|
Butaxamine
Butaxamine (INN, also known as butoxamine) is a β2-selective beta blocker. Its primary use is in experimental situations in which blockade of β2 receptors is necessary to determine the activity of the drug (i.e. if the β2 receptor is completely blocked, but the given effect is still present, the given effect is not a characteristic of the β2 receptor). It has no clinical use. An alternative name is α-(1- 'tert''-butylaminothyl)-2,5-dimethoxybenzyl alcohol. See also * Bupropion * Methoxamine Methoxamine is an α1-adrenergic receptor agonist, somewhat similar in structure to butaxamine and 2,5-DMA. It is no longer marketed. See also * Sertraline * Phenylephrine * Synephrine * Phentolamine Phentolamine, sold under the brand n ... References Beta blockers Phenylethanolamines Tert-butyl compounds {{antihypertensive-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Blockers
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage cardiac arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythms, and to protect the heart from a second myocardial infarction, heart attack after a first heart attack (preventative healthcare, secondary prevention). They are also widely used to treat hypertension, high blood pressure, although they are no longer the first choice for initial treatment of most patients. Beta blockers are competitive antagonists that block the receptor sites for the endogenous catecholamines Adrenaline, epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) on beta receptor, adrenergic beta receptors, of the sympathetic nervous system, which mediates the fight-or-flight response. Some block activation of all types of β-adrenergic receptors and others are selective for one of the three known types of beta receptors, designated β1, β2 and β3 receptors. Beta-1 adrenergic receptor, β1-adrenergic receptors are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Blocker
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage cardiac arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythms, and to protect the heart from a second myocardial infarction, heart attack after a first heart attack (preventative healthcare, secondary prevention). They are also widely used to treat hypertension, high blood pressure, although they are no longer the first choice for initial treatment of most patients. Beta blockers are competitive antagonists that block the receptor sites for the endogenous catecholamines Adrenaline, epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) on beta receptor, adrenergic beta receptors, of the sympathetic nervous system, which mediates the fight-or-flight response. Some block activation of all types of β-adrenergic receptors and others are selective for one of the three known types of beta receptors, designated β1, β2 and β3 receptors. Beta-1 adrenergic receptor, β1-adrenergic receptors are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-2 Adrenergic Receptor
The beta-2 adrenergic receptor (β2 adrenoreceptor), also known as ADRB2, is a cell membrane-spanning beta-adrenergic receptor The adrenergic receptors or adrenoceptors are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that are targets of many catecholamines like norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline) produced by the body, but also many medications like beta ... that binds epinephrine (adrenaline), a hormone and neurotransmitter whose signaling, via adenylate cyclase stimulation through trimeric Gs proteins, increased Cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cAMP, and downstream L-type calcium channel interaction, mediates physiologic responses such as smooth muscle relaxation and bronchodilation. Robert J.Lefkowitz and Brian Kobilka studied beta 2 adrenergic receptor as a model system which rewarded them the 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry “for groundbreaking discoveries that reveal the inner workings of an important family of such receptors: G-protein-coupled-receptors†... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Activity
In pharmacology, biological activity or pharmacological activity describes the beneficial or adverse effects of a drug on living matter. When a drug is a complex chemical mixture, this activity is exerted by the substance's active ingredient or pharmacophore but can be modified by the other constituents. Among the various properties of chemical compounds, pharmacological/biological activity plays a crucial role since it suggests uses of the compounds in the medical applications. However, chemical compounds may show some adverse and toxic effects which may prevent their use in medical practice. Activity is generally dosage-dependent. Further, it is common to have effects ranging from beneficial to adverse for one substance when going from low to high doses. Activity depends critically on fulfillment of the ADME criteria. To be an effective drug, a compound not only must be active against a target, but also possess the appropriate ADME (Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
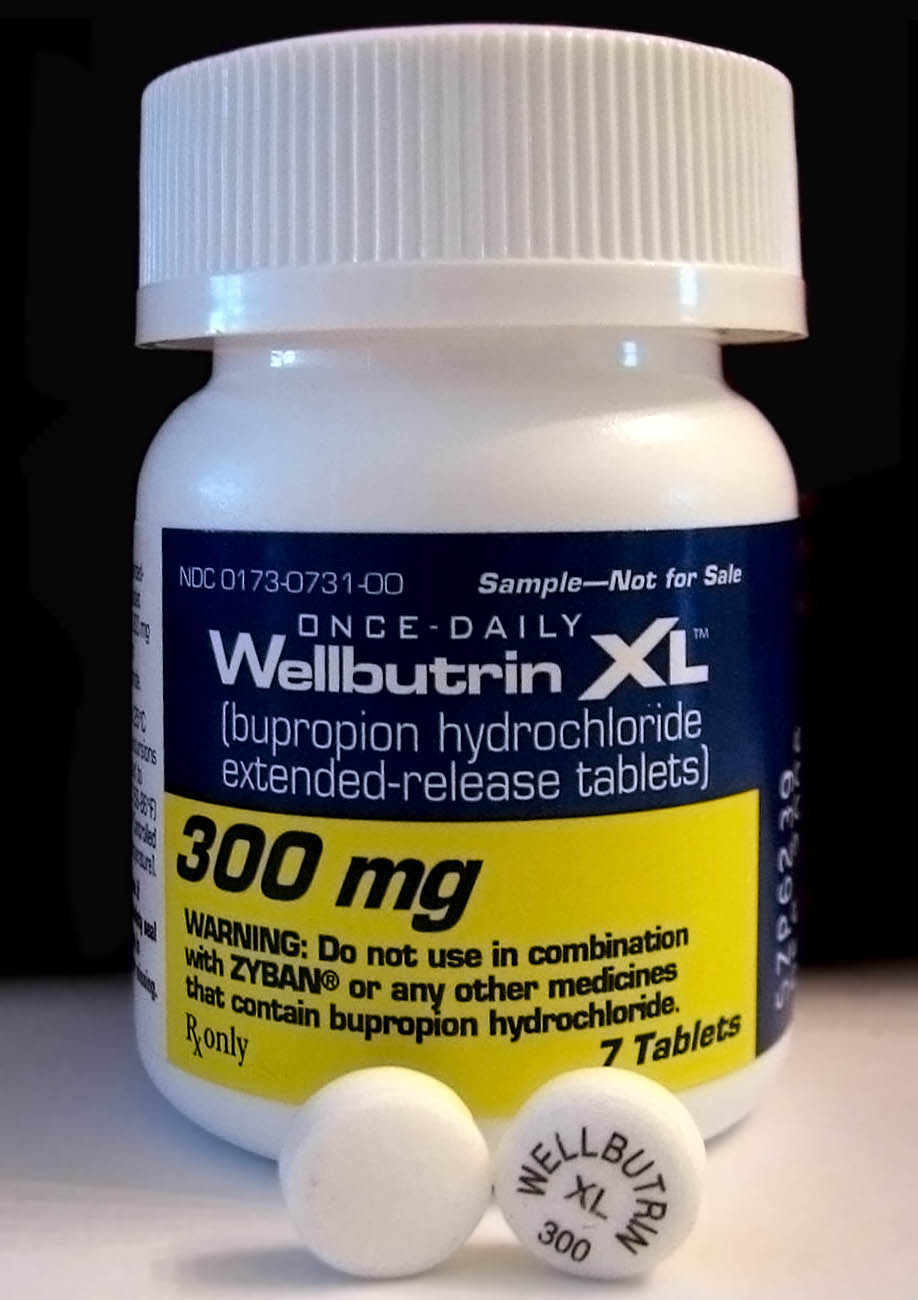
Bupropion
Bupropion, sold under the brand names Wellbutrin and Zyban among others, is an atypical antidepressant primarily used to treat major depressive disorder and to support smoking cessation. It is also popular as an add-on medication in the cases of "incomplete response" to the first-line selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressant. Bupropion has several features that distinguish it from other antidepressants: it does not usually cause sexual dysfunction; it is not associated with weight gain and sleepiness, and it is more effective than SSRIs at improving symptoms of hypersomnia and fatigue. Bupropion does, however, carry a much higher risk of seizure than many other antidepressants and extreme caution must be taken in patients with a history of seizure disorder. Common adverse effects of bupropion with the greatest difference from placebo are dry mouth, nausea, constipation, insomnia, anxiety, tremor, and excessive sweating. Raised blood pressure is notable. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methoxamine
Methoxamine is an α1-adrenergic receptor agonist, somewhat similar in structure to butaxamine and 2,5-DMA. It is no longer marketed. See also * Sertraline * Phenylephrine * Synephrine * Phentolamine Phentolamine, sold under the brand name Regitine among others, is a reversible nonselective α- adrenergic antagonist. Mechanism Its primary action is vasodilation due to α1 blockade. Non-selective α-blockers can cause a much more pronounced ... * Midodrine References Alpha-1 adrenergic receptor agonists Substituted amphetamines Phenol ethers Phenylethanolamines {{respiratory-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |