Peres (Alignment) * President of the Supreme Court – Meir Shamgar * Chief of General Staff – Moshe Levi * Government of Israel – 20th Government of Israel until 13 September, 21st Government of Israel Events * 23 July – The Israeli legislative election ends. The Alignment party wins a narrow victory, again becoming the largest party in the Knesset, but cannot form a government with any of the smaller parties. As a result, a national unity government with Likud is established. It is agreed that Alignment leader Shimon Peres and Likud leader Yitzhak Shamir will each hold the post of Prime Minister for two years. * 13 September – Shimon Peres presents the Twenty-first government of Israel and begins to serve as Prime Minister. * 21 November – The first immigrants in Operation Moses arrive from Ethiopi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of Israel
The president of the State of Israel ( he, נְשִׂיא מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, Nesi Medinat Yisra'el, or he, נְשִׂיא הַמְדִינָה, Nesi HaMedina, President of the State) is the head of state of Israel. The position is largely a ceremonial role, with executive power vested in the cabinet led by the prime minister. The incumbent president is Isaac Herzog, who took office on 7 July 2021. Presidents are elected by the Knesset for a single seven-year term. Election The President of Israel is elected by an absolute majority in the Knesset, by secret ballot. If no candidate receives an absolute majority of votes in the first or second round of voting, the candidate with the least votes is eliminated in each subsequent round, if needed until only two remain. From 1949 to 2000, the president was elected for a five-year term, and was allowed to serve up to two terms in office. Since 2000, the president serves a single seven-year term. Any Israeli residen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east and northeast, Kenya to the south, South Sudan to the west, and Sudan to the northwest. Ethiopia has a total area of . As of 2022, it is home to around 113.5 million inhabitants, making it the 13th-most populous country in the world and the 2nd-most populous in Africa after Nigeria. The national capital and largest city, Addis Ababa, lies several kilometres west of the East African Rift that splits the country into the African and Somali tectonic plates. Anatomically modern humans emerged from modern-day Ethiopia and set out to the Near East and elsewhere in the Middle Paleolithic period. Southwestern Ethiopia has been proposed as a possible homeland of the Afroasiatic langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ran Danker
Ran Danker ( he, רן דנקר; born Khalil Yosef Danker on January 7, 1984) is an Israeli–American actor, singer and model. He starred in hit Israeli series such as ''HaShir Shelanu'' (2004–2007), ''The Gordin Cell'' (2012–2015), '' Miguel'' (2018) and more. Danker received an Ophir Award nomination for Best Supporting Actor for his role in '' Eyes Wide Open'' (2009). Danker was also nominated for an Ophir Award for Best Actor for his role in ''Doubtful'' (2017). Early life Danker was born in Norfolk, Virginia, United States, to a Jewish family. He is the son of Israeli actor Eli Danker. He went to Israel with his mother when he was two years old after his parents' divorce. He grew up in the Bavli neighborhood in Tel Aviv. During that time he was a member of the Ha-Horesh tribe choir of the scouts youth movement. Towards his Junior High year, Ran and his mother moved to Poleg, Netanya. Between high school and his army service, Ran participated in a few TV commerc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Har Amasa
Har Amasa ( he, הַר עֲמָשָׂא, ''lit.'' Mount Amasa) is a Moshav shitufi in the south of Israel. Located near the Yatir Forest 20 kilometres south of Hebron and 14 km northwest of Arad, it is the only member of the Tamar Regional Council to be located in the highlands outside the Jordan Rift Valley. In it had a population of . It was named after the nearby Mount Amasa (859 m), which was in turn named after Amasa son of Ithra the Israelite (2 Samuel 17:25). History The village was founded as a kibbutz of the United Kibbutz Movement on June 30, 1983. However, gradually changed its character over the next 20 years. In 2003, it was transferred to the authority of the Agricultural Union movement, and it was preparing to expand to include many new residents in a less formal framework, while still preserving its social fabric. In 2006, Ynet reported that five families in the kibbutz were undergoing a religious conversion through Chabad. According to certain membe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Community Settlement (Israel)
A community settlement ( he, יישוב קהילתי, ''Yishuv Kehilati'') is a type of village in Israel and the West Bank. While in an ordinary town anyone may buy property, in a community settlement the village's residents are organized in a cooperative. They have the power to approve or veto a sale of a house or a business to any buyer. Residents of a community settlement may have a particular shared ideology, religious perspective, or desired lifestyle which they wish to perpetuate by accepting only like-minded individuals. For example, a family-oriented community settlement that wishes to avoid becoming a retirement community may choose to accept only young married couples as new residents. As distinct from the traditional Israeli development village, typified by the kibbutz and moshav, the community settlement emerged in the 1970s as a non-political movement for new urban settlements in Israel.Aharon Kellerman''Society and Settlement: Jewish Land of Israel in the Twenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestinian Militants
Palestinian political violence refers to acts of violence perpetrated for political ends in relation to the State of Palestine or in connection with Palestinian nationalism. Common political objectives include self-determination in and sovereignty over Palestine,de Waart, 1994p. 223 Referencing Article 9 of ''The Palestinian National Charter of 1968''. The Avalon Project has a copy herDe Waal, 2004pp. 29–30. or the "liberation of Palestine" and recognition of a Palestinian state, either in place of both Israel and the Palestinian territories, or solely in the Palestinian territories.Schulz, 1999p. 161 More limited goals include the release of Palestinian prisoners or the Palestinian right of return. Other motivations include personal grievances, trauma or revenge.Avishai Margalit“The Suicide Bombers,'at New York Review of Books, January 16, 2003 :'the main motivating force for the suicide bombers seems to be the desire for spectacular revenge.'Peter Beinart'The American Jewi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Operations
A military operation is the coordinated military actions of a state, or a non-state actor, in response to a developing situation. These actions are designed as a military plan to resolve the situation in the state or actor's favor. Operations may be of a combat or non-combat nature and may be referred to by a code name for the purpose of national security. Military operations are often known for their more generally accepted common usage names than their actual operational objectives. Types of military operations Military operations can be classified by the scale and scope of force employment, and their impact on the wider conflict. The scope of military operations can be: * Theater: this describes an operation over a large, often continental, area of operation and represents a strategic national commitment to the conflict, such as Operation Barbarossa, with general goals that encompass areas of consideration outside the military, such as the economic and political impact of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Campaign
A military campaign is large-scale long-duration significant military strategy plan incorporating a series of interrelated military operations or battles forming a distinct part of a larger conflict often called a war. The term derives from the plain of Campania, a place of annual wartime operations by the armies of the Roman Republic. Definition 1. A military campaign denotes the time during which a given military force conducts combat operations in a given area (often referred to as AO, area of operation). A military campaign may be executed by either a single Armed Service, or as a combined services campaign conducted by land, naval, air, cyber and space forces. 2. The purpose of a military campaign is to achieve a particular desired resolution of a military conflict as its strategic goal. This is constrained by resources, geography and/or season. A campaign is measured relative to the technology used by the belligerents to achieve goals, and while in the pre-industrial E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counter-terrorism
Counterterrorism (also spelled counter-terrorism), also known as anti-terrorism, incorporates the practices, military tactics, techniques, and strategies that governments, law enforcement, business, and intelligence agencies use to combat or eliminate terrorism. Counterterrorism strategies are a government's motivation to use the instruments of national power to defeat terrorists, the organizations they maintain, and the networks they contain. If definitions of terrorism are part of a broader insurgency, counterterrorism may employ counterinsurgency measures. The United States Armed Forces uses the term foreign internal defense for programs that support other countries' attempts to suppress insurgency, lawlessness, or subversion, or to reduce the conditions under which threats to national security may develop. History The first counter-terrorism body formed was the Special Irish Branch of the Metropolitan Police, later renamed the Special Branch after it expanded its scope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cremisan Valley
The Cremisan Valley is a valley located on the seam line between the West Bank and Jerusalem. The valley is one of the last green areas in the Bethlehem district, with vast stretches of agricultural lands and recreational grounds. The Salesian Sisters Convent and School, the Salesian Monastery and Cremisan Cellars are located in the valley. Salesian Sisters Convent and School The main convent and monastery are part of the Salesian order, founded by Don Bosco. The convent and school were opened in 1960 and have around 400 students in their primary school, kindergarten, as well as the school for children with learning disabilities. The school also hosts a number of community activities in the afternoons and summer camps. Cremisan Monastery The monastery, located on a hill 850 meters above sea level, is five kilometers from Bethlehem. It was built in 1885 on ruins of a 7th century Byzantine monastery. The main monastery, housed in a building featuring stone floors, thick wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
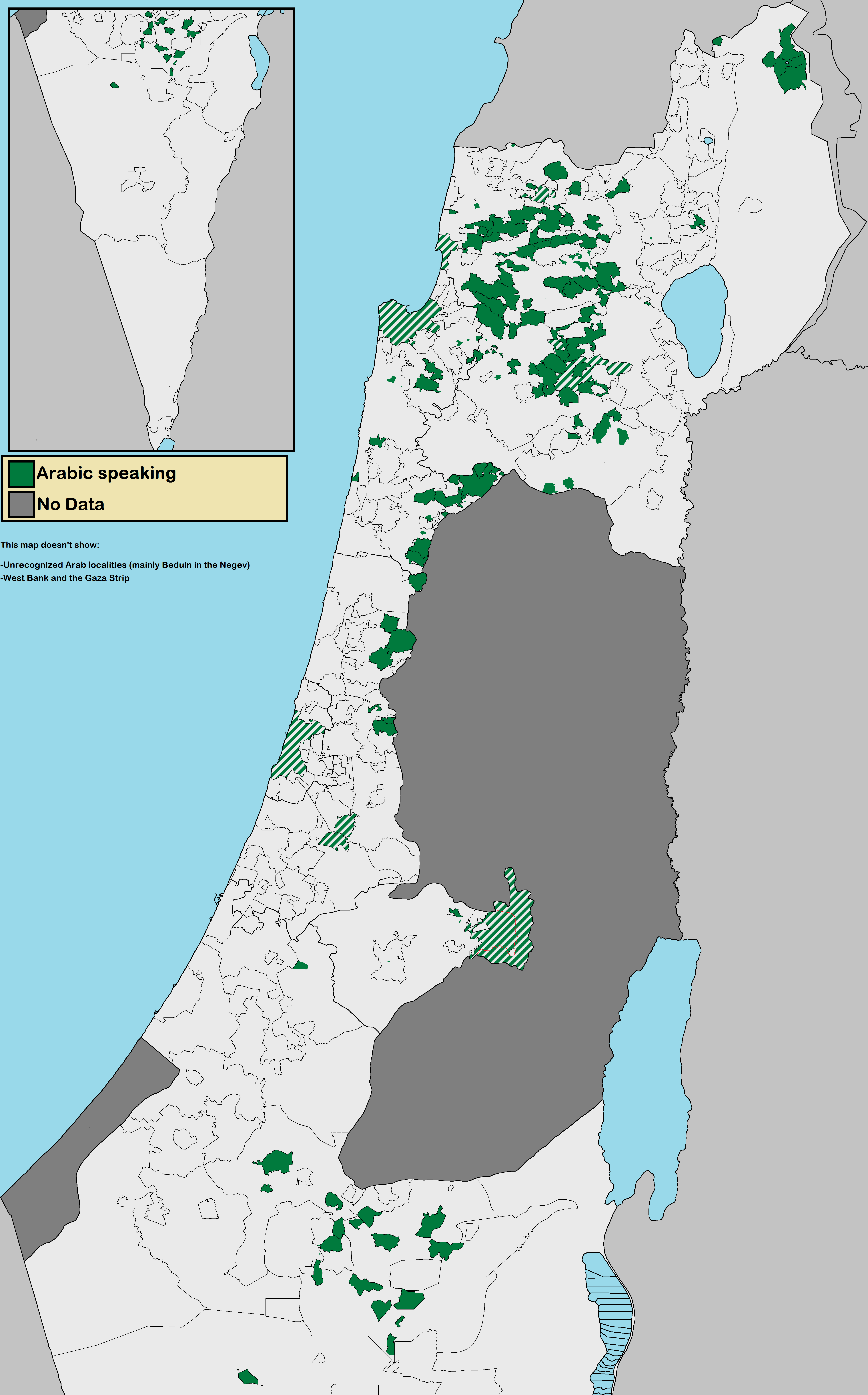
Arab Citizens Of Israel
The Arab citizens of Israel are the largest ethnic minority in the country. They comprise a hybrid community of Israeli citizens with a heritage of Palestinian citizenship, mixed religions (Muslim, Christian or Druze), bilingual in Arabic and Hebrew, and with varying social identities. Self-identification as Palestinian citizens of Israel has sharpened in recent years, alongside distinct identities including Galilee and Negev Bedouin, the Druze people, and Arab Christians and Arab Muslims who do not identify as Palestinians. In Arabic, commonly used terms to refer to Israel's Arab population include 48-Arab ( ar, عرب 48, Arab Thamaniya Wa-Arba'in, label=none) and 48-Palestinian (). Since the Nakba, the Palestinians that have remained within Israel's 1948 borders have been colloquially known as "48-Arabs". In Israel itself, Arab citizens are commonly referred to as Israeli-Arabs or simply as ''Arabs''; international media often uses the term Arab-Israeli to distinguish Ara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shin Bet
The Israel Security Agency (ISA; he, שֵׁירוּת הַבִּיטָּחוֹן הַכְּלָלִי; ''Sherut ha-Bitaẖon haKlali''; "the General Security Service"; ar, جهاز الأمن العام), better known by the acronym Shabak ( he, שב״כ; ; ar, شاباك) or the Shin Bet (a two-letter Hebrew abbreviation of "Security Service"), is Israel's internal security service. Its motto is "''Magen veLo Yera'e''" (, lit. "Shield and not seen" or "The unseen shield"). The Shin Bet's headquarters are located in northwest Tel Aviv, north of Yarkon Park. It is one of three principal organizations of the Israeli intelligence community, alongside Aman (military intelligence) and Mossad (foreign intelligence service). Organization Shabak is believed to have three operational wings: *The Arab Department: responsible primarily for Arab-related counterterrorism activities in Israel, the West Bank, and the Gaza Strip. *The Israel and Foreigners Department: formerly named the Non-A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |