|
Buenos Aires City Legislature Palace
The Buenos Aires Legislature Palace ( es, Palacio de la Legislatura de la Ciudad de Buenos Aires) houses the Legislature of the City of Buenos Aires, Argentina. It is an architectural landmark in the city's Montserrat district, situated in a triangular block bounded by the streets Hipólito Yrigoyen Street, Presidente Julio A. Roca Avenue and Perú Street. Built of grey granite, it has a Neoclassical design. The building is open to the public on week-days only. The building contains the Esteban Echeverría Library, ''Salón Rosado'' (also known as the " Eva Perón Hall"), and a carillon which, when it was installed in 1930, was the largest in South America. History A lot southwest of the Plaza de Mayo was set aside for the building's construction. The building's design was awarded through a competition to local architect Héctor Ayerza. Approved and budgeted by the council in 1926, Ayerza's eclectic design drew heavily from French Neoclassical architecture. The foundation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beaux-Arts Architecture
Beaux-Arts architecture ( , ) was the academic architectural style taught at the École des Beaux-Arts in Paris, particularly from the 1830s to the end of the 19th century. It drew upon the principles of French neoclassicism, but also incorporated Renaissance and Baroque elements, and used modern materials, such as iron and glass. It was an important style in France until the end of the 19th century. History The Beaux-Arts style evolved from the French classicism of the Style Louis XIV, and then French neoclassicism beginning with Style Louis XV and Style Louis XVI. French architectural styles before the French Revolution were governed by Académie royale d'architecture (1671–1793), then, following the French Revolution, by the Architecture section of the Académie des Beaux-Arts. The Academy held the competition for the Grand Prix de Rome in architecture, which offered prize winners a chance to study the classical architecture of antiquity in Rome. The formal neoclassicism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clock Tower
Clock towers are a specific type of structure which house a turret clock and have one or more clock faces on the upper exterior walls. Many clock towers are freestanding structures but they can also adjoin or be located on top of another building. Some other buildings also have clock faces on their exterior but these structures serve other main functions. Clock towers are a common sight in many parts of the world with some being iconic buildings. One example is the Elizabeth Tower in London (usually called "Big Ben", although strictly this name belongs only to the bell inside the tower). Definition There are many structures which may have clocks or clock faces attached to them and some structures have had clocks added to an existing structure. According to the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat a structure is defined as a building if at least fifty percent of its height is made up of floor plates containing habitable floor area. Structures that do not meet this crite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alan Parker
Sir Alan William Parker (14 February 1944 – 31 July 2020) was an English filmmaker. His early career, beginning in his late teens, was spent as a copywriter and director of television advertisements. After about ten years of filming adverts, many of which won awards for creativity, he began screenwriting and directing films. Parker was known for using a wide range of filmmaking styles and working in differing genres. He directed musicals, including ''Bugsy Malone'' (1976), '' Fame'' (1980), ''Pink Floyd – The Wall'' (1982), '' The Commitments'' (1991) and ''Evita'' (1996); true-story dramas, including '' Midnight Express'' (1978), '' Mississippi Burning'' (1988), '' Come See the Paradise'' (1990) and ''Angela's Ashes'' (1999); family dramas, including ''Shoot the Moon'' (1982), and horrors and thrillers including ''Angel Heart'' (1987) and ''The Life of David Gale'' (2003). His films won nineteen BAFTA awards, ten Golden Globes and six Academy Awards. His film '' Birdy'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
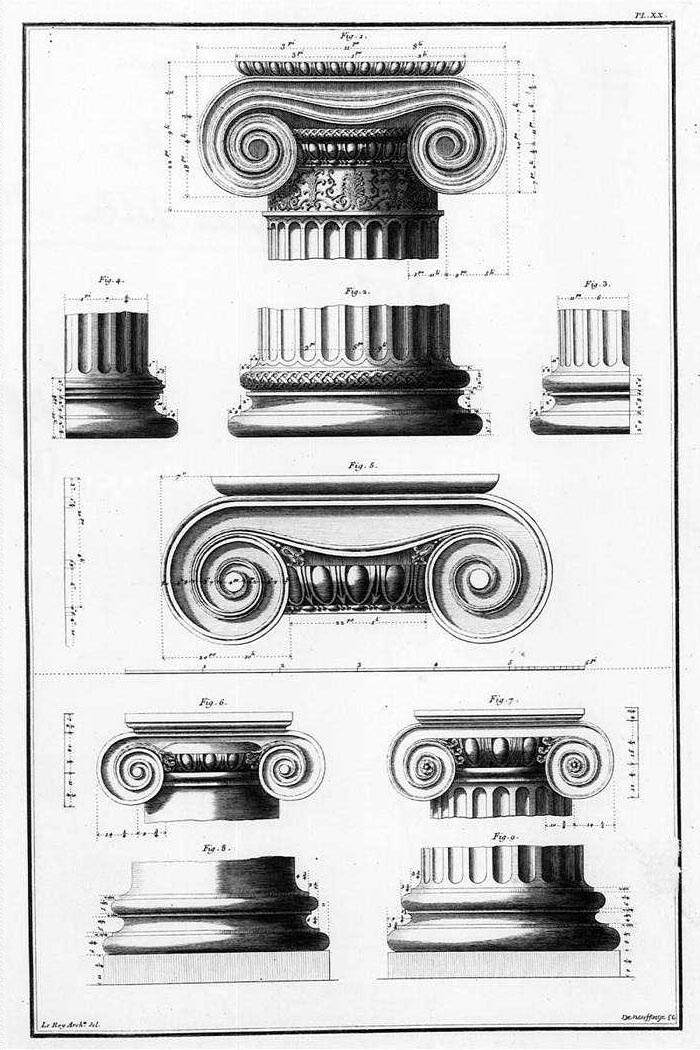
Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. The Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital, which have been the subject of much theoretical and practical discourse, based on a brief and obscure passage i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palace Of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 1995 has been managed, under the direction of the Ministry of Culture (France), French Ministry of Culture, by the Public Establishment of the Palace, Museum and National Estate of Versailles. Some 15,000,000 people visit the palace, park, or gardens of Versailles every year, making it one of the most popular tourist attractions in the world. Louis XIII built a simple hunting lodge on the site of the Palace of Versailles in 1623 and replaced it with a small château in 1631–34. Louis XIV expanded the château into a palace in several phases from 1661 to 1715. It was a favorite residence for both kings, and in 1682, Louis XIV moved the seat of his court and government to Versailles, making the palace the ''de facto'' capital of France. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galerie Des Glaces
The Hall of Mirrors (french: Grande Galerie, Galerie des Glaces, Galerie de Louis XIV) is a grand Baroque style gallery and one of the most emblematic rooms in the royal Palace of Versailles near Paris, France. The grandiose ensemble of the hall and its adjoining salons was intended to illustrate the power of the absolutist monarch Louis XIV. Located on the first floor ('' piano nobile'') of the palace's central body, it faces west towards the Palace Gardens. The Hall of Mirrors has been the scene of events of great historic significance, including the Proclamation of the German Empire and the signing of the Treaty of Versailles. Cultural and historical background Construction In 1623 King Louis XIII ordered the construction of a modest two-story hunting lodge at Versailles, which he soon enlarged to a château from 1631 to 1634. His son Louis XIV declared the site his future permanent residence in 1661 and ordered the transformation into an extensive residence in sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microfilm
Microforms are scaled-down reproductions of documents, typically either photographic film, films or paper, made for the purposes of transmission, storage, reading, and printing. Microform images are commonly reduced to about 4% or of the original document size. For special purposes, greater optical reductions may be used. Three formats are common: microfilm (reels), microfiche (flat sheets), and aperture cards. Microcards, also known as "micro-opaques", a format no longer produced, were similar to microfiche, but printed on cardboard rather than photographic film. History Using the daguerreotype process, John Benjamin Dancer was one of the first to produce microphotographs, in 1839. He achieved a reduction ratio of 160:1. Dancer refined his reduction procedures with Frederick Scott Archer's wet collodion process, developed in 1850–51, but he dismissed his decades-long work on microphotographs as a personal hobby and did not document his procedures. The idea that microphotogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José Hernández (writer)
José Hernández (born José Rafael Hernández y Pueyrredón; November 10, 1834 – October 21, 1886) was an Argentine journalist, poet, and politician best known as the author of the epic poem ''Martín Fierro''. Biography Hernández, whose ancestry was Spanish, was born on a farm near San Martín (Buenos Aires Province). His father was a majordomo or foreman of a series of cattle ranches. His career was to be an alternation between stints on the ''Federal'' side in the civil wars of Argentina and Uruguay and life as a newspaperman, a short stint as an employee of a commercial firm, and a period as stenographer to the legislature of the Confederation. Hernández founded the newspaper ''El Río de la Plata'', which advocated local autonomy, abolition of the conscripted "frontier contingents", and election of justices of the peace, military commanders, and school boards. He opposed immigration, because he believed it undermined the pastoral foundation of the region's wealth. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buenos Aires Cabildo
The Cabildo of Buenos Aires ( es, Cabildo de Buenos Aires) is the public building in Buenos Aires that was used as seat of the town council during the colonial era and the government house of the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata. Today the building is used as a museum. History Mayor Manuel de Frías proposed the building of the cabildo in what is now the Plaza de Mayo on March 3, 1608, since the government of the city lacked such a building. Its construction financed with taxes from the port of Buenos Aires, the building was finished in 1610 but was soon found to be too small and had to be expanded. In 1682, due to lack of maintenance, the building was almost in ruins, and the construction was planned of a new cabildo that was two stories high and 11 arches wide. Construction of the new building did not start until 23 July 1725, was suspended in 1728, and restarted in 1731. Soon construction was, however, again suspended due to lack of funds. The tower of the new cabildo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viceroyalty Of The Río De La Plata
The Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata ( es, Virreinato del Río de la Plata or es, Virreinato de las Provincias del Río de la Plata) meaning "River of the Silver", also called "Viceroyalty of the River Plate" in some scholarly writings, in southern South America, was the last to be organized and also the shortest-lived of the Viceroyalties of the Spanish Empire in the Americas. The name ''"Provincias del Río de la Plata"'' was formally adopted in 1810 during the Cortes of Cádiz to designate the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata The Viceroyalty was established in 1776 from several former Viceroyalty of Perú dependencies that mainly extended over the Río de la Plata Basin, roughly the present-day territories of Argentina, Chile, Bolivia, Paraguay and Uruguay, extending inland from the Atlantic Coast. The colony of Spanish Guinea (present-day Equatorial Guinea) also depended administratively on the Viceroyalty of Rio de la Plata. Buenos Aires, located on the western sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visigothic Spain
The Visigothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of the Goths ( la, Regnum Gothorum), was a kingdom that occupied what is now southwestern France and the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th to the 8th centuries. One of the Germanic successor states to the Western Roman Empire, it was originally created by the settlement of the Visigoths under King Wallia in the province of Gallia Aquitania in southwest Gaul by the Roman government and then extended by conquest over all of Hispania. The Kingdom maintained independence from the Eastern Roman or Byzantine Empire, whose attempts to re-establish Roman authority in Hispania were only partially successful and short-lived. The Visigoths were romanized central Europeans who had moved west from the Danube Valley. They became foederati of Rome, and wanted to restore the Roman order against the hordes of Vandals, Alans and Suebi. The Western Roman Empire fell in 476 AD; therefore, the Visigoths believed they had the right to take the territo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)