|
Buli Languages
The South Halmahera languages are the branch of Austronesian languages found along the southeast coast of the island of Halmahera in the Indonesian province of North Maluku. Irarutu is spoken in the east of the Bomberai Peninsula in West Papua province. Most of the languages are only known from short word lists, but Taba and Buli are fairly well attested. They are not related to the North Halmahera languages, which are notable for being non-Austronesian. However, Ternatan influence is considerable, a legacy of the historical dominance of the Ternate Sultanate. Classification The South Halmahera languages are listed below according to ''Glottolog'' 4.0's classification, with alternate names and dialects listed from Kamholz (2014: 17):Kamholz, David (2014). Austronesians in Papua: Diversification and change in South Halmahera–West New Guinea'. Ph.D. dissertation, University of California, Berkeley. https://escholarship.org/uc/item/8zg8b1vd *East Makian – Gane **Gane (G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maluku Islands
The Maluku Islands (; Indonesian: ''Kepulauan Maluku'') or the Moluccas () are an archipelago in the east of Indonesia. Tectonically they are located on the Halmahera Plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone. Geographically they are located east of Sulawesi, west of New Guinea, and north and east of Timor. Lying within Wallacea (mostly east of the biogeographical Weber Line), the Maluku Islands have been considered as a geographical and cultural intersection of Asia and Oceania. The islands were known as the Spice Islands because of the nutmeg, mace and cloves that were exclusively found there, the presence of which sparked colonial interest from Europe in the sixteenth century. The Maluku Islands formed a single province from Indonesian independence until 1999, when it was split into two provinces. A new province, North Maluku, incorporates the area between Morotai and Sula, with the arc of islands from Buru and Seram to Wetar remaining within the existing Maluku Province. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of The Maluku Islands
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of methods, including spoken, sign, and written language. Many languages, including the most widely-spoken ones, have writing systems that enable sounds or signs to be recorded for later reactivation. Human language is highly variable between cultures and across time. Human languages have the properties of productivity and displacement, and rely on social convention and learning. Estimates of the number of human languages in the world vary between and . Precise estimates depend on an arbitrary distinction (dichotomy) established between languages and dialects. Natural languages are spoken, signed, or both; however, any language can be encoded into secondary media using auditory, visual, or tactile stimuli – for example, writing, whistl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gebe Language
Gebe, or Minyaifuin, is an Austronesian language of eastern Indonesia, spoken on the islands between Halmahera and Waigeo Waigeo is an island in Southwest Papua province of eastern Indonesia. The island is also known as Amberi, or Waigiu. It is the largest of the four main islands in the Raja Ampat Islands Raja Ampat, or the ''Four Kings'', is an archipelago loc .... References Further reading * South Halmahera–West New Guinea languages Languages of western New Guinea Halmahera {{indonesia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sawai Language
The Sawai language (also Weda) is a South Halmahera language of Austronesian stock spoken in the Weda and Gane Timor districts of southern Halmahera, northern Maluku Province, Indonesia. There are approximately 12,000 speakers. Sounds Below is a description of the Kobe dialect of Sawai spoken in the villages of Lelilef Woyebulan and Kobe Peplis, as well as from Whistler (1995). Consonants Sawai has 15 consonants: Vowels Sawai has 8 vowel A vowel is a syllabic speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness and also in quantity (leng ...s: Syllable Sawai has the following syllable structure: : (C)(C)V(C) Examples: References Bibliography * Burquest, Donald A.; & Laidig, Wyn D. (Eds.). (1992). ''Phonological studies in four languages of Maluku''. The Summer Institute of Linguistics and the University of Texas at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patani Language
Patani is an Austronesian language of southern Halmahera, Indonesia Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine .... References South Halmahera–West New Guinea languages Languages of Indonesia Halmahera {{Indonesia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maba Language (Indonesia)
Maba is a South Halmahera language of southern Halmahera, Indonesia Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine .... References South Halmahera–West New Guinea languages Languages of Indonesia Halmahera {{Indonesia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gane Language
Gane is an Austronesian language of southern Halmahera, Indonesia Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ..., spoken by the Gane people. There are estimated to be roughly 5200 native speakers of the language. It is closely related to the Taba language. References South Halmahera–West New Guinea languages Languages of Indonesia Halmahera {{Indonesia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glottolog
''Glottolog'' is a bibliographic database of the world's lesser-known languages, developed and maintained first at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany (between 2015 and 2020 at the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History in Jena, Germany). Its main curators include Harald Hammarström and Martin Haspelmath. Overview Sebastian Nordhoff and Harald Hammarström created the Glottolog/Langdoc project in 2011. The creation of ''Glottolog'' was partly motivated by the lack of a comprehensive language bibliography, especially in ''Ethnologue''. Glottolog provides a catalogue of the world's languages and language families and a bibliography on the world's less-spoken languages. It differs from the similar catalogue '' Ethnologue'' in several respects: * It tries to accept only those languages that the editors have been able to confirm both exist and are distinct. Varieties that have not been confirmed, but are inherited from anothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
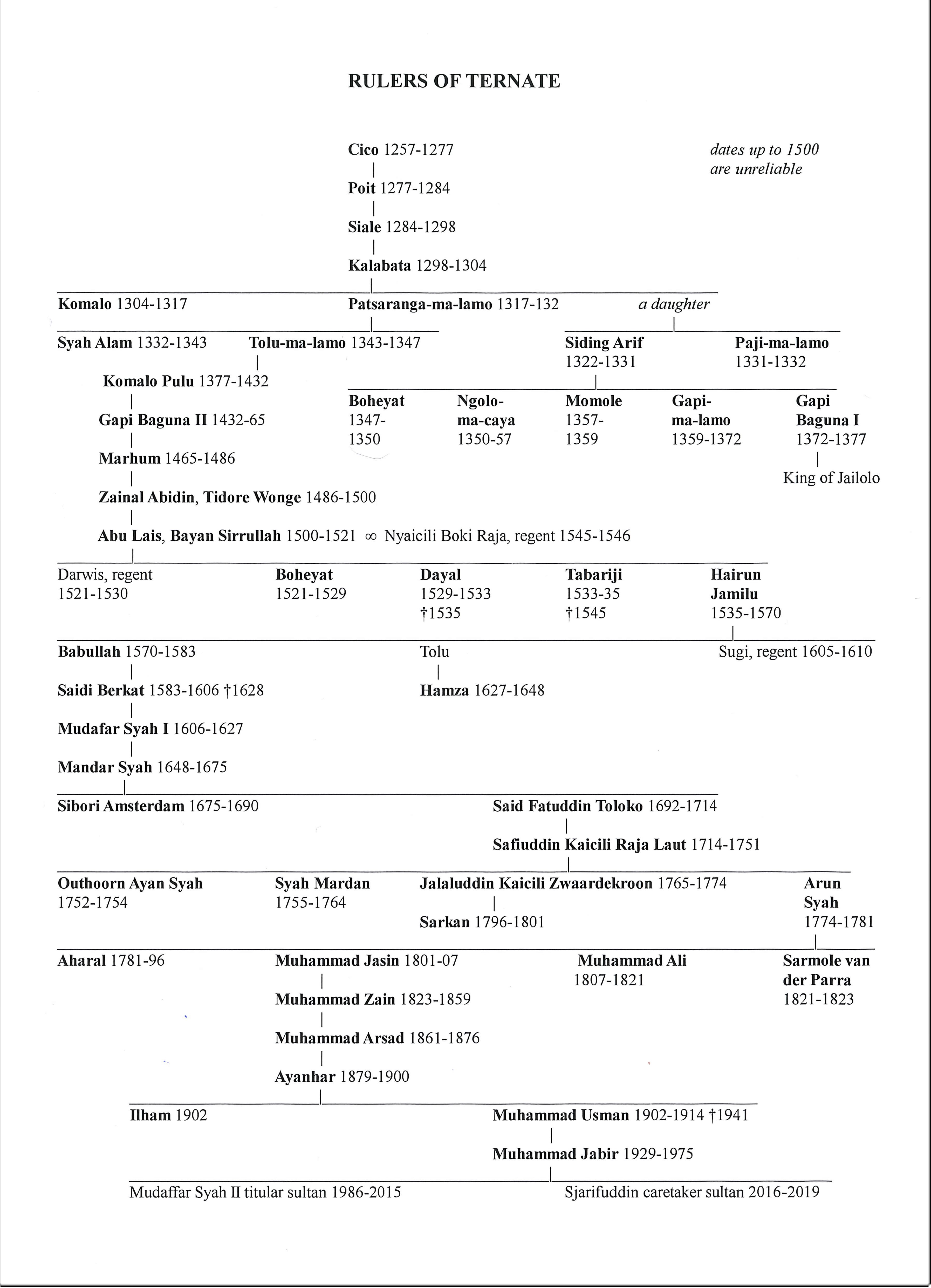
Sultanate Of Ternate
The Sultanate of Ternate (Jawi alphabet: كسلطانن ترنتاي), previously also known as the Kingdom of Gapi is one of the oldest Muslim kingdoms in Indonesia besides Tidore, Jailolo, and Bacan. The Ternate kingdom was established by Momole Cico, the first leader of Ternate, with the title Baab Mashur Malamo, traditionally in 1257. It reached its Golden Age during the reign of Sultan Baabullah (1570–1583) and encompassed most of the eastern part of Indonesia and a part of southern Philippines. Ternate was a major producer of cloves and a regional power from the 15th to 17th centuries. The dynasty founded by Baab Mashur Malamo continues to the present, as does the Sultanate itself, although it no longer holds any political power. History Pre-colonial period The sultanate was originally named the Kingdom of Gapi, but later changed the name to be based on that of its capital, Ternate. Originally there were four villages in Ternate and led by clan leaders called Mom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ternate Language
Ternate is a language of northern Maluku, eastern Indonesia. It is spoken by the , who inhabit the island of Ternate and some other areas of the archipelago, including the western coast of Halmahera, Hiri, Obi, Kayoa, and the Bacan Islands. Historically, it served as the primary language of the Sultanate of Ternate, famous for its role in the spice trade. It has established itself as a lingua franca of the North Maluku province. A North Halmahera language, it is unlike most languages of Indonesia which belong to the Austronesian language family. This language should be distinguished from Ternate Malay (North Moluccan Malay), a local Malay-based creole which it has heavily influenced. Ternate serves as the first language of ethnic Ternateans, mainly in the rural areas, while Ternate Malay is nowadays used as a means of interethnic and trade communication, particularly in the urban part of the island. More recently, there has been a language shift from Ternate towards Malay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Halmahera Languages
The North Halmahera languages are a family of languages spoken in the northern and eastern parts of the island of Halmahera and some neighboring islands in Indonesia. The southwestern part of the island is occupied by the unrelated South Halmahera languages, which are a subgroup of Austronesian. They may be most closely related to the languages of the Bird's Head region of West Papua, but this is not well-established. The languages were possibly brought to the region as a result of migration from New Guinea, likely predating the arrival of Austronesian languages. The best known North Halmaheran language is Ternate (50,000 native speakers), which is a regional lingua franca and which, along with Tidore, were the languages of the rival medieval Ternate and Tidore sultanates, famous for their role in the spice trade. Genetic and areal relations The North Halmahera languages are classified by some to be part of a larger West Papuan family, along with the languages of the Bird's H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |