|
Bunostegos
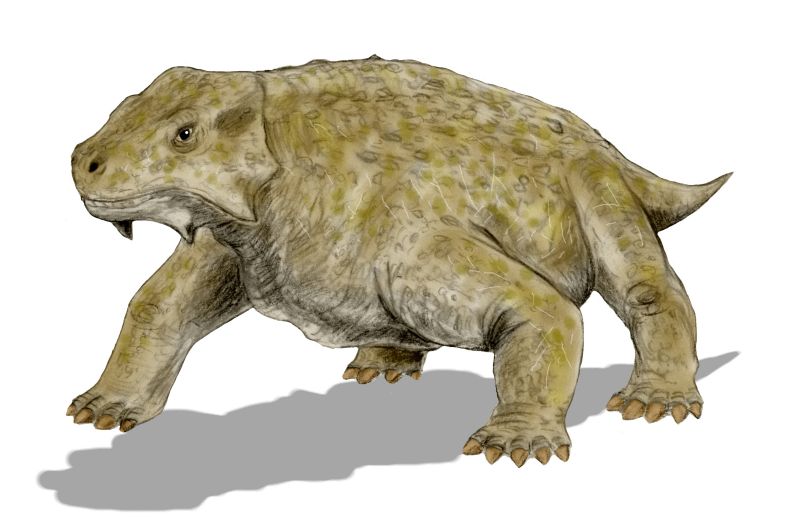
''Bunostegos'' ("knobbly kullroof") is an extinct genus of pareiasaur parareptile from the Late Permian of the Agadez Region in Niger. The type species, ''Bunostegos akokanensis'', was named from the Moradi Formation in 2003. It was a cow-sized animal with a distinctive skull that had large bony knobs, similar in form to those of other pareiasaurs but far larger. The species appears to have lived in a desert in the centre of the supercontinent of Pangaea. Analysis of the limb bones (including the scapulocoracoid, humerus, radius, ulna, pelvis, and femur) was published in 2015, and revealed that ''Bunostegos'' walked upright on four limbs, with the body held above ground. This new information directly suggests that it could be the first tetrapod with a fully erect gait. Description The animal has been described as about the size of a modern cow with a knobbly skull and bony plate armor on its back." Its teeth show it to have been a plant eater. It lived in an isolated desert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pareiasaur
Pareiasaurs (meaning "cheek lizards") are an extinct clade of large, herbivorous parareptiles. Members of the group were armoured with scutes which covered large areas of the body. They first appeared in southern Pangea during the Middle Permian, before becoming globally distributed during the Late Permian. Pareiasaurs were the largest reptiles of the Permian, reaching sizes equivalent to those of contemporary therapsids. Pareiasaurs became extinct at the end of the Permian during the Permian-Triassic extinction event. Description Pareiasaurs ranged in size from long, and may have weighed up to . They were stocky, with short tails, small heads, robust limbs, and broad feet. The cow-sized species '' Bunostegos'', which lived 260 million years ago, is the earliest known example of a tetrapod with a fully erect posture as its legs were positioned directly under its body. Pareiasaurs were protected by bony scutes called osteoderms that were set into the skin. Their heavy skulls wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2003 In Paleontology
Plants Conifers Angiosperms Gnetophytes Fungi Arthropods Arachnids Insects Conodont paleozoology German paleontologist and stratigraphy, stratigrapher Heinz Walter Kozur (1942-2013) described the conodont genus ''Carnepigondolella''. Vertebrate paleozoology Parareptiles Non-avian dinosaurs Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list. Newly named birds Plesiosaurs Pterosaurs Synapsids Non-mammalian Mammals References {{portal, Paleontology [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akokan, Niger
Akokan is a mining town in the Arlit Department of the Agadez Region of northern-central Niger. It is located about southwest of Arlit in the Sahara Desert, and roughly north of Agadez. It is considered to be Niger's "second uranium town". SOMAIR and COMINAK (Compagnie minière d'Akokan), run by Areva and the Nigerien state, operate uranium mines in the vicinity of the towns of Akokan and Arlit. In the maps of the area, Akokan is classified under "Mine - Agadez-Niger". The Tuareg and Toubou people are local to the area. History The Akokan deposit was initially prospected by a France-Japan-Niger tripartite affiliation in the early 1970s. In 1975, underground mining at Akokan was estimated to require over $100 million in investment. Today over 100,000 people live in Akokan and Arlit. Greenpeace has expressed concerns over the high radiation levels found on the streets of Akokan. Afasto, south of Akokan, was the site of newly discovered uranium reserves in 2001. The operational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moradi Formation
The Moradi Formation is a geological formation in Niger. It is of Late Permian age. It is informally divided into three subunits. The lower portion of the formation consists of red mudstone, with muddy calcareous sandstone and quartz-granlule conglomerate present as lenses. The middle portion consists of muddy siltstone in thick beds interbedded with red argillaceous sandstone. The lower two thirds of the upper portion of the formation consist of red siltstone intercalated with channel lag intraformational conglomerates, while the upper third consists of barchanoid shaped lenses of conglomeratic sandstone with ventifacts. These facies are indicatived of deposition under arid conditions, with less than of annual rainfall in the Central Pangean desert, with annual temperatures of , but with ephemeral water presence including lakes. Fossil content The formation is known for its fossils, including the temnospondyls '' Nigerpeton'' and '' Saharastega, ''the pareiasaur ''Bunosteg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
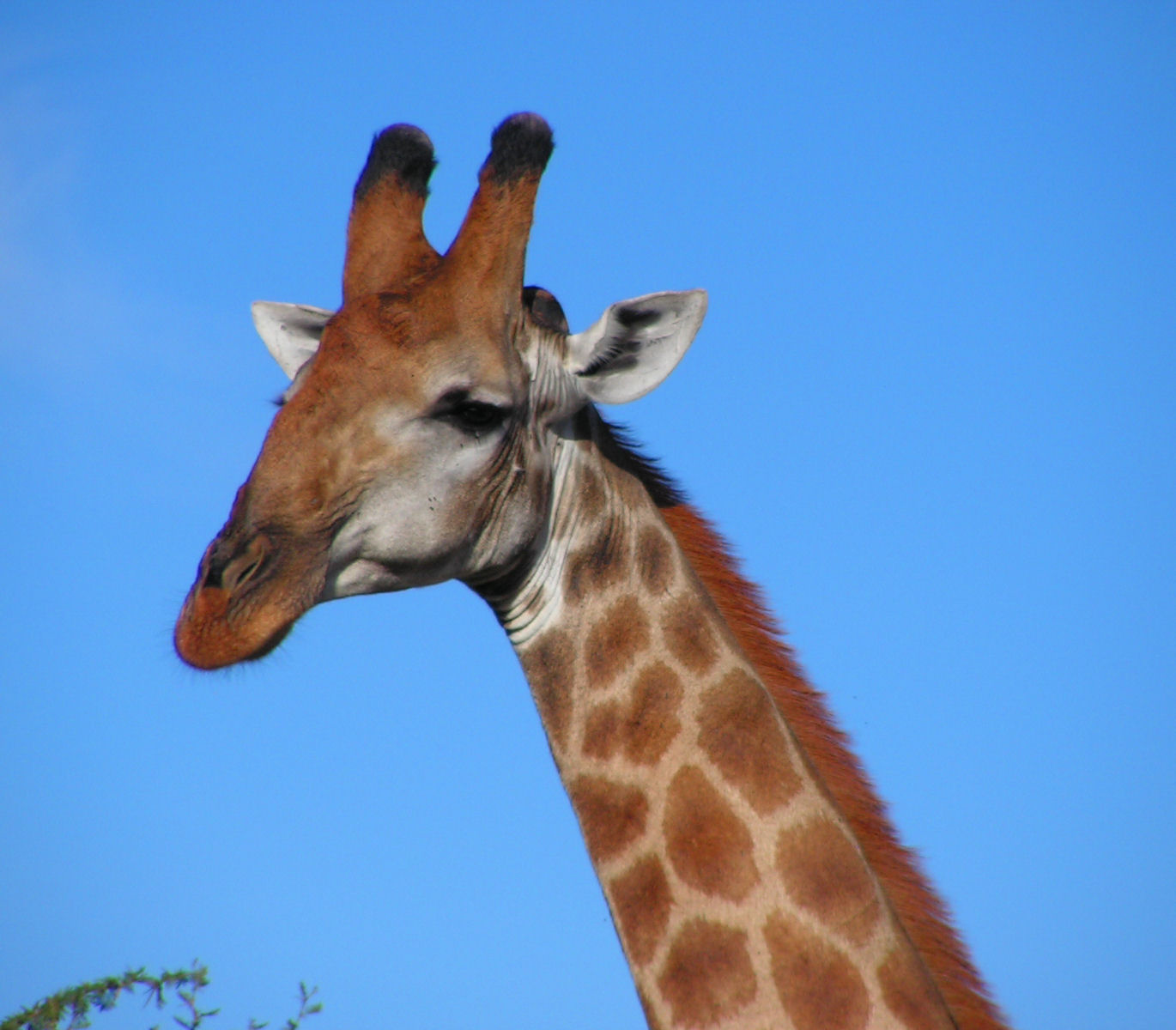
Ossicone
Ossicones are columnar or conical skin-covered bone structures on the heads of giraffes, male okapi, and some of their extinct relatives. Ossicones are distinguished from the superficially similar structures of horns and antlers by their unique development and a permanent covering of skin and fur. Structure Giraffe ossicones consist of a highly vascularized and innervated bone core covered with vascularized and innervated skin. The base of an ossicone is attached to the skull with vascularized innervated connective tissue. Ossicones are formed at late gestation, but in early development they are not bony and not fused to the skull yet. Ossicones usually fuse to the skull at sexual maturity. All male and female giraffes have a pair of parietal ossicones on the parietal bones of the skull. Males also usually have a single median ossicone on the frontal bone that is larger in northern animals and smaller in southern giraffes. Giraffes can also have small additional paired occipita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of the forearm as the little finger. It runs parallel to the radius, the other long bone in the forearm. The ulna is usually slightly longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. Therefore, the radius is considered to be the larger of the two. Structure The ulna is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. It is broader close to the elbow, and narrows as it approaches the wrist. Close to the elbow, the ulna has a bony process, the olecranon process, a hook-like structure that fits into the olecranon fossa of the humerus. This prevents hyperextension and forms a hinge joint with the trochlea of the humerus. There is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton). The pelvic region of the trunk includes the bony pelvis, the pelvic cavity (the space enclosed by the bony pelvis), the pelvic floor, below the pelvic cavity, and the perineum, below the pelvic floor. The pelvic skeleton is formed in the area of the back, by the sacrum and the coccyx and anteriorly and to the left and right sides, by a pair of hip bones. The two hip bones connect the spine with the lower limbs. They are attached to the sacrum posteriorly, connected to each other anteriorly, and joined with the two femurs at the hip joints. The gap enclosed by the bony pelvis, called the pelvic cavity, is the section of the body underneath the abdomen and mainly consists of the reproductive organs (sex organs) and the rectum, while the pelvic f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates with the tibia (shinbone) and patella (kneecap), forming the knee joint. By most measures the two (left and right) femurs are the strongest bones of the body, and in humans, the largest and thickest. Structure The femur is the only bone in the upper leg. The two femurs converge medially toward the knees, where they articulate with the proximal ends of the tibiae. The angle of convergence of the femora is a major factor in determining the femoral-tibial angle. Human females have thicker pelvic bones, causing their femora to converge more than in males. In the condition ''genu valgum'' (knock knee) the femurs converge so much that the knees touch one another. The opposite extreme is ''genu varum'' (bow-leggedness). In the general populatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (pelycosaurs, extinct therapsids and all extant mammals). Tetrapods evolved from a clade of primitive semiaquatic animals known as the Tetrapodomorpha which, in turn, evolved from ancient lobe-finned fish (sarcopterygians) around 390 million years ago in the Middle Devonian period; their forms were transitional between lobe-finned fishes and true four-limbed tetrapods. Limbed vertebrates (tetrapods in the broad sense of the word) are first known from Middle Devonian trackways, and body fossils became common near the end of the Late Devonian but these were all aquatic. The first crown-tetrapods (last common ancestors of extant tetrapods capable of terrestrial locomotion) appeared by the very early Carboniferous, 350 million years ago. The specific aquatic ancestors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lopingian
The Lopingian is the uppermost series/last epoch of the Permian. It is the last epoch of the Paleozoic. The Lopingian was preceded by the Guadalupian and followed by the Early Triassic. The Lopingian is often synonymous with the informal terms late Permian or upper Permian. The name was introduced by Amadeus William Grabau in 1931 and derives from Leping, Jiangxi in China. It consists of two stages/ ages. The earlier is the Wuchiapingian and the later is the Changhsingian. The International Chronostratigraphic Chart (v2018/07) provides a numerical age of 259.1 ±0.5 Ma. If a Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) has been approved, the lower boundary of the earliest stage determines numerical age of an epoch. The GSSP for the Wuchiapingian has a numerical age of 259.8 ± 0.4 Ma. Evidence from Milankovitch cycles suggests that the length of an Earth day during this epoch was approximately 22 hours. The Lopingian ended with the Permian–Triassic extinction event. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giraffe
The giraffe is a large African hoofed mammal belonging to the genus ''Giraffa''. It is the tallest living terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant on Earth. Traditionally, giraffes were thought to be one species, ''Giraffa camelopardalis'', with nine subspecies. Most recently, researchers proposed dividing them into up to eight extant species due to new research into their mitochondrial and nuclear DNA, as well as morphological measurements. Seven other extinct species of ''Giraffa'' are known from the fossil record. The giraffe's chief distinguishing characteristics are its extremely long neck and legs, its horn-like ossicones, and its spotted coat patterns. It is classified under the family Giraffidae, along with its closest extant relative, the okapi. Its scattered range extends from Chad in the north to South Africa in the south, and from Niger in the west to Somalia in the east. Giraffes usually inhabit savannahs and woodlands. Their food source is leaves, frui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes (tubercles, sometimes called tuberosities). The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes (trochlea & capitulum), and 3 fossae (radial fossa, coronoid fossa, and olecranon fossa). As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons. Etymology The word "humerus" is derived from la, humerus, umerus meaning upper arm, shoulder, and is linguistically related to Gothic ''ams'' shoulder and Greek ''ōmos''. Structure Upper extremity The upper or pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |