|
Bullmastiff
The Bullmastiff is a British breed of dog of mastiff type and large size, with a solid build and a short muzzle. It was developed as a guard dog in the nineteenth century by cross-breeding the English Mastiff with the now-extinct Old English Bulldog. It was recognised as a breed by The Kennel Club in 1924. History The origins of the Bullmastiff are unclear. In the eighteenth century, in some regions of England, the Old English Mastiff and English Bulldog were commonly inter-bred to produce dogs suitable for work guarding people and their property. By the beginning of the twentieth century this cross-breed was in widespread use as an aid to gamekeepers in the control of poaching. They were bred by gamekeepers for strength, size and speed using a cross of the tough, heavy and aggressive Bulldog of the nineteenth century with the large, strong, less aggressive Mastiff.Walkey B. The Bullmastiff Fancier's Manual. Sechelt B.C., Canada: Coast Arts Publishing; 1992 As a result, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bullmastiff (13)
The Bullmastiff is a British breed of dog of mastiff type and large size, with a solid build and a short muzzle. It was developed as a guard dog in the nineteenth century by cross-breeding the English Mastiff with the now-extinct Old English Bulldog. It was recognised as a breed by The Kennel Club in 1924. History The origins of the Bullmastiff are unclear. In the eighteenth century, in some regions of England, the Old English Mastiff and English Bulldog were commonly inter-bred to produce dogs suitable for work guarding people and their property. By the beginning of the twentieth century this cross-breed was in widespread use as an aid to gamekeepers in the control of poaching. They were bred by gamekeepers for strength, size and speed using a cross of the tough, heavy and aggressive Bulldog of the nineteenth century with the large, strong, less aggressive Mastiff.Walkey B. The Bullmastiff Fancier's Manual. Sechelt B.C., Canada: Coast Arts Publishing; 1992 As a result, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bullmastiff Junghund 1 Jahr
The Bullmastiff is a British breed of dog of mastiff type and large size, with a solid build and a short muzzle. It was developed as a guard dog in the nineteenth century by cross-breeding the English Mastiff with the now-extinct Old English Bulldog. It was recognised as a breed by The Kennel Club in 1924. History The origins of the Bullmastiff are unclear. In the eighteenth century, in some regions of England, the Old English Mastiff and English Bulldog were commonly inter-bred to produce dogs suitable for work guarding people and their property. By the beginning of the twentieth century this cross-breed was in widespread use as an aid to gamekeepers in the control of poaching. They were bred by gamekeepers for strength, size and speed using a cross of the tough, heavy and aggressive Bulldog of the nineteenth century with the large, strong, less aggressive Mastiff.Walkey B. The Bullmastiff Fancier's Manual. Sechelt B.C., Canada: Coast Arts Publishing; 1992 As a result, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastiff
A mastiff is a large and powerful type of dog. Mastiffs are among the largest dogs, and typically have a short coat, a long low-set tail and large feet; the skull is large and bulky, the muzzle broad and short ( brachycephalic) and the ears drooping and pendant-shaped. European and Asian records dating back 3,000 years show dogs of the mastiff type. Mastiffs have historically been guard dogs, protecting homes and property, although throughout history they have been used as hunting dogs, war dogs and for blood sports, such as fighting each other and other animals, including bulls, bears and even lions. Historical and archaeological evidence suggests that mastiffs have long been distinct in both form and function from the similarly large livestock guardian dogs from which they were most likely developed; they also form separate genetic populations. The Fédération Cynologique Internationale and some kennel clubs group the two types together as molossoid dogs; some modern li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastiff
A mastiff is a large and powerful type of dog. Mastiffs are among the largest dogs, and typically have a short coat, a long low-set tail and large feet; the skull is large and bulky, the muzzle broad and short ( brachycephalic) and the ears drooping and pendant-shaped. European and Asian records dating back 3,000 years show dogs of the mastiff type. Mastiffs have historically been guard dogs, protecting homes and property, although throughout history they have been used as hunting dogs, war dogs and for blood sports, such as fighting each other and other animals, including bulls, bears and even lions. Historical and archaeological evidence suggests that mastiffs have long been distinct in both form and function from the similarly large livestock guardian dogs from which they were most likely developed; they also form separate genetic populations. The Fédération Cynologique Internationale and some kennel clubs group the two types together as molossoid dogs; some modern li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Mastiff
The English Mastiff, or simply the Mastiff, is a British dog breed of very large size. Likely descended from the ancient Alaunt and Pugnaces Britanniae, with a significant input from the Alpine Mastiff in the 19th century. Distinguished by its enormous size, massive head, short coat in a limited range of colours, and always displaying a black mask, the Mastiff is noted for its gentle and loving nature. The lineage of modern dogs can be traced back to the early 19th century, but the modern type was stabilised in the 1880s and refined since. Following a period of sharp decline, the Mastiff has increased its worldwide popularity. Throughout its history the Mastiff has contributed to the development of a number of dog breeds, some generally known as mastiff-type dogs or, confusingly, just as "mastiffs". It is the largest living canine, outweighing the wolf by up to 50 kg (110 lbs) on average. Appearance With a massive body, broad skull and head of generally square appearance, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progressive Retinal Atrophy
Progressive retinal atrophy (PRA) is a group of genetic diseases seen in certain breeds of dogs and, more rarely, cats. Similar to retinitis pigmentosa in humans, it is characterized by the bilateral degeneration of the retina, causing progressive vision loss culminating in blindness. The condition in nearly all breeds is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait, with the exception of the Siberian Husky (inherited as an X chromosome linked trait) and the Bullmastiff (inherited as an autosomal dominant trait). There is no treatment. Types of PRA In general, PRAs are characterised by initial loss of rod photoreceptor cell function followed by that of the cones and for this reason night blindness is the first significant clinical sign for most dogs affected with PRA. As other retinal disorders, PRA can be divided into either dysplastic disease, where the cells develop abnormally, and degenerative, where the cells develop normally but then degenerate during the dog's lifetime. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Dog Breeds
This list of dog breeds includes both extant and extinct dog breeds, varieties, landraces, and dog types. A research article on dog genomics published in Science/AAAS defines modern dog breeds as "a recent invention defined by conformation to a physical ideal and purity of lineage". Extant breeds, landraces, varieties and types Note: not all dogs listed below are recognized breeds by an official breed registry that can certify the dog is a purebred, including The Kennel Club (TKC - 1873), the oldest and first official dog breed registry in the world, located in the United Kingdom, and the three oldest breed registries in North America, and largest in the world, including the American Kennel Club (AKC - 1884), United Kennel Club (UKC - 1898), and Canadian Kennel Club (CKC - 1888). A–C D–K L–R S–Z Extinct breeds, landraces, varieties and types Notes References Citations Bibliography * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{DE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulldog
The Bulldog is a British breed of dog of mastiff type. It may also be known as the English Bulldog or British Bulldog. It is of medium size, a muscular, hefty dog with a wrinkled face and a distinctive pushed-in nose."Get to Know the Bulldog" , 'The American Kennel Club'. Retrieved 29 May 2014 It is commonly kept as a ; in 2013 it was in twelfth place on a list of the breeds most frequently registered worldwide. The Bulldog has a longstanding association with British culture; the BB ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elbow Dysplasia
Elbow dysplasia is a condition involving multiple developmental abnormalities of the elbow-joint in the dog, specifically the growth of cartilage or the structures surrounding it. These abnormalities, known as 'primary lesions', give rise to osteoarthritic processes.Quoted from: Elbow dysplasia is a common condition of certain breeds of dogs. Most primary lesions are related to osteochondrosis, a disease of the joint cartilage, and osteochondritis dissecans (OCD), the separation of a flap of cartilage on the joint surface. Other common causes of elbow dysplasia include an ununited anconeal process (UAP) and fragmented or ununited medial coronoid process (FCP or FMCP). Osteochondritis dissecans is difficult to diagnose clinically as the animal may only exhibit an unusual gait. Consequently, OCD may be masked by, or misdiagnosed as, other skeletal and joint conditions such as hip dysplasia. The problem develops in puppyhood, although often is subclinical, and there may be pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
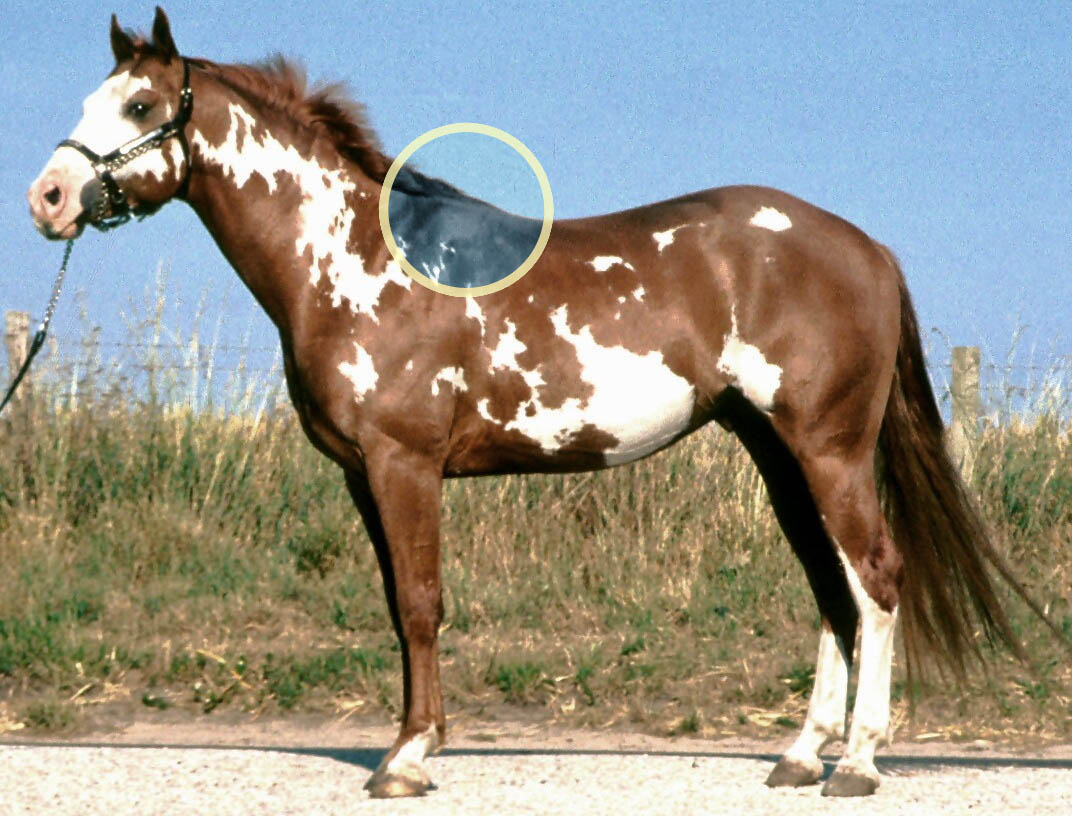
Withers
The withers is the ridge between the shoulder blades of an animal, typically a quadruped. In many species, it is the tallest point of the body. In horses and dogs, it is the standard place to measure the animal's height. In contrast, cattle are often measured to the top of the hips. The term (pronounced ) derives from Old English ''wither'' (“against”), because it is the part of a draft animal that pushes against a load. Horses The withers in horses are formed by the dorsal spinal processes of roughly the 3rd through 11th thoracic vertebrae, which are unusually long in this area. Most horses have 18 thoracic vertebrae. The processes at the withers can be more than long. Since they do not move relative to the ground as the horse's head does, the withers are used as the measuring point for the height of a horse. Horses are sometimes measured in hands – one hand is . Horse heights are extremely variable, from small pony breeds to large draft breeds. The height at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachycephalic
Brachycephaly (derived from the Ancient Greek '' βραχύς'', 'short' and '' κεφαλή'', 'head') is the shape of a skull shorter than typical for its species. It is perceived as a desirable trait in some domesticated dog and cat breeds, notably the pug and Persian, and can be normal or abnormal in other animal species. In humans, the cephalic disorder is known as flat head syndrome, and results from premature fusion of the coronal sutures, or from external deformation. The coronal suture is the fibrous joint that unites the frontal bone with the two parietal bones of the skull. The parietal bones form the top and sides of the skull. This feature can be seen in Down syndrome. In anthropology, human populations have been characterized as either dolichocephalic (long-headed), mesaticephalic (moderate-headed), or brachycephalic (short-headed). The usefulness of the cephalic index was questioned by Giuseppe Sergi, who argued that cranial morphology provided a better ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hip Dysplasia (canine)
In dogs, hip dysplasia is an abnormal formation of the hip socket that, in its more severe form, can eventually cause lameness and arthritis of the joints. It is a genetic (polygenic) trait that is affected by environmental factors. It is common in many dog breeds, particularly the larger breeds, and is the most common single cause of arthritis of the hips. During growth, both the ball (the head of the femur, or thighbone) and the socket in the pelvis (acetabulum) must grow at equal rates. In hip dysplasia, this uniform growth during puppyhood does not occur. The result is laxity (looseness) of the joint, followed by degenerative joint disease (DJD) or osteoarthritis (OA), which is the body's attempt to stabilize the loose hip joint. Overview Normal hip anatomy In the normal anatomy of the hip joint, the almost spherical end of the femur head (the caput, or caput ossis femoris) fits into the acetabulum (a concave socket located in the pelvis). The bony surfaces of the femur he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)