|
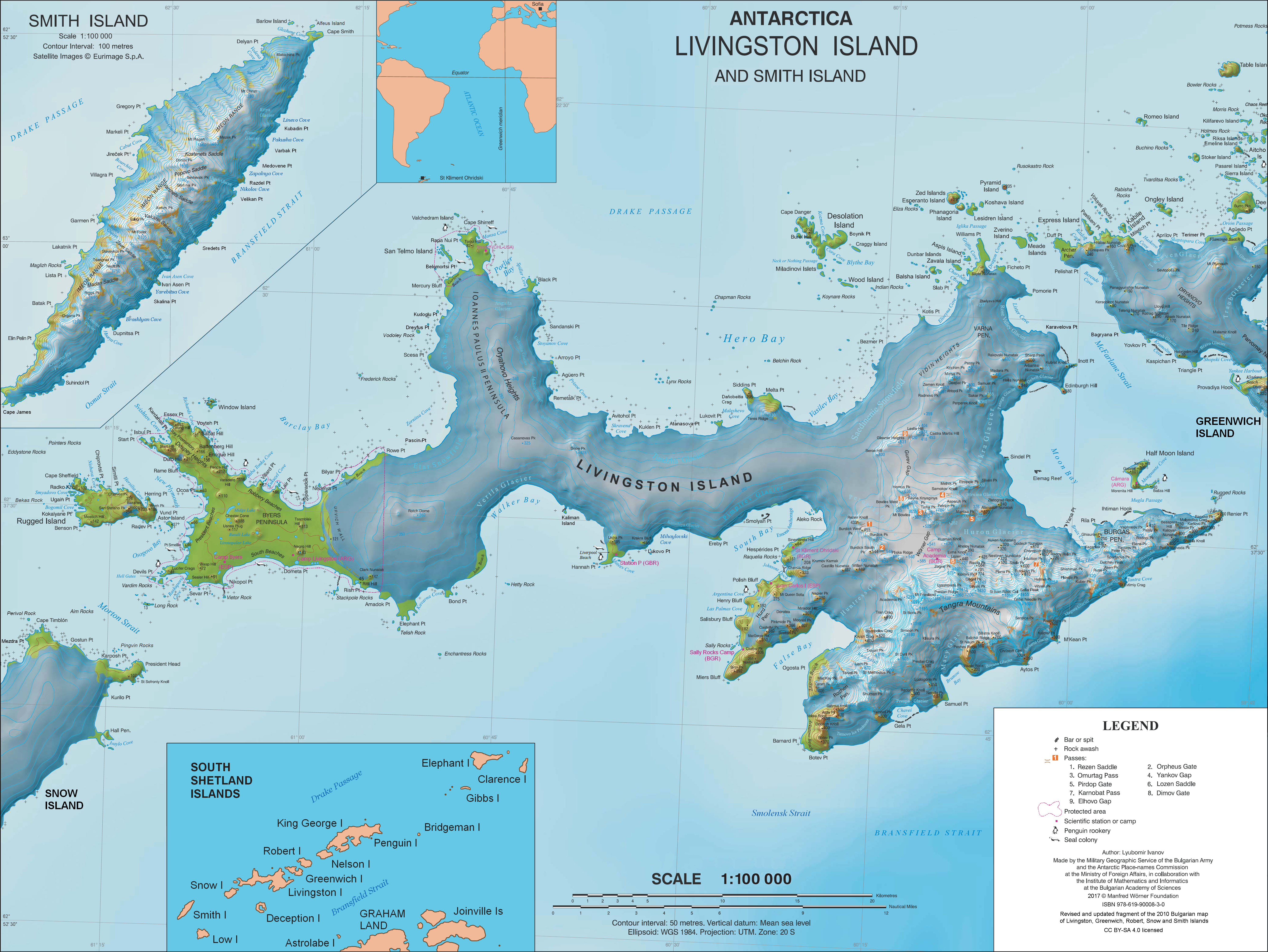
Buena Nueva Cove
Buena Nueva Cove is a small open cove, 900 m wide and indenting for 200 m the northwest coast of False Bay, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica southeast of MacGregor Peaks and east of Castro Peak on Hurd Peninsula. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers. The feature is named after the ship ''Buena Nueva'' in which the Spanish navigator Gabriel de Castilla made his voyage south of Drake Passage in 1603. Location The cove's midpoint is located at which is 3.03 km northeast of Miers Bluff and 2.9 km west-northwest of Ogosta Point, Rozhen Peninsula Rozhen Peninsula ( bg, полуостров Рожен, poluostrov Rozhen, ) extends 9 km in the southwest direction towards Barnard Point, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica, and 8.8 km wide. It is bounded by ... (British mapping in and 1968, detailed Spanish mapping in 1991, and Bulgarian mapping in 2005 and 2009). Maps Isla Livingston: Penínsul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
False Bay, Livingston Island
False Bay () is a bay long, which lies between Barnard Point and Miers Bluff on the south side of Livingston Island, in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The glaciers Hurd Ice Cap, Huntress, Ruen Icefall, Peshtera and Charity feed the bay. It was probably first entered and charted by Captain Nathaniel Palmer in November 1820, and was likely named because of the possibility in thick weather of confusion between this feature and nearby South Bay, where Johnsons Dock Johnsons Dock is a sheltered 500 m wide cove indenting for 900 m the northwest coast of Hurd Peninsula on Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. It is part of South Bay entered north of Ballester Point. Surmounted by C ... was frequented by the early sealers. Maps Chart of South Shetland including Coronation Island, &c.from the exploration of the sloop Dove in the years 1821 and 1822 by George Powell Commander of the same. Scale ca. 1:200000. London: Laurie, 1822 South Shetland I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Shetland Islands
The South Shetland Islands are a group of Antarctic islands with a total area of . They lie about north of the Antarctic Peninsula, and between southwest of the nearest point of the South Orkney Islands. By the Antarctic Treaty of 1959, the islands' sovereignty is neither recognized nor disputed by the signatories and they are free for use by any signatory for non-military purposes. The islands have been claimed by the United Kingdom since 1908 and as part of the British Antarctic Territory since 1962. They are also claimed by the governments of Chile (since 1940, as part of the Antártica Chilena province) and Argentina (since 1943, as part of Argentine Antarctica, Tierra del Fuego Province). Several countries maintain research stations on the islands. Most of them are situated on King George Island, benefitting from the airfield of the Chilean base Eduardo Frei. There are sixteen research stations in different parts of the islands, with Chilean stations being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MacGregor Peaks
MacGregor Peaks are rocky peaks rising to 350 m in the south part of Hurd Peninsula, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The peaks are named after Captain Christopher MacGregor, Master of the British sealing vessel ''Minstrel'' that visited the South Shetlands in 1820–21. Location The peaks are centred at which is 710 m southwest of Castellvi Peak, 2.83 km west-southwest of Moores Peak and 4.9 km northwest of Canetti Peak Canetti Peak ( bg, връх Канети, vrah Kaneti, ) is a 400 m peak in the Friesland Ridge, Tangra Mountains, eastern Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The peak has precipitous and ice-free western slopes and ove ... (British mapping in 1968, Spanish in 1991, and Bulgarian in 2005 and 2009). Maps Isla Livingston: Península Hurd.Mapa topográfico de escala 1:25000. Madrid: Servicio Geográfico del Ejército, 1991. (Map reproduced on p. 16 of the linked work) * L.L. Ivanov et al. Antarct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castro Peak
Castro Peak ( bg, връх Кастро, vrah Kastro, ) is a peak rising to 306 m on Hurd Peninsula, Livingston Island. Situated 750 m south-southwest of MacGregor Peaks and 1.87 km northeast of Binn Peak. Spanish early mapping in 1991. Named for Vicente Castro, mountain guide at Juan Carlos I Antarctic Base who took part in the first ascent of the peak during the 2003/04 season. Maps Isla Livingston: Península Hurd.Mapa topográfico de escala 1:25000. Madrid: Servicio Geográfico del Ejército, 1991. (Map reproduced on p. 16 of the linked work) * L.L. Ivanov et al. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich Island, South Shetland Islands. Scale 1:100000 topographic map. Sofia: Antarctic Place-names Commission of Bulgaria, 2005. * L.L. IvanovAntarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2009. Antarctic Digital Database (ADD).Scale 1:250000 topographic map of Antarcti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurd Peninsula
Hurd Peninsula lies between South Bay and False Bay on the south coast of Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The Spanish Juan Carlos I Antarctic Base and the Bulgarian St. Kliment Ohridski Base are situated on its west coast. The peninsula was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1961 for Captain Thomas Hurd, Royal Navy, the second Hydrographer to the British Admiralty, 1808–23, who instituted a regular system of nautical surveys, and under whose authority Lieutenant Edward Bransfield's 1820 survey of the Bransfield Strait area was published in November 1822. Location The midpoint of the peninsula is located at (Detailed Spanish mapping in 1991, and Bulgarian in 2005 and 2009). Maps Chart of South Shetland including Coronation Island, &c.from the exploration of the sloop Dove in the years 1821 and 1822 by George Powell Commander of the same. Scale ca. 1:200000. London: Laurie, 1822. South Shetland Islands.Scale 1:200000 topographic m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seal Hunting
Seal hunting, or sealing, is the personal or commercial hunting of seals. Seal hunting is currently practiced in ten countries: United States (above the Arctic Circle in Alaska), Canada, Namibia, Denmark (in self-governing Greenland only), Iceland, Norway, Russia, Finland and Sweden. Most of the world's seal hunting takes place in Canada and Greenland. The Canadian Department of Fisheries and Oceans (DFO) regulates the seal hunt in Canada. It sets quotas (total allowable catch – TAC), monitors the hunt, studies the seal population, works with the Canadian Sealers' Association to train sealers on new regulations, and promotes sealing through its website and spokespeople. The DFO set harvest quotas of over 90,000 seals in 2007; 275,000 in 2008; 280,000 in 2009; and 330,000 in 2010. The actual kills in recent years have been less than the quotas: 82,800 in 2007; 217,800 in 2008; 72,400 in 2009; and 67,000 in 2010. In 2007, Norway claimed that 29,000 harp seals were killed, Russ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabriel De Castilla
Gabriel de Castilla (1577 – c. 1620) was a Spanish explorer and navigator. A native of Palencia, it has been argued that he was an early explorer of Antarctica.Vázquez de Acuña, Isidoro. ''Don Gabriel de Castilla primer avistador de la Antártica'' en Revista de Marina 1993 N° 2, Valparaíso: Armada de Chile (p. 4). Biography In March 1603, Castilla was at the head of an expedition that weighed anchor from Valparaiso. Under his control were three ships: the galleon ''Jesús María'', of 600 tons and 30 cannons, ''Nuestra Señora de la Visitación'' (which had belonged to Richard Hawkins) and ''Nuestra Señora de las Mercedes''. The expedition was entrusted by the Viceroy of Peru, Luis de Velasco, marqués de Salinas, to suppress the incursions of Dutch privateers in the seas to the south of Chile. Historians conjecture that they penetrated to a latitude of (64° S) in the Southern Ocean, south of Drake Passage. If correct, this would be the farthest south that anyone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drake Passage
The Drake Passage (referred to as Mar de Hoces Hoces Sea"in Spanish-speaking countries) is the body of water between South America's Cape Horn, Chile and the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica. It connects the southwestern part of the Atlantic Ocean (Scotia Sea) with the southeastern part of the Pacific Ocean and extends into the Southern Ocean. The Drake Passage is considered one of the most treacherous voyages for ships to make. Currents at its latitude meet no resistance from any landmass, and waves top , hence its reputation as "the most powerful convergence of seas". As the Drake Passage is the narrowest passage around Antarctica, its existence and shape strongly influence the circulation of water around Antarctica and the global oceanic circulation, as well as the global climate. The bathymetry of the Drake Passage plays an important role in the global mixing of oceanic water. It is one of the most treacherous bodies of water on earth. History Sailing south from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miers Bluff
Miers Bluff is the point forming the southwest extremity of Hurd Peninsula, the southeast side of the entrance to South Bay (Livingston Island), South Bay and the northwest side of the entrance to False Bay (Livingston Island), False Bay, on Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The name "Elephant Point", given by Robert Fildes in 1820–22 to Elephant Point, another feature, has been for a number of years applied in error to this bluff. It is now approved as originally intended and a new name has been substituted for the feature here described. The point is named after John Miers (botanist), John Miers, British engineer and botanist who travelled to Chile in 1818 and was responsible for the publication in 1820 of the first chart of the South Shetland Islands, based on the work of William Smith (mariner), William Smith. Location The point is located at () which is northwest of Barnard Point, southeast of Hannah Point and southwest of Napier Peak (British ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |