|
BuxWV
The Buxtehude-Werke-Verzeichnis ("Buxtehude Works Catalogue", commonly abbreviated to BuxWV) is the catalogue and the numbering system used to identify musical works by the German-Danish Baroque composer Dieterich Buxtehude (c. 1637 – 9 May 1707). It was compiled by Georg Karstädt and published in 1974 as ''Thematisch-Systematisches Verzeichnis der Musikalischen Werke von Dietrich Buxtehude''. The second edition, published in 1985, contains minor additions and corrections. The catalogue is organized thematically, not chronologically, and contains 275 individual pieces. The ''Anhang'' ("Appendix") adds 13 spurious and falsely attributed works. The fourteen trio sonatas (BuxWV 252–265) were the only works published during Buxtehude's lifetime. Originally issued in two volumes, the first seven are now commonly referred to as Buxtehude's opus 1 and the next seven as opus 2. Vocal music Cantatas (1–112) * BuxWV 1 — ''Accedite gentes, accurite populi'' * BuxWV 2 — ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dieterich Buxtehude
Dieterich Buxtehude (; ; born Diderik Hansen Buxtehude; c. 1637 – 9 May 1707) was a Danish organist and composer of the Baroque period, whose works are typical of the North German organ school. As a composer who worked in various vocal and instrumental idioms, Buxtehude's style greatly influenced other composers, such as Johann Sebastian Bach. Buxtehude is considered one of the most important composers of the 17th century. Life Early years in Denmark He is thought to have been born with the name Diderich Buxtehude.Snyder, Kerala J. Dieterich Buxtehude: Organist in Lübeck. New York: Schirmer Books, 1987. His parents were Johannes (Hans Jensen) Buxtehude and Helle Jespersdatter. His father originated from Oldesloe in the Duchy of Holstein, which at that time was a part of the Danish realms in Northern Germany. Scholars dispute both the year and country of Dieterich's birth, although most now accept that he was born in 1637 in Helsingborg, Skåne at the time part of De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fried- Und Freudenreiche Hinfarth
("With peace and joy"), BuxWV 76, is the common name for a piece of funeral music composed by Dieterich Buxtehude as an homage to his father in 1674. The composer named the work (Departure enriched by Peace and Joy) when he published it the same year. It is a bundle of two compositions, the earlier , BuxWV 76a, a setting of Luther's hymn composed in 1671 reflecting the death of Menno Hanneken, and the elegy (Song of mourning, lament), BuxWV 76b, an aria in seven stanzas. The incipit of the elegy, "", translates roughly to "Even if death must separate us". It is one of few compositions published during Buxtehude's lifetime. History In 1671, Buxtehude composed funeral music on the death of , a superintendent and minister at the Marienkirche in Lübeck, where Buxtehude performed his concert series, the ''Abendmusiken''. Buxtehude composed a canon, ''Divertisons nous'' (BuxWV 124), written in an album of Menno's son and dated 1670, showing that he had good relations with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mit Fried Und Freud (Buxtehude)
("With peace and joy"), BuxWV 76, is the common name for a piece of funeral music composed by Dieterich Buxtehude as an homage to his father in 1674. The composer named the work (Departure enriched by Peace and Joy) when he published it the same year. It is a bundle of two compositions, the earlier , BuxWV 76a, a setting of Luther's hymn composed in 1671 reflecting the death of Menno Hanneken, and the elegy (Song of mourning, lament), BuxWV 76b, an aria in seven stanzas. The incipit of the elegy, "", translates roughly to "Even if death must separate us". It is one of few compositions published during Buxtehude's lifetime. History In 1671, Buxtehude composed funeral music on the death of , a superintendent and minister at the Marienkirche in Lübeck, where Buxtehude performed his concert series, the ''Abendmusiken''. Buxtehude composed a canon, ''Divertisons nous'' (BuxWV 124), written in an album of Menno's son and dated 1670, showing that he had good relations with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klag-Lied
("With peace and joy"), BuxWV 76, is the common name for a piece of funeral music composed by Dieterich Buxtehude as an homage to his father in 1674. The composer named the work (Departure enriched by Peace and Joy) when he published it the same year. It is a bundle of two compositions, the earlier , BuxWV 76a, a setting of Luther's hymn composed in 1671 reflecting the death of Menno Hanneken, and the elegy (Song of mourning, lament), BuxWV 76b, an aria in seven stanzas. The incipit of the elegy, "", translates roughly to "Even if death must separate us". It is one of few compositions published during Buxtehude's lifetime. History In 1671, Buxtehude composed funeral music on the death of , a superintendent and minister at the Marienkirche in Lübeck, where Buxtehude performed his concert series, the ''Abendmusiken''. Buxtehude composed a canon, ''Divertisons nous'' (BuxWV 124), written in an album of Menno's son and dated 1670, showing that he had good relations with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrygian Mode
The Phrygian mode (pronounced ) can refer to three different musical modes: the ancient Greek ''tonos'' or ''harmonia,'' sometimes called Phrygian, formed on a particular set of octave species or scales; the Medieval Phrygian mode, and the modern conception of the Phrygian mode as a diatonic scale, based on the latter. Ancient Greek Phrygian The octave species (scale) underlying the ancient-Greek Phrygian ''tonos'' (in its diatonic genus) corresponds to the medieval and modern Dorian mode. The terminology is based on the '' Elements'' by Aristoxenos (fl. c. 335 BC), a disciple of Aristotle. The Phrygian ''tonos'' or ''harmonia'' is named after the ancient kingdom of Phrygia in Anatolia. In Greek music theory, the ''harmonia'' given this name was based on a ''tonos'', in turn based on a scale or octave species built from a tetrachord which, in its diatonic genus, consisted of a series of rising intervals of a whole tone, followed by a semitone, followed by a whole tone. : In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
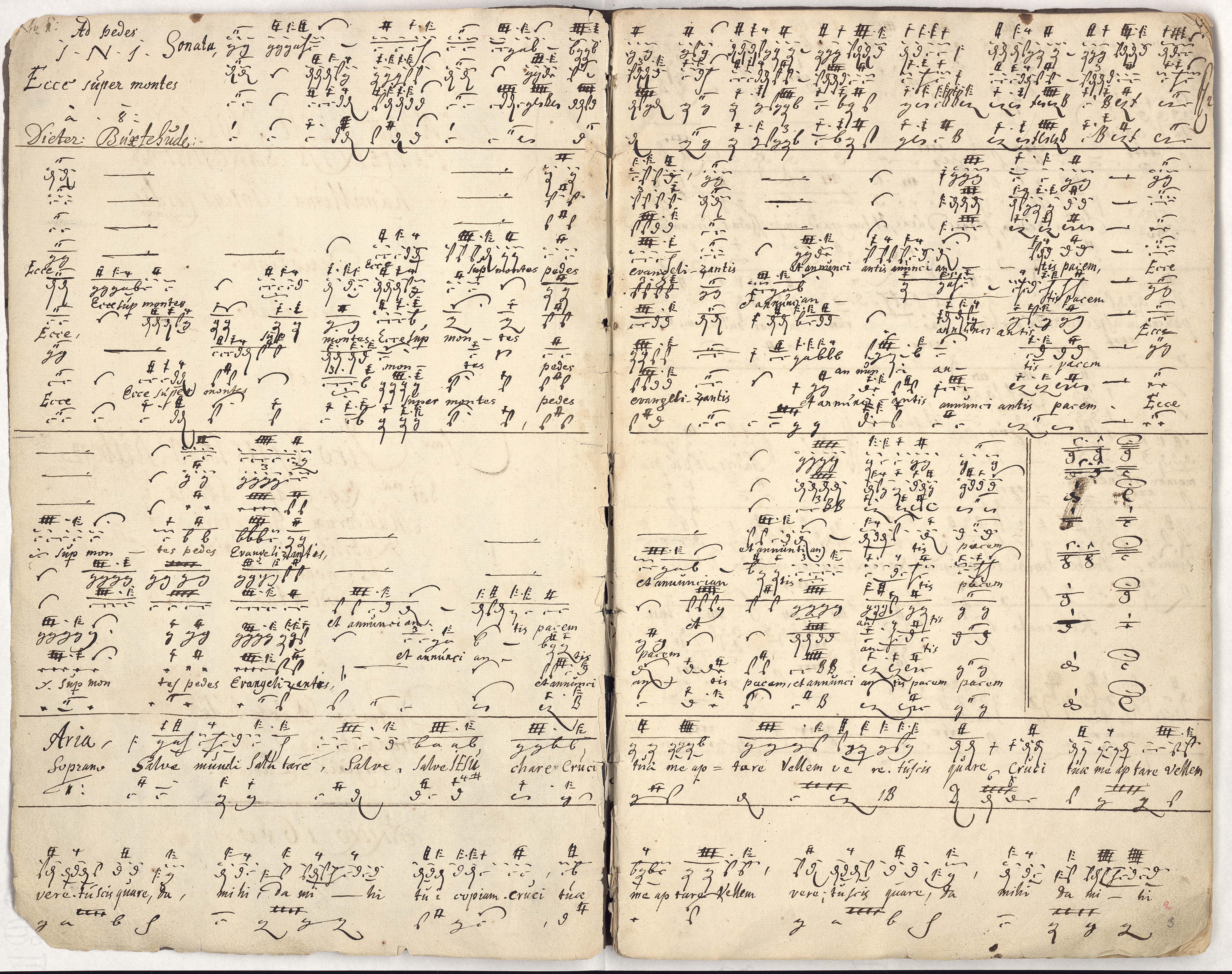
Membra Jesu Nostri
''Membra Jesu nostri'', BuxWV 75, is a cycle of seven cantatas composed in 1680 by Dieterich Buxtehude and dedicated to Gustaf Düben. More specifically and fully it is, in Buxtehude’s phrase, a ''�devotionedecantata,”'' or “sung devotion,” titled ''Membra Jesu nostri patientis sanctissima'', which translates from the Latin as ''Limbs Most Holy of Our Suffering Jesus''. Regarding genre, the cycle consists in seven concerto-aria cantatas, a form that had emerged in Germany in the 1660s. The stanzas of its main text are drawn from the medieval hymn ''Salve mundi salutare'', also known as the ''Rhythmica oratio'', formerly ascribed to Bernard of Clairvaux but now thought to be by Arnulf of Leuven. Each cantata addresses a part of Jesus’ crucified body: feet, knees, hands, side, breast, heart and face; in each, Biblical words referring to the limb frame verses of the hymn’s text. Structure Each cantata in ''Membra Jesu nostri'' is divided into six sections; an instrume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesu, Meine Freude
"" (; Jesus, my joy) is a hymn in German, written by Johann Franck in 1650, with a melody, Zahn No. 8032, by Johann Crüger. The song first appeared in Crüger's hymnal in 1653. The text addresses Jesus as joy and support, versus enemies and the vanity of existence. The poetry is bar form, with irregular lines from 5 to 8 syllables. The melody repeats the first line as the last, framing each of the six stanzas. Several English translations have been made of the hymn, including Catherine Winkworth's "Jesu, priceless treasure" in 1869, and it has appeared in around 40 hymnals. There have been choral and organ settings of the hymn by many composers, including by Johann Sebastian Bach in a motet, BWV 227, for unaccompanied chorus, and a chorale prelude, BWV 610, for organ. In the modern German Protestant hymnal, '' Evangelisches Gesangbuch'', it is No. 396. Text The text is presented in six stanzas of nine lines each. It is in bar form; three lines form the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trio Sonata
The trio sonata is a genre, typically consisting of several movements, with two melody instruments and basso continuo. Originating in the early 17th century, the trio sonata was a favorite chamber ensemble combination in the Baroque era. Basic structure The trio sonata typically consisted of three parts, two violins and (basso) continuo. However, the two violins could be substituted with pairs of flutes, recorders, oboes, or violin and viola da gamba. The third part, the continuo, has two components. First, it includes the bass line, which commonly was played by a bass viol, violone, violoncello, or bassoon. Second, it includes a harmony-producing instrument, such as a small organ, a harpsichord, or a theorbo. The continuo could be performed by two or more performers; a cellist to play the bass line and a harpsichordist or organist to focus on the harmonies. Because there normally are two people playing the continuo part, there are usually four players in all. This accounts for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartholomäus Gesius
Bartholomäus Gesius (also: ''Göß'', ''Gese'', – 1613) was a German theologian, church musician, composer and hymn writer. He worked at Schloss Muskau and in Frankfurt (Oder) and is known for choral Passions in German and Latin and for the melody and first setting of the Easter hymn "Heut triumphieret Gottes Sohn", which was used in several compositions including a cantata by Dieterich Buxtehude and a chorale prelude by Johann Sebastian Bach (BWV 630), concluding the Easter section of his ''Orgelbüchlein''. Life Born in Müncheberg, Gesius studied theology between 1578 and 1585 at the Alma Mater Viadrina in Frankfurt (Oder). He worked from 1582 as Kantor (church musician) in Müncheberg and from 1587 as teacher and musician at Schloss Muskau (now a World Heritage Site). In 1588, he began to compose a Passion after the Gospel of John in German, a ''St John Passion'' for five-part chorus. In spring of 1593, Gesius became Kantor at the Marienkirche, Frankfurt (Oder) and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantata
A cantata (; ; literally "sung", past participle feminine singular of the Italian verb ''cantare'', "to sing") is a vocal composition with an instrumental accompaniment, typically in several movements, often involving a choir. The meaning of the term changed over time, from the simple single-voice madrigal of the early 17th century, to the multi-voice "cantata da camera" and the "cantata da chiesa" of the later part of that century, from the more substantial dramatic forms of the 18th century to the usually sacred-texted 19th-century cantata, which was effectively a type of short oratorio. Cantatas for use in the liturgy of church services are called church cantata or sacred cantata; other cantatas can be indicated as secular cantatas. Several cantatas were, and still are, written for special occasions, such as Christmas cantatas. Christoph Graupner, Georg Philipp Telemann and Johann Sebastian Bach composed cycles of church cantatas for the occasions of the liturgical year. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wie Soll Ich Dich Empfangen
"Wie soll ich dich empfangen" ("Ah! Lord, how shall I meet Thee", literally: How shall I receive you) is a Christian hymn for Advent by Paul Gerhardt. It was first published in 1653 in the fifth edition of the hymnal ''Praxis Pietatis Melica'' by Johann Crüger, who also created a melody. Johann Sebastian Bach used it as a chorale in his ''Christmas Oratorio'', but with a different melody. Catherine Winkworth translated five of its ten stanzas. History Paul Gerhardt wrote the lyrics in the first person, beginning with the theme, the question how to receive Jesus who is expected to arrive. The poet alludes to biblical narrations, such as his entry into Jerusalem and the parable of the ten virgins. The lyricist was also inspired by prophetic words from the Old Testament. The hymn appeared first in the fifth edition of the hymnal ''Praxis Pietatis Melica'' by Johann Crüger in 1653. Text The song is structured in ten stanzas of eight lines each, in bar form. The singer, speaking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erhalt Uns, Herr, Bei Deinem Wort
"" ("Keep us, Lord, faithful to your word" or "Lord, keep us in Thy Word and Work") is a Lutheran hymn by Martin Luther with additional stanzas by Justus Jonas, first published in 1542. It was used in several musical settings, including the chorale cantata by Johann Sebastian Bach, ''Erhalt uns, Herr, bei deinem Wort'', BWV 126. History Luther wrote the hymn probably in 1541 when a prayer service was held in Wittenberg against the perceived danger of the Turks when Ferdinand of Austria lost most of Hungary to the Ottoman Empire at Siege of Buda. The second line of the first verse reads "und steur' des Papsts und Türken Mord" (And control the murder by the Pope and Turks). Luther may have contributed the hymn for a boys' choir. It was published as a broadsheet in 1542. In Klug's hymnal ''Geistliche Lieder'' it was titled a "A hymn for the children to sing against the two arch-enemies of Christ, and His Holy Church, the Pope and the Turks" ("Ein Kinderlied, zu singen wider die ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |