|
Bullseye (shooting Competition)
NRA Precision Pistol, formerly known as NRA Conventional Pistol, is a national bullseye shooting discipline organized in the United States by the National Rifle Association of America. Emphasis is on accuracy and precision, and participants shoot handguns at paper targets at fixed distances and time limits. Other organizations in the United States and Canada have established rules and keep records of similar disciplines, including the Civilian Marksmanship Program (CMP) in the United States. Bullseye pistol was the inspiration for the ISSF international 25 m Standard Pistol (82 feet) event and like the ISSF pistol events, the development of skills required to shoot one-handed at and bullseye targets at , respectively, takes considerable training to achieve proficiency. Courses of fire All courses of fire are from a standing position using a one-handed grip at two different targets depending on the distance and type of match. The slow-fire targets have the 8–10 rings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M1911
The M1911 (Colt 1911 or Colt Government) is a single-action, recoil-operated, semi-automatic pistol chambered for the .45 ACP cartridge. The pistol's formal U.S. military designation as of 1940 was ''Automatic Pistol, Caliber .45, M1911'' for the original model adopted in March 1911, and ''Automatic Pistol, Caliber .45, M1911A1'' for the improved M1911A1 model which entered service in 1926. The designation changed to ''Pistol, Caliber .45, Automatic, M1911A1'' in the Vietnam War era. Designed by John Browning, the M1911 is the best-known of his designs to use the short recoil principle in its basic design. The pistol was widely copied, and this operating system rose to become the preeminent type of the 20th century and of nearly all modern centerfire pistols. It is popular with civilian shooters in competitive events such as the International Defensive Pistol Association and International Practical Shooting Confederation. The U.S. military procured around 2.7 million M1911 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
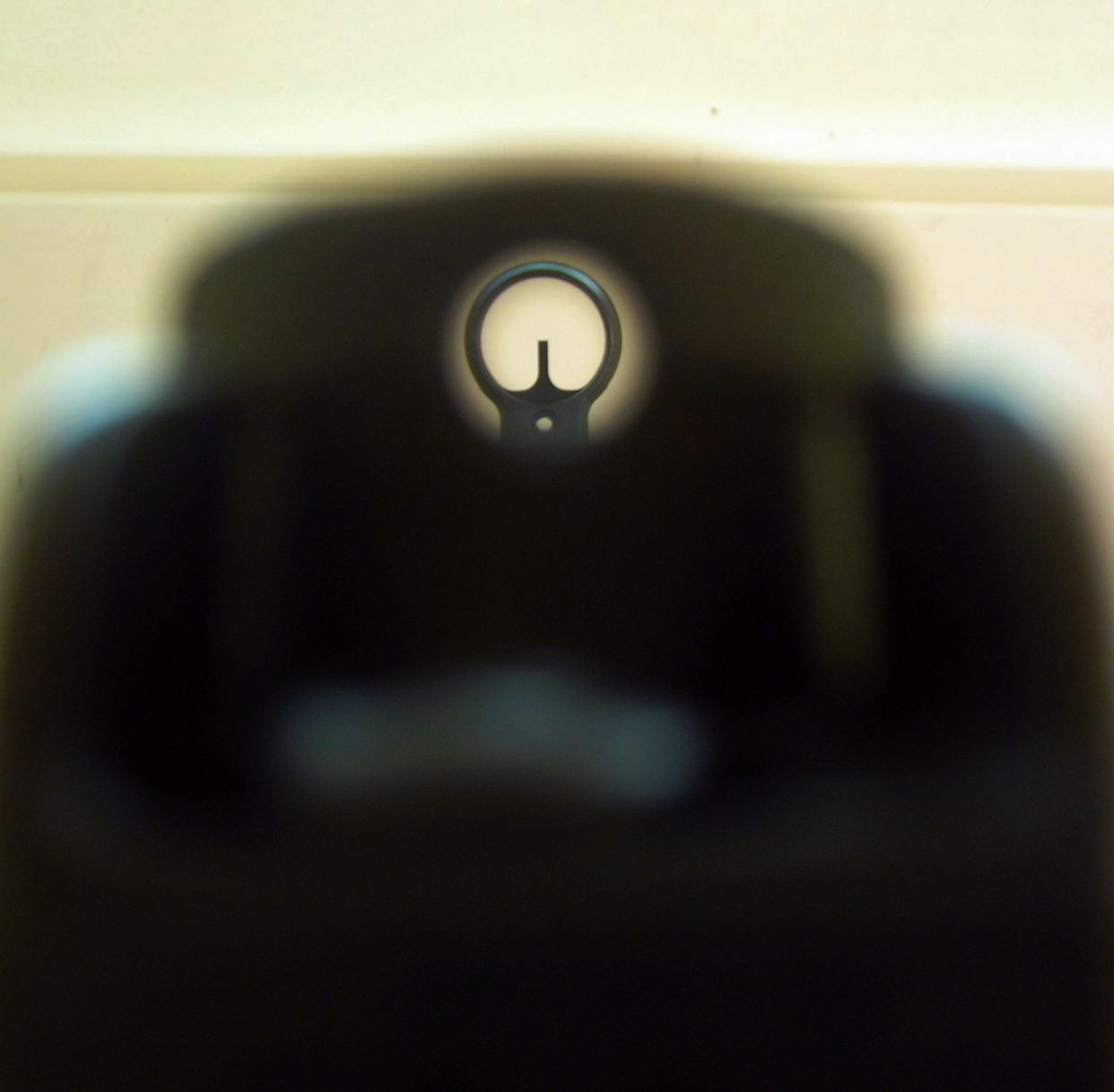
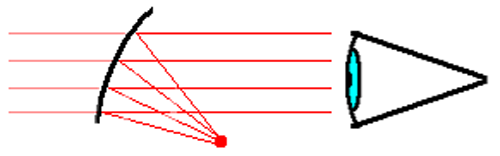
Iron Sights
Iron sights are a system of physical alignment markers (usually made of metallic material) used as a sighting device to assist the accurate aiming of ranged weapons (such as a firearm, airgun, crossbow or even compound bow), or less commonly as a primitive finder sight for optical telescopes. The earliest sighting device, it relies completely on the viewer's naked eye (mostly under ambient lighting), and is distinctly different to optical sights such as telescopic sights, reflector (reflex) sights, holographic sights and laser sights, which make use of optical manipulation and/or active illumination, as well as the newer optoelectronics, which use digital imaging and even incorporate augmented reality. Iron sights are typically composed of two components mounted perpendicularly above the weapon's bore axis: a rear sight nearer (or ''proximally'') to the shooter's eye, and a front sight farther forward (or ''distally'') near the muzzle. During aiming, the shooter aligns h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
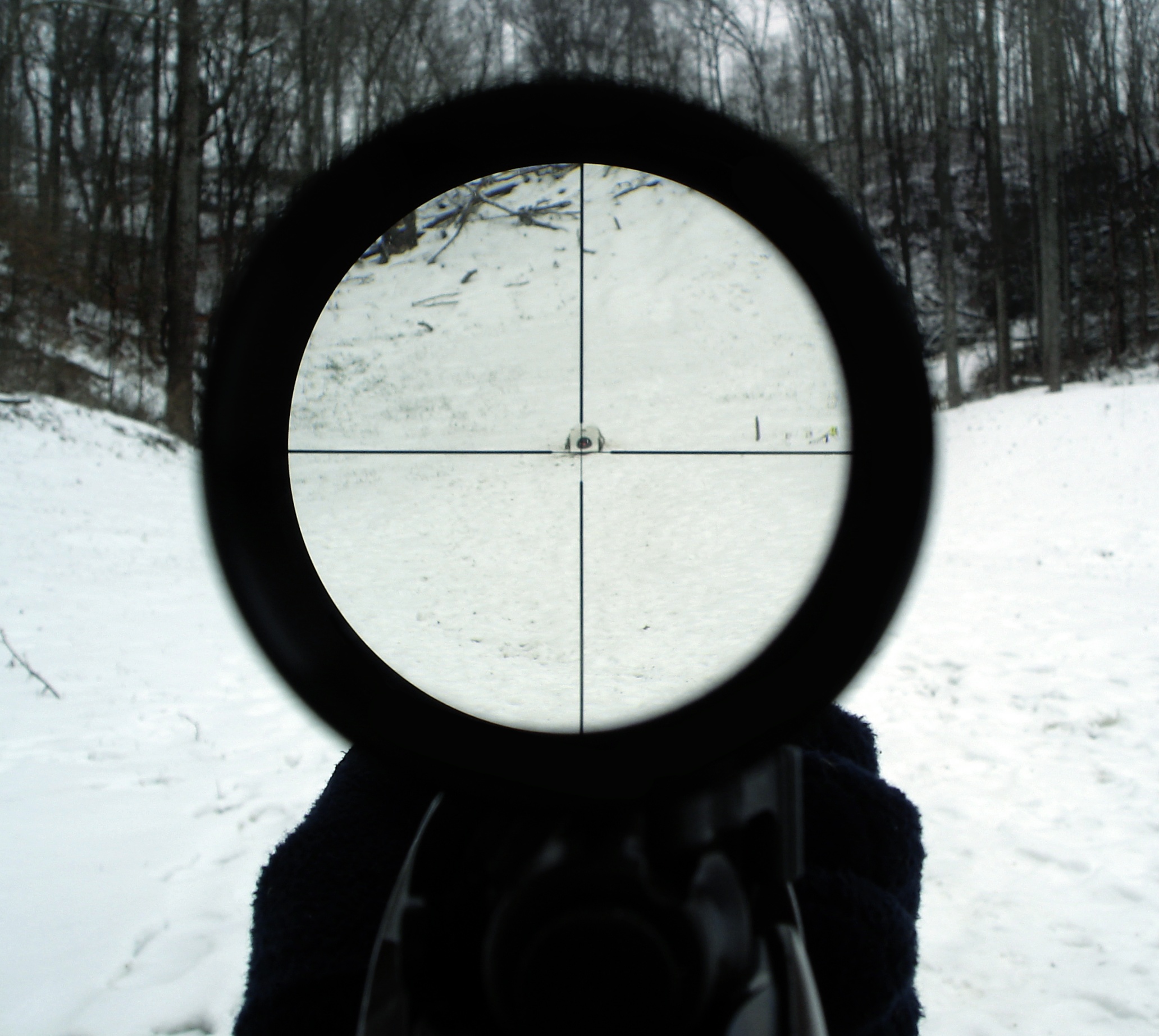
Telescopic Sight
A telescopic sight, commonly called a scope informally, is an optical sighting device based on a refracting telescope. It is equipped with some form of a referencing pattern – known as a ''reticle'' – mounted in a focally appropriate position in its optical system to provide an accurate point of aim. Telescopic sights are used with all types of systems that require magnification in addition to reliable visual aiming, as opposed to non-magnifying iron sights, reflector (reflex) sights, holographic sights or laser sights, and are most commonly found on long-barrel firearms, particularly rifles, usually via a scope mount. The optical components may be combined with optoelectronics to add night vision or smart device features. History The first experiments directed to give shooters optical aiming aids go back to the early 17th century. For centuries, different optical aiming aids and primitive predecessors of telescopic sights were created that had practical or pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Dot Sight
A red dot sight is a common classification for a type of non- magnifying reflector (or reflex) sight for firearms, and other devices that require aiming, that gives the user a point of aim in the form of an illuminated red dot. A standard design uses a red light-emitting diode (LED) at the focus of collimating optics which generates a dot-style illuminated reticle that stays in alignment with the weapon the sight is attached to, regardless of eye position (nearly parallax free). They are considered to be fast-acquisition and easy-to-use gun sights for civilian target shooting, hunting, or in police and military applications. Aside from firearm applications, they are also used on cameras and telescopes. On cameras they are used to photograph flying aircraft, birds in flight, and other distant, quickly moving subjects. Telescopes have a narrow field of view and therefore are often equipped with a secondary "finder scope" such as a red dot sight. Description The typical configur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Sights
Iron sights are a system of physical alignment markers (usually made of metallic material) used as a sighting device to assist the accurate aiming of ranged weapons (such as a firearm, airgun, crossbow or even compound bow), or less commonly as a primitive finder sight for optical telescopes. The earliest sighting device, it relies completely on the viewer's naked eye (mostly under ambient lighting), and is distinctly different to optical sights such as telescopic sights, reflector (reflex) sights, holographic sights and laser sights, which make use of optical manipulation and/or active illumination, as well as the newer optoelectronics, which use digital imaging and even incorporate augmented reality. Iron sights are typically composed of two components mounted perpendicularly above the weapon's bore axis: a rear sight nearer (or ''proximally'') to the shooter's eye, and a front sight farther forward (or ''distally'') near the muzzle. During aiming, the shooter aligns h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
22 Long Rifle
The .22 Long Rifle or simply .22 LR or 22 (metric designation: 5.6×15mmR) is a long-established variety of .22 caliber rimfire ammunition originating from the United States. It is used in a wide range of rifles, pistols, revolvers, smoothbore shotguns, and submachine guns. In terms of units sold it is by far the most common ammunition in the world today. Common uses include hunting and shooting sports. Ammunition produced in .22 Long Rifle is effective at short ranges, has little recoil, and is cheap to purchase, making it ideal for training. History American firearms manufacturer J. Stevens Arms & Tool Company introduced the .22 Long Rifle cartridge in 1887. The round owes its origin to the .22 BB Cap of 1845 and the .22 Short of 1857. It combined the case of the .22 Long of 1871 with a bullet, giving it a longer overall length, a higher muzzle velocity and superior performance as a hunting and target round, rendering the .22 Extra Long cartridges obsolete. The .22 LR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
38 Super
The .38 Super, also known as .38 Super +P, .38 Super Auto, .38 Super Automatic, .38 Super Automatic +P, or 9×23mmSR, is a pistol cartridge that fires a bullet. It was introduced in the late 1920s as a higher pressure loading of the .38 ACP, also known as .38 Auto. The older .38 ACP cartridge propels a bullet at , whereas the .38 Super pushes the same bullet at . The .38 Super has gained distinction as the caliber of choice for many top practical shooting competitors; it remains one of the dominant calibers in IPSC competition.Boatman, Robert H.: ''Living With the 1911: A Fresh Look at the Fighting Gun'', p. 15. Paladin Press, January 2005. Design The cartridge was designed for use in the M1911 pistol and was capable of penetrating automobile bodies of the late 1920s. When the .357 Magnum was introduced in 1935, this advantage of the .38 Super was no longer enough to lure police departments and officers from the traditional double-action revolver. The .38 Super retains the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
38 Special
38 Special may refer to: * .38 Special The .38 Special, also commonly known as .38 S&W Special (not to be confused with .38 S&W), .38 Smith & Wesson Special, .38 Spl, .38 Spc, (pronounced "thirty-eight special"), or 9x29mmR is a rimmed, centerfire cartridge designed by Smith & ..., a revolver cartridge * 38 Special (band), an American rock band ** ''38 Special'' (album), an album from the 38 Special band {{Disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
380 ACP '', 2001
{{Numberdis ...
38 may refer to: * 38 (number), the natural number following 37 and preceding 39 *one of the years 38 BC, AD 38, 1938, 2038 *.38, a caliber of firearms and cartridges **.38 Special, a revolver cartridge *'' Thirty-Eight: The Hurricane That Transformed New England'', a 2016 book by Stephen Long *"Thirty Eight", a song by Karma to Burn from the album ''Almost Heathen ''Almost Heathen'' is the third studio album by the stoner rock band Karma to Burn, released in 2001 via Spitfire Records. It was the last album released before their seven-year disbandment in 2002. The album was reissued in 2022 by Heavy Psych Sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
32 ACP
.32 ACP (Automatic Colt Pistol, also known as .32 Automatic) is a centerfire pistol cartridge. It is a semi-rimmed, straight-walled cartridge developed by firearms designer John Browning, initially for use in the FN M1900 semi-automatic pistol. It was introduced in 1899 by Fabrique Nationale, and is also known as the 7.65×17mmSR Browning or 7.65 mm Browning Short. History John Browning engineered a number of modern semi-automatic pistol mechanisms and cartridges. As his first pistol cartridge, the .32 ACP needed a straight wall for reliable blowback operation as well as a small rim for reliable feeding from a box magazine. The cartridge headspaces on the rim.Wilson, R. K. ''Textbook of Automatic Pistols'', p.254. Plantersville, SC: Small Arms Technical Publishing Company, 1943. The cartridge was a success and was adopted by dozens of countries and many governmental agencies. When the .32 ACP cartridge was introduced, it was immediately popular and was available in sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |