|
1848 In Germany
Events from the year 1848 in Germany. Incumbents * King of Bavaria – Ludwig I. (until 20 March 1848); Maximilian II (since 20 March 1848) * King of Hanover – Ernest Augustus * King of Prussia – Frederick William IV * King of Saxony – Frederick Augustus II Events * 17 March - Poem In Kümmernis und Dunkelheit was written in London by German poet Ferdinand Freiligrath. * February - Publication of The Communist Manifesto * April - Hecker uprising in Baden * 9 April - Battle of Bov * 9 April - Foundation of Münchner Neueste Nachrichten * 20 April - Battle on the Scheideck * 23 April - Battle of Schleswig * 23 April - Battle of Mysunde * 24 April - Skirmish of Oversø * 1 May - 1848 German federal election * 7 May - Start of magazine Kladderadatsch * 11 May - Baden mutiny * 18 May - 379 deputies assembled in the Kaisersaal in Frankfurt am Main walked solemnly to the Paulskirche to hold the first session of the German national assembly, under its chairman (by seniori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its 16 constituent states have a total population of over 84 million in an area of . It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and Czechia to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its main financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Settlement in what is now Germany began in the Lower Paleolithic, with various tribes inhabiting it from the Neolithic onward, chiefly the Celts. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Schleswig
The Battle of Schleswig occurred near Dannevirke on Easter morning, 23 April 1848 as the second battle of the First Schleswig War of 1848–1850. Prussia had just entered the war and had sent almost 12,000 troops to Schleswig-Holstein. Counting reserves, General Wrangel commanded in total more than 18,000 men – almost three times the size of the Danish forces. The German Reich troops did not participate in the battle, but their presence forced the Danes to fight defensively against the Prussians. Battle On a cold and wet spring morning, the Germans went on the attack. The plan of the Prussian leader, General von Wrangel, was to move the army up to a point just south of Dannevirke, camp there, and attack the following day. But the Prussian Guard on the right wing (which at that time was a good distance in front of the left wing) arrived at the rally and met virtually no Danes, so the commander decided to go against Bustrup and Frederiksberg (Kratbjerg). Here, southeast of Bus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casino Faction
The Casino faction (in German ''Casino-Fraktion'' or simply ''Casino'') was a moderate liberal faction within the Frankfurt Parliament formed on June 25, 1848. Like most of the factions in the parliament, its name was a reference to the usual meeting place of its members in Frankfurt am Main. Casino was the largest and most influential faction at Paulskirche. Its members were for the most part national liberals. Casino was a faction of moderate left-wingers or liberals,Martin Kitchen''A History of Modern Germany: 1800 to the Present'' 2nd ed. Chichester, West Sussex/Malden, Massachusetts: Wiley-Blackwell, 2012, . or right-centrists. Its members were overwhelmingly drawn from the intelligentsia of Prussia and the rest of Northern Germany, and the group's political positions were closer to those of the right wing in the Prussian assembly than to the center-right there, whose positions corresponded to those of center-left factions at Frankfurt. With approximately 130 members, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provisorische Zentralgewalt
The Provisorische Zentralgewalt (, ''Provisional Central Power'') was the provisional government of the Frankfurt Parliament (1848–49). Since this all-German national assembly had not been initiated by the German Confederation, it was lacking not only major constitutional bodies, such as a head of state and a government, but also legal legitimation. A modification of the '' Bundesakte'', the constitution of the German Confederation, could have brought about such legitimation, but as it would have required the unanimous support of all 38 signatory states this was practically impossible. Partially for this reason, influential European powers such as France and Russia declined to recognize the Parliament. The delegates on the left wanted to solve this situation by creating a revolutionary parliamentary government, but, on 24 June 1848, the majority (450 – 100) voted for a compromise, the so-called Provisional Central Power. Formation of the Central Power On 24 June 1848, Pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neue Rheinische Zeitung
The ''Neue Rheinische Zeitung: Organ der Demokratie'' ("New Rhenish Newspaper: Organ of Democracy") was a German daily newspaper, published by Karl Marx in Cologne between 1 June 1848 and 19 May 1849. It is recognised by historians as one of the most important dailies of the Revolutions of 1848 in Germany. The paper was regarded by its editors and readers as the successor of an earlier Cologne newspaper, the '' Rheinische Zeitung'' ("Rhenish Newspaper"), also edited for a time by Karl Marx, which had been suppressed by state censorship over five years earlier. Publication history Establishment The ''Neue Rheinische Zeitung: Organ der Demokratie'' ("New Rhenish Newspaper: Organ of Democracy") was founded 1 June 1848 in Cologne (Köln), part of Rhineland. The paper was established by Karl Marx, Frederich Engels, as well as leading members of the Communist League living in Cologne immediately upon the return of Marx and Engels to Germany following the outbreak of the 1848 Revolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
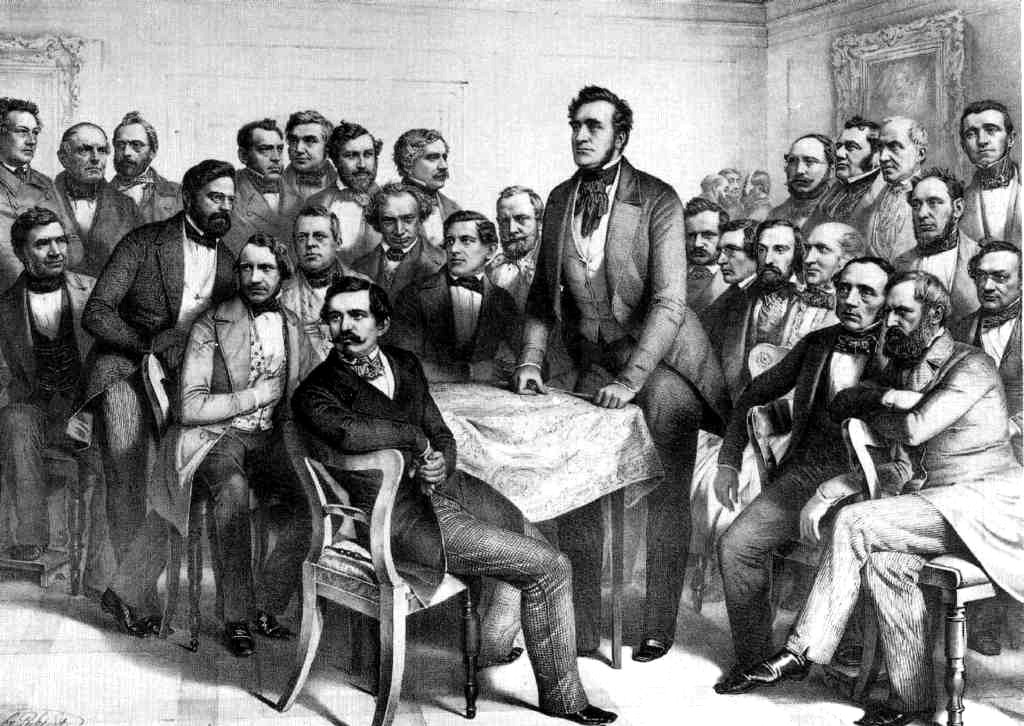
Frankfurt Parliament
The Frankfurt Parliament (german: Frankfurter Nationalversammlung, literally ''Frankfurt National Assembly'') was the first freely elected parliament for all German states, including the German-populated areas of Austria-Hungary, elected on 1 May 1848 (see German federal election, 1848). The session was held from 18 May 1848 to 31 May 1849, in the Paulskirche at Frankfurt am Main. Its existence was both part of and the result of the "March Revolution" within the states of the German Confederation. After long and controversial debates, the assembly produced the so-called Frankfurt Constitution (''Paulskirchenverfassung'' or St. Paul's Church Constitution, officially the ''Verfassung des Deutschen Reiches'') which proclaimed a German Empire based on the principles of parliamentary democracy. This constitution fulfilled the main demands of the liberal and nationalist movements of the Vormärz and provided a foundation of basic rights, both of which stood in opposition to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Von Gagern
Heinrich Wilhelm August Freiherr von Gagern (20 August 179922 May 1880) was a statesman who argued for the unification of Germany. Early career The third son of Hans Christoph Ernst, Baron von Gagern, a liberal statesman from Nassau, Heinrich von Gagern was born at Bayreuth, educated at the military academy at Munich and, as an officer in the service of the duke of Nassau, fought at Waterloo. Leaving the service after the war, he studied jurisprudence at Heidelberg, Göttingen and Jena, where he became a member of the Urburschenschaft. In 1819, he went for a while to Geneva to complete his studies. In 1821 he began his official career as a lawyer in the grand-duchy of Hesse, and in 1832 was elected to the second chamber. Already at the universities he had proclaimed his Liberal sympathies as a member of the ''Burschenschaft'', and he now threw himself into open opposition to the unconstitutional spirit of the Hessian government, an attitude which led to his dismissal from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Lang (politician)
Fregattenleutnant (Frigate Lieutenant) Friedrich Lang was a World War I flying ace. He emerged from obscurity to begin his military career in 1912 by training for sea duty. He was serving on SMS Balaton when World War I began. In March 1916, he transferred to aviation duty. He would score five confirmed aerial victories by war's end. He was one of only two flying aces of the Austro-Hungarian Navy, the other being Gottfried von Banfield. Postwar, Lang lapsed back into obscurity. Early life Friedrich Lang was born an Austrian citizen of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, though his birth date and birthplace are unknown. After completing secondary school, he joined the Austro-Hungarian Navy. On 11 September 1912, he was sent to Naval Cadet School for basic training. Sea service After completion of training, Lang served on several vessels. Having served with distinction, he was appointed as a Seekadett on 1 February 1914. He was still shipboard as the First World War began. Aboard the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frankfurt Am Main
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian dialects, Hessian: , "Franks, Frank ford (crossing), ford on the Main (river), Main"), is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the List of cities in Germany by population, fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on its namesake Main (river), Main River, it forms a continuous conurbation with the neighboring city of Offenbach am Main and Frankfurt Rhein-Main Regional Authority, its urban area has a population of over 2.3 million. The city is the heart of the larger Rhine-Main metropolitan region, which has a population of more than 5.6 million and is Germany's Metropolitan regions in Germany, second-largest metropolitan region after the Rhine-Ruhr region. Frankfurt's central business district, the Bankenviertel, lies about northwest of the geographic centre of the EU, geographic center of the EU at Gadheim, Lower Franconia. Like France and Franc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baden Mutiny
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in South Germany, in earlier times on both sides of the Upper Rhine but since the Napoleonic Wars only East of the Rhine. History The margraves of Baden originated from the House of Zähringen. Baden is named after the margraves' residence, in Baden-Baden. Hermann II of Baden first claimed the title of Margrave of Baden in 1112. A united Margraviate of Baden existed from this time until 1535, when it was split into the two Margraviates of Baden-Durlach and Baden-Baden. Following a devastating fire in Baden-Baden in 1689, the capital was moved to Rastatt. The two parts were reunited in 1771 under Margrave Charles Frederick. The restored Margraviate with its capital Karlsruhe was elevated to the status of electorate in 1803. In 1806, the Electorate of Baden, receiving territorial additions, became the Grand Duchy of Baden. The Grand Duchy of Baden was a state within the German Confederation until 1866 and the German Empire until 1918, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
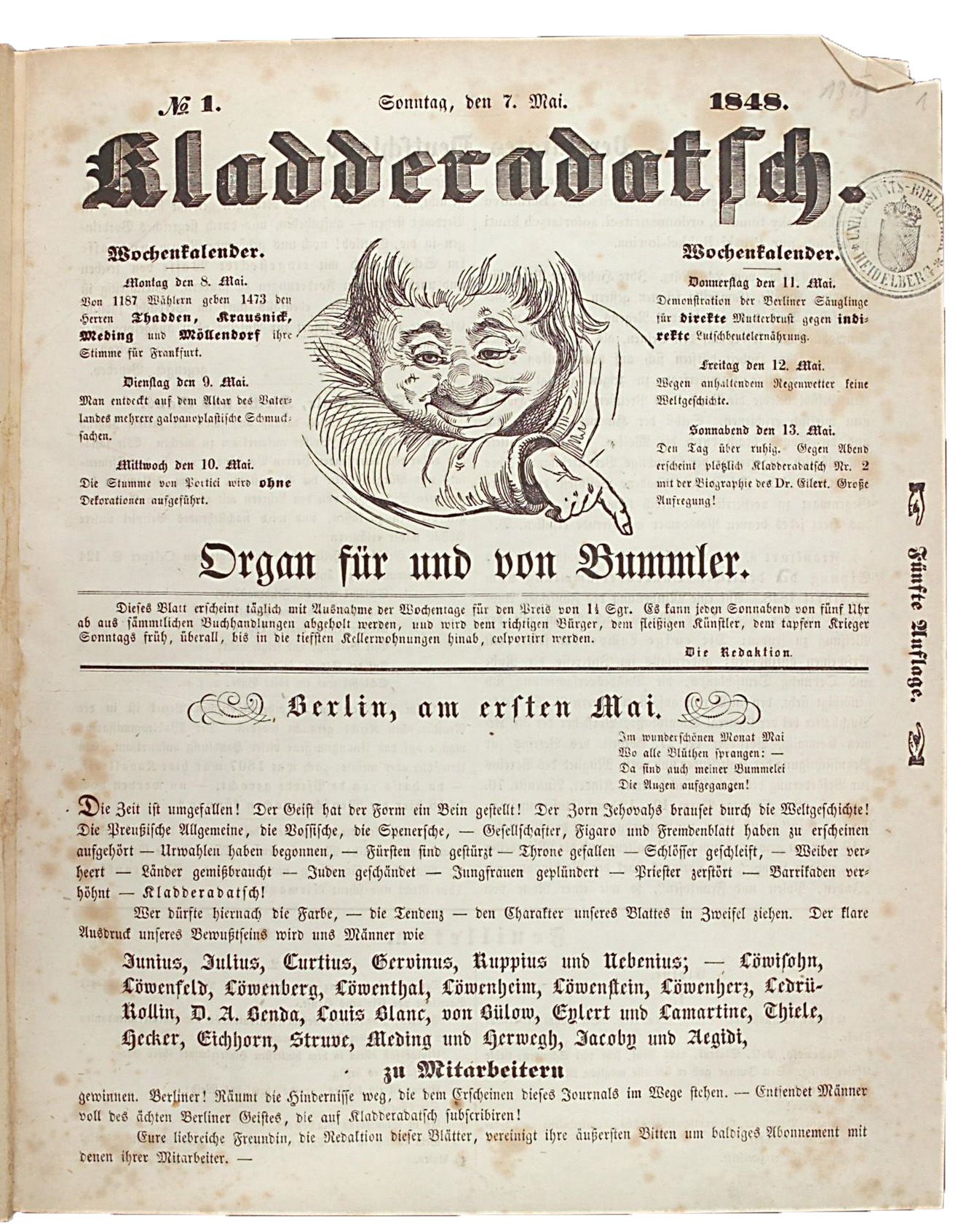
Kladderadatsch
''Kladderadatsch'' (onomatopoeic for "Crash") was a satirical German-language magazine first published in Berlin on 7 May 1848. It appeared weekly or as the ''Kladderadatsch'' put it: "daily, except for weekdays." It was founded by Albert Hofmann and David Kalisch, the latter the son of a Jewish merchant and the author of several works of comedy.Library: Kladderadatsch (1848-1944) {{DEFAULTSORT:Kladderadatsch Defunct magazines published in Germany German-language magazines Satirical magazines published in Germany Magazines established in 1848 Magazines disestablished in 1944 Magazines published in Berlin 1848 establishments in Germany 1944 disestablishments in Germany Conservative magazines published in Germany ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)