|
1275
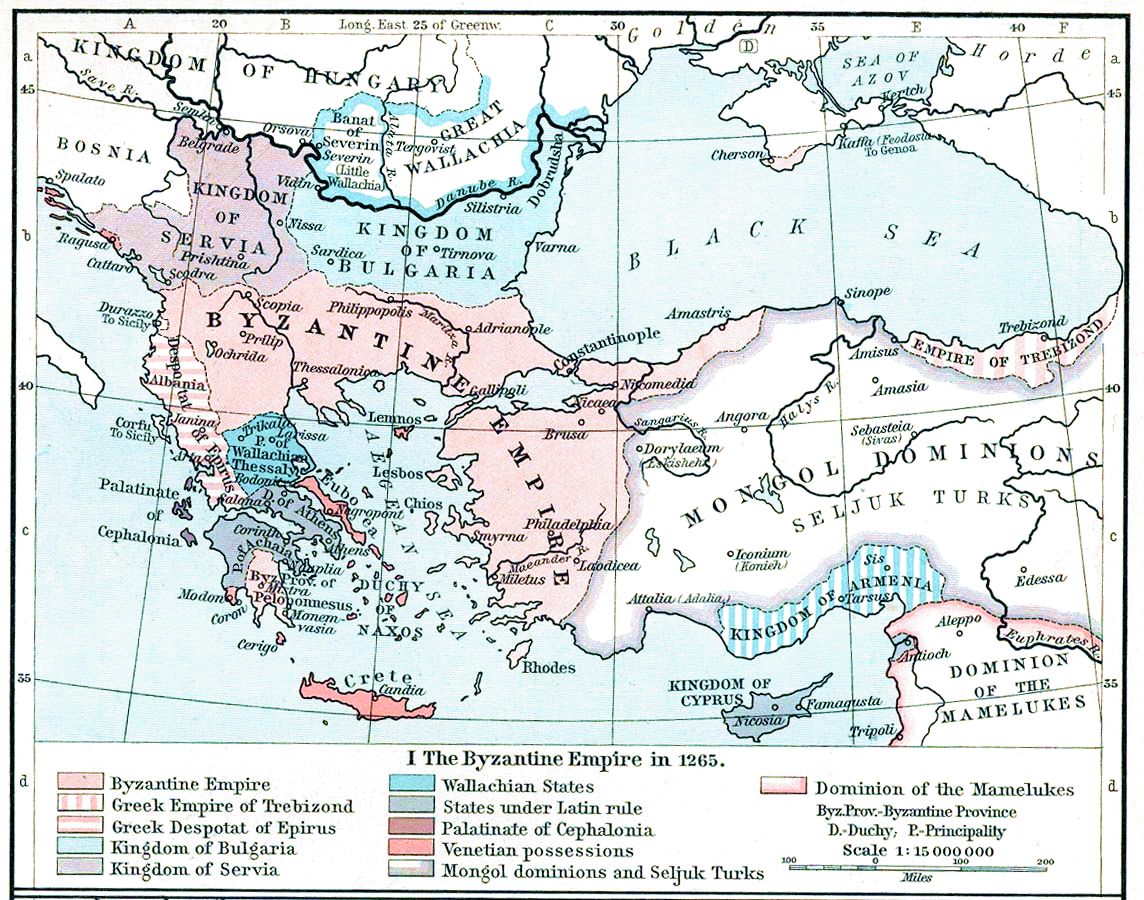
Year 1275 (Roman numerals, MCCLXXV) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Battle of Neopatras: Emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos assembles a Byzantine expeditionary force (some 30,000 men), mostly mercenaries from Second Bulgarian Empire, Bulgaria, Kingdom of Serbia (medieval), Serbia and the Sultanate of Rum. He places these forces under his own brother, John Palaiologos (brother of Michael VIII), John Palaiologos, and General Alexios Kaballarios. Michael sends them against Thessaly, and is supported by the Byzantine navy led by Admiral Alexios Doukas Philanthropenos, who is ordered to attack the Latin principalities and prevent them from aiding John I Doukas of Thessaly, John I ("Angelos"), ruler of Thessaly. John is caught by surprise by the rapid advance of the Byzantine forces and is bottled up with a garrison in his capital of Ypati, Neopatras, which the Byzantines proceed to lay siege. John manages to es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad II Of Granada
Muhammad II () (also known by the epithet ''al-Faqih'', " the canon-lawyer", – 8 April 1302; reigned from 1273 until his death) was the second Nasrid ruler of the Emirate of Granada in Al-Andalus on the Iberian Peninsula, succeeding his father, Muhammad I. Already experienced in matters of state when he ascended the throne, he continued his father's policy of maintaining independence in the face of Granada's larger neighbours, the Christian kingdom of Castile and the Muslim Marinid state of Morocco, as well as an internal rebellion by his family's former allies, the Banu Ashqilula. After he took the throne, he negotiated a treaty with Alfonso X of Castile, in which Castile agreed to end support for the Banu Ashqilula in exchange for payments. When Castile took the money but maintained its support for the Banu Ashqilula, Muhammad turned towards Abu Yusuf of the Marinids. The Marinids sent a successful expedition against Castile, but relations soured when the Marinids treat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Yusuf Yaqub Ibn Abd Al-Haqq
Abu Yusuf Yaqub ibn Abd al-Haqq () (c. 1212 – 20 March 1286) was a Marinid ruler of Morocco. He was the fourth son of Marinid founder Abd al-Haqq, and succeeded his brother Abu Yahya in 1258. He died in 1286. He was the son of Abd al-Haqq I and Oum el-Iman bint Ali el-Bethary, a Zenata woman. Some sources add her mother to be known as Oum el Youm and a daughter of a Zenata clan leader of the Tafersit region. History The Marinids had been fighting the Almohads for supremacy over Morocco since the 1210s. At the time of Abu Yahya's death in July, 1258, the Marinids were installed in Fez and controlled eastern and northern Morocco, the Almohads reduced to the southerly districts around their capital, Marrakech. Although Abu Yahya had designated his son as successor in Fez, Abu Yusuf Yaqub, then a governor in Taza, managed, with only a little difficulty, to displace his nephew and get himself acknowledged as emir of the Marinids. In September, 1260, in a surprise a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexios Doukas Philanthropenos
Alexios Doukas Philanthropenos (, died ) was a Byzantine nobleman and distinguished admiral, with the rank of and later , during the reign of Michael VIII Palaiologos (). Biography Alexios is the first important member of the Philanthropenos family mentioned in the sources. He first appears in George Akropolites's history in autumn 1255 as a military commander in the region of Ohrid — perhaps as (governor) of the local (province) — during the wars of Theodore II Laskaris () against the Bulgarians... Throughout the 1260s, Philanthropenos carried the high title of . Theoretically, he was subordinate to the Michael Laskaris, but the latter was old and infirm, and Philanthropenos exercised the ''de facto'' command of the Byzantine navy.. In 1262 or 1263, soon after the recapture of Constantinople from the Latin Empire, Emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos sent him to raid the Latin possessions of the Aegean Sea. This was the first major expedition undertaken by Palaiologos' rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Demetrias
The Battle of Demetrias was a sea engagement fought at Volos in Greece in the early 1270s between a Byzantine fleet and the assembled forces of the Latin barons of Euboea (Negroponte) and Crete. The battle was fierce, and initially in favour of the Latins, but the timely arrival of Byzantine reinforcements tipped the scale, resulting in a crushing Byzantine victory. Background In the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade and the dissolution of the Byzantine Empire in 1204, the Aegean Sea, once Byzantium's naval heartland, was dominated by a hodgepodge of Latin principalities, protected by the naval might of the Republic of Venice. Following the recapture of Constantinople and the restoration of the Byzantine Empire in 1261, one of the chief priorities of Emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos () was the defence of his capital from a Venetian attack. Consequently, he sought an alliance with Venice's major antagonist, the Republic of Genoa, while he began building up his own navy. With the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emirate Of Granada
The Emirate of Granada, also known as the Nasrid Kingdom of Granada, was an Emirate, Islamic polity in the southern Iberian Peninsula during the Late Middle Ages, ruled by the Nasrid dynasty. It was the last independent Muslim state in Western Europe. Muslims had been present in the Iberian Peninsula, which they called Al-Andalus, since 711. By the late 12th century, following the Reconquista, expansion of Christian kingdoms in the north, the area of Muslim control had been reduced to the southern parts of the peninsula governed by the Almohad Caliphate. After Almohad control retreated in 1228, the ambitious Muhammad I of Granada, Muhammad I Ibn al-Ahmar rose to power and established the Nasrid dynasty in control of a sizeable portion of this territory, roughly corresponding to the modern Spanish provinces of Province of Granada, Granada, Province of Almería, Almería, and Province of Málaga, Málaga. By 1250, the Nasrid emirate was the last independent Muslim polity in the pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Neopatras
The Battle of Neopatras was fought in the early 1270s between a Byzantine army besieging the city of Neopatras and the forces of John I Doukas, ruler of Thessaly. The battle was a rout for the Byzantine army, which was caught by surprise and defeated by a much smaller but more disciplined force. Background In 1259, the Empire of Nicaea, led by Michael VIII Palaiologos (), had achieved a great victory in the Battle of Pelagonia against a coalition of its major European foes, the Despotate of Epirus, the Kingdom of Sicily, and the Principality of Achaia. This victory had in large measure been achieved through the defection of John Doukas, the illegitimate child of Michael II of Epirus. This victory enabled Palaiologos to consolidate his territories in Europe; further, the weakening of Epirus and the Latin states allowed him to carry out the reconquest of Constantinople in 1261 and to re-establish the Byzantine Empire, with himself as emperor. The Nicaean forces failed however t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael VIII Palaiologos
Michael VIII Palaiologos or Palaeologus (; 1224 – 11 December 1282) reigned as Byzantine emperor from 1261 until his death in 1282, and previously as the co-emperor of the Empire of Nicaea from 1259 to 1261. Michael VIII was the founder of the Palaiologos, Palaiologan dynasty that would rule the Byzantine Empire until the Fall of Constantinople in 1453. He Reconquest of Constantinople, recovered Constantinople from the Latin Empire in 1261 and transformed the Empire of Nicaea into a Byzantine Empire under the Palaiologos dynasty, restored Byzantine Empire. His reign saw considerable recovery of Byzantine power, including the enlargement of the Byzantine army and Byzantine navy, navy. It also included the reconstruction of the city of Constantinople, and the increase of its population. His re-establishment of the University of Constantinople contributed to the Palaeologan Renaissance, a cultural flowering between the 13th and 15th centuries. It was also at this time that the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Palaiologos (brother Of Michael VIII)
John Doukas Palaiologos (, 1225/30 – 1274) was a Byzantine aristocrat, brother to Emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos (r. 1259–1282), who served as the commander-in-chief of the Byzantine army. He played a prominent part in his brother's military campaigns, most notably in the crucial victory at the Battle of Pelagonia, but also in repeated campaigns against Epirus and against the Turks in Asia Minor. He retired from active service after his defeat at Neopatras, and died shortly after. Biography Early life and first successes John Doukas Palaiologos was born sometime after 1225 and before 1230, the son of Andronikos Palaiologos, the ''megas domestikos'' of the Empire of Nicaea, and his first wife Theodora Palaiologina. John was their second son, after the future emperor Michael Palaiologos, and the fourth child overall. Nothing is known of him until 1256, when he appears to have been sent to Rhodes. The reasons for this is unclear; possibly to take charge of the military, fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guglielmo II Da Verona
Guglielmo II da Verona (died 1273/1275) was a Lombard noble from the triarchy of Negroponte (Euboea), considered by earlier historians as a triarch and a marshal of the principality of Achaea in Frankish Greece. He was the second son of Guglielmo I da Verona, ruler of the southern third ("triarchy") of Euboea. According to earlier historians following K. Hopf, he succeeded to this position upon his father's death in 1263/6. He was also thought to have become Baron of Passavant and marshal in the Principality of Achaea from an hypothetical marriage to Margaret de Neuilly, because he was improperly called "marshal" in Sanudo's ''Istoria di Romania''. These views have been challenged by Raymond-Joseph Loenertz in the 1960s. He married Catherine, a niece of William II of Villehardouin, with whom he had no known child. Guglielmo was killed in the Battle of Demetrias, which took place either in 1273 or in 1275 in the area of modern Volos Volos (; ) is a coastal port c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceuta
Ceuta (, , ; ) is an Autonomous communities of Spain#Autonomous cities, autonomous city of Spain on the North African coast. Bordered by Morocco, it lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. Ceuta is one of the special member state territories and the European Union, special member state territories of the European Union. It was a regular municipalities in Spain, municipality belonging to the province of Cádiz prior to the passing of its Statute of Autonomy in March 1995, as provided by the Spanish Constitution, henceforth becoming an autonomous city. Ceuta, like Melilla and the Canary Islands, was classified as a free port before Spain joined the European Union. Its population is predominantly Christian and Islam in Spain, Muslim, with a small minority of Sephardic Jews and Sindhi Hindus, from Pakistan. Spanish language, Spanish is the official language, while Moroccan Darija, Darija Arabic is also widely spoken. Names The name Abyla has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John I De La Roche
John I de la Roche (died 1280) succeeded his father, Guy I, as Duke of Athens in 1263. He was cultured and chivalrous, spoke fluent Greek, and read Herodotus. In 1275, John, with 300 knights, relieved Neopatras, which had been blockaded by a Byzantine mercenary army. It was at this battle that he said "'Great are their numbers but few among them are true men," quoting Herodotus, who said, of the Battle of Thermopylae, "the Persian are great in their numbers but true men are far and few." The next year (1276), the Byzantine Emperor Michael VIII Palaeologus invaded Euboea and Thessaly. John joined Gilbert of Verona to march to the relief of Negroponte, which was under attack by Licario. During a battle six miles to the north, at Vatonda, John was thrown from his horse and captured, along with Gilbert and many other knights. In 1280 he died and was succeeded by his brother William. References * Gregorovius, Ferdinand. ''Geschichte der Stadt Athen im Mittelater''. Stuttgart: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John I Doukas Of Thessaly
John I Doukas (), Latinized as Ducas, was an illegitimate son of Michael II Komnenos Doukas, Despot of Epirus in –1268. After his father's death, he became ruler of Thessaly from to his own death in 1289. From his father's family he is also inaccurately known as John Angelos. Married to a Thessalian Vlach woman, John first appears leading Vlach troops alongside his father in the lead-up to the Battle of Pelagonia in 1259. His defection to the camp of Emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos was crucial in the battle, which ended with the crushing defeat of the Epirotes' Latin allies and opened the way for the recovery of Constantinople and the re-establishment of the Byzantine Empire under Palaiologos in 1261. John quickly returned to the side of his father and brother, Nikephoros, and assisted them in recovering Epirus and Thessaly. After Michael II died, John Doukas became ruler of Thessaly with his seat at Neopatras, whence Western chroniclers often erroneously called him "Duke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |