|
Buddhist Publication Society
The Buddhist Publication Society (BPS) is a publishing house with charitable status whose objective is to disseminate the teaching of Gautama Buddha. It was founded in Kandy, Sri Lanka in 1958 by two Sri Lankan lay Buddhists, A.S. Karunaratna and Richard Abeyasekera, and a European-born Buddhist monk, Nyanaponika Thera. Originally conceived as a limited effort to publish small, affordable books on fundamental Buddhist topics, the Society expanded in scope in response to the reception of their early publishing efforts. The Buddhist Publication society's publications reflect the perspective of the Theravada denomination of Buddhism, drawing heavily from the P─üli Canon for source material. The BPS supplies Buddhist literature to over 3,000 subscriber members throughout 80 countries. Its titles have been translated into many languages, including German, French, Spanish, Portuguese, Czech, Hindi, and Chinese. Publications The Buddhist Publication Society publishes a variety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charitable Organization
A charitable organization or charity is an organization whose primary objectives are philanthropy and social well-being (e.g. educational, religious or other activities serving the public interest or common good). The legal definition of a charitable organization (and of charity) varies between countries and in some instances regions of the country. The regulation, the tax treatment, and the way in which charity law affects charitable organizations also vary. Charitable organizations may not use any of their funds to profit individual persons or entities. (However, some charitable organizations have come under scrutiny for spending a disproportionate amount of their income to pay the salaries of their leadership). Financial figures (e.g. tax refund, revenue from fundraising, revenue from sale of goods and services or revenue from investment) are indicators to assess the financial sustainability of a charity, especially to charity evaluators. This information can impact a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
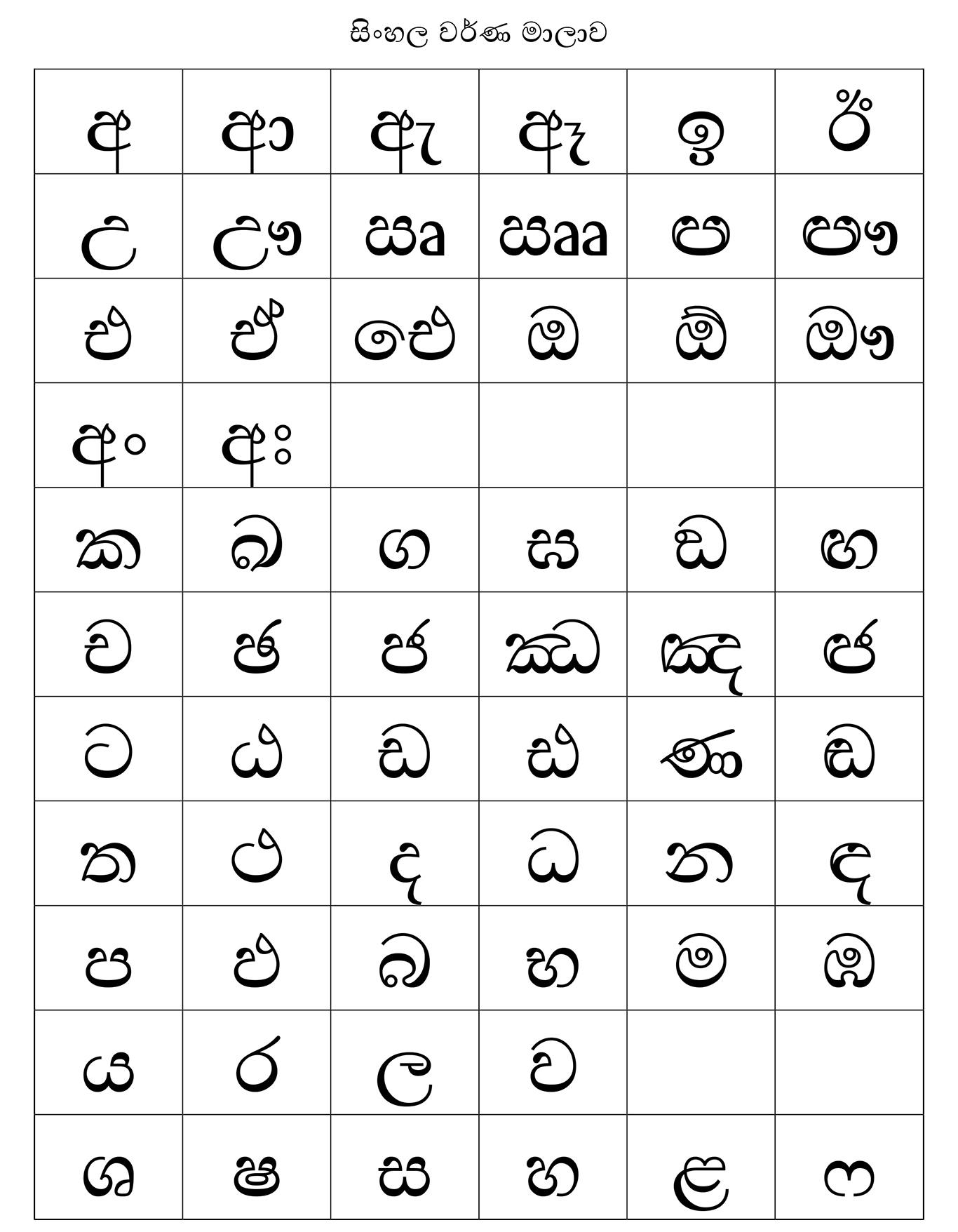
Sinhalese Language
Sinhala ( ; , ''siṁhala'', ), sometimes called Sinhalese (), is an Indo-Aryan language primarily spoken by the Sinhalese people of Sri Lanka, who make up the largest ethnic group on the island, numbering about 16 million. Sinhala is also spoken as the first language by other ethnic groups in Sri Lanka, totalling about 2 million people as of 2001. It is written using the Sinhala script, which is a Brahmic script closely related to the Grantha script of South India. Sinhala is one of the official and national languages of Sri Lanka. Along with Pali, it played a major role in the development of Theravada, Theravada Buddhist literature. The early form of the Sinhala language, is attested as early as the 3rd century BCE. The language of these inscriptions with long vowels and aspirated consonants is a Prakrit similar to Magadhi, a regional associate of the Middle Indian Prakrits that has been used during the time of the Buddha. The closest relatives are the Vedda language (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammalawa Saddhatissa
Hammalawa Saddhatissa Maha Thera (1914ŌĆō1990) was an ordained Buddhist monk, missionary and author from Sri Lanka, educated in Varanasi, London, and Edinburgh. He was a contemporary of Walpola Rahula, also of Sri Lanka. Early life Saddhatissa was born in 1914 Hammalawa, a hamlet in the northwest of Sri Lanka. He ordained as a s─ümaß╣ćera (novice monk) at the age of twelve in 1926. He received his early education at the Sastrodaya Pirivena at Sandalankawa and continued his higher studies at Vidyodaya Pirivena, Colombo, where he passed the final examinations with honours. Missionary work in India The Maha Bodhi Society invited Saddhatissa to become a missionary (''dharmaduta'') monk in India like his contemporary Henepola Gunaratana. In order to teach to Indians he learnt Indian languages such as Hindi, Urdu and Punjabi. While in India, he came to know B. R. Ambedkar, who reportedly obtained advice from him on how to draft the Indian constitution along the lines of the vinaya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ajahn Chah
Chah Subhaddo ( th, ÓĖŖÓĖ▓ ÓĖ¬ÓĖĖÓĖĀÓĖ▒ÓĖŚÓ╣éÓĖŚ, known in English as Ajahn Chah, occasionally with honorific titles '' Luang Por'' and ''Phra'') also known by his honorific name "Phra Bodhi├▒─üß╣ćathera" ( th, ÓĖ×ÓĖŻÓĖ░Ó╣éÓĖ×ÓĖśÓĖ┤ÓĖŹÓĖ▓ÓĖōÓ╣ĆÓĖ¢ÓĖŻ, Chao Khun Bodhinyana Thera; 17 June 1918 – 16 January 1992) was a Thai Buddhist monk. He was an influential teacher of the ''Buddhadhamma'' and a founder of two major monasteries in the Thai Forest Tradition. Respected and loved in his own country as a man of great wisdom, he was also instrumental in establishing Theravada Buddhism in the West. Beginning in 1979 with the founding of ''Cittaviveka'' (commonly known as Chithurst Buddhist Monastery) in the United Kingdom, the Forest Tradition of Ajahn Chah has spread throughout Europe, the United States and the British Commonwealth. The dhamma talks of Ajahn Chah have been recorded, transcribed and translated into several languages. More than one million people, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sayadaw U Pandita
Sayadaw U Paß╣ćßĖŹita ( my, ßĆåßĆøßĆ¼ßĆÉßĆ▒ßĆ¼ßĆ║ ßĆ”ßĆĖßĆĢßĆÅßĆ╣ßĆŹßĆŁßĆÉ, ; also ''Ov─üd─ücariya Say─üdo ┼¬ Paß╣ćßĖŹit─übhivaß╣üsa''; 28 July 1921 ŌĆō 16 April 2016) was one of the foremost masters of Vipassan─ü. He trained in the Theravada Buddhist tradition of Myanmar. A successor to the late Mah─üsi Say─üdaw, he has taught many of the Western teachers and students of the Mah─üsi style of Vipassan─ü meditation. He was the abbot o Meditation Centerin Yangon, Myanmar. Early life and education U Paß╣ćßĖŹita was born in 1921 in Insein in greater Rangoon (now Yangon) during British colonial rule. He became a novice at age twelve, and ordained at age twenty. After decades of study, he passed the rigorous series of government examinations in the Therav─üda Buddhist texts, gaining the Dhamm─ücariya (Dhamma teacher) degree in 1952. U Paß╣ćßĖŹita began practicing Vipassana under the guidance of Mah─üsi Say─üdaw beginning in 1950. Career In 1955, he left his position as a teache ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahasi Sayadaw
Mah─üs─½ Say─üdaw U Sobhana ( my, ßĆÖßƤßĆ¼ßĆģßĆŖßĆ║ßĆåßĆøßĆ¼ßĆÉßĆ▒ßĆ¼ßĆ║ ßĆ”ßĆĖßĆ×ßĆ▒ßĆ¼ßĆśßĆö, ; 29 July 1904 ŌĆō 14 August 1982) was a Burmese Theravada Buddhist monk and meditation master who had a significant impact on the teaching of vipassan─ü (insight) meditation in the West and throughout Asia. In his style of practice, derived from the so-called New Burmese Method of U N─ürada, the meditator lives according to Buddhist morality as a prerequisite for meditation practice. Meditation itself entails the practice of "bare insight," using ''satipaß╣Łß╣Łh─üna'', the four foundations of mindfulness, to anchor the attention on the sensations of the rising and falling of the abdomen during breathing, observing carefully any other sensations or thoughts. This is coupled to reflection on the Buddhist teachings on causality, thereby gaining insight into ''anicca'', '' dukkha'', and ''anatt─ü'' and attaining stream entry. Mah─üs─½ Say─üdaw was a questioner and final editor at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ledi Sayadaw
Ledi Sayadaw U ├æaß╣ćadhaja ( my, ßĆ£ßĆÜßĆ║ßĆÉßĆ«ßĆåßĆøßĆ¼ßĆÉßĆ▒ßĆ¼ßĆ║ ßĆ”ßĆĖßĆēßĆ¼ßĆÅßĆōßĆć, ; 1 December 1846 ŌĆō 27 June 1923) was an influential Theravada Buddhist monk. He was recognized from a young age as being developed in both the theory ( Abhidhamma) and practice of Buddhism and so was revered as being scholarly. He wrote many books on Dhamma in Burmese and these were accessible even to a serious lay person, hence he was responsible for spreading Dhamma to all levels of society and reviving the traditional practice of Vipassan─ü meditation, making it more available for renunciates and lay people alike. Biography Sayadaw began his studies at age 20 in Mandalay at Thanjaun. While there he was considered to be a bright and ambitious young monk but his work was scholarly; there is no evidence that Sayadaw engaged in a serious meditation practice during his years in Mandalay. Leaving Mandalay after a great fire in 1883 caused the loss of his home and his written work to that ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Webu Sayadaw
Webu Sayadaw ( my, ßĆØßĆ▒ßĆśßĆ░ ßĆåßĆøßĆ¼ßĆÉßĆ▒ßĆ¼ßĆ║, ; 17 February 1896 – 26 June 1977) was a Theravada Buddhist monk, and vipassan─ü master, best known for giving all importance to diligent practice, rather than scholastic achievement. Early life Ven. Webu Sayadaw was born to Daw Kyin Nu and U Lu Pe in 1896 in British Burma near Khin U township in modern-day Sagaing Division. He underwent the usual monk's training in the P─üli scriptures from the age of nine, when he became a novice, until he was twenty-seven. His monastic name was . Monk and teacher In 1923 (seven years after his ordination), he left the monastery and spent four years in solitude. He practiced (and later taught) the technique of ─Ćn─üp─ünasati (awareness of the in-breath and out-breath). He said that by working with this practice to a very deep level of concentration, one is able to develop Vipassan─ü (insight) into the essential characteristics of all experience: anicca (impermanence), anatta (e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narada Mahathera
Narada Mahathera ( si, ÓČ▒ÓĘÅÓČ╗ÓČ» ÓČĖÓĘäÓĘÅ ÓĘāÓĘŖÓČ«ÓĘĆÓĘÆÓČ╗ÓČ║ÓČ▒ÓĘŖ ÓĘĆÓĘäÓČ▒ÓĘŖÓĘāÓĘÜ), born Sumanapala Perera (14 July 1898 – 2 October 1983) was a Theravada Buddhist monk, scholar, translator, educator and Buddhist missionary who was for many years the Superior of Vajiraramaya in Colombo, Sri Lanka. He was a popular figure in his native country, Sri Lanka, and beyond. Biography He was born in Kotahena, Colombo to a middle-class family, educated at St. Benedict's College and Ceylon University College, and ordained at the age of eighteen. In 1929 he represented Sri Lanka at the opening ceremony for the new Mulagandhakuti vihara at Sarnath, India, and in 1934 he visited Indonesia, the first Theravadan monk to do so in more than 450 years. During this opportunity he planted and blessed a bodhi tree in southeastern side of Borobudur on 10 March 1934, and some Upasakas were ordained as monks. From that point on he travelled to many countries to conduct missionary work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katukurunde Nyanananda Thera
Most Ven. Kaß╣Łukurunde ├æ─üß╣ćananda Maha Thera (10 July 1940 ŌĆō 22 February 2018) (sometimes spelled Nyanananda or Nanananda in English, sometimes called Gnanananda in Sinhala, Sinhalese: ÓČģÓČŁÓĘÆ ÓČ┤ÓĘ¢ÓČóÓĘŖŌĆŹÓČ║ ÓČÜÓȦÓĘöÓČÜÓĘöÓČ╗ÓĘöÓČ▒ÓĘŖÓČ»ÓĘÜ ÓČżÓĘÅÓČ½ÓĘÅÓČ▒ÓČ▒ÓĘŖÓČ» ÓČĖÓĘäÓĘÅ ÓČ«ÓĘÜÓČ╗) was a Sri Lankan inhalaBhikkhu (Buddhist Monk) and Buddhist scholar. He is best known for the research monograph ''Concept and Reality in Early Buddhist Thought'' and the exploratory study ''The Magic of the Mind''. Ven. ├æ─üß╣ćananda was the abbot of Pothgulgala Aranya, a small forest monastery in Devalegama, Sri Lanka. Early life Ven. ├æ─üß╣ćananda was born in 1940 to a Sinhala Buddhist family in Galle District in Sri Lanka. He received his school education from Mahinda College, Galle. In 1962 he graduated from the University of Peradeniya specializing in Pali Studies, and served as an assistant lecturer in Pali at the same university for a brief period of time. He renounc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhikkhu Ñanamoli
A ''bhikkhu'' (Pali: ÓżŁÓż┐ÓżĢÓźŹÓż¢Óźü, Sanskrit: ÓżŁÓż┐ÓżĢÓźŹÓżĘÓźü, ''bhikß╣Żu'') is an ordained male in Buddhist monasticism. Male and female monastics ("nun", ''bhikkhun─½'', Sanskrit ''bhikß╣Żuß╣ć─½'') are members of the Sangha (Buddhist community). The lives of all Buddhist monastics are governed by a set of rules called the pr─ütimokß╣Ża or p─ütimokkha. Their lifestyles are shaped to support their spiritual practice: to live a simple and meditative life and attain nirvana. A person under the age of 20 cannot be ordained as a bhikkhu or bhikkhuni but can be ordained as a ┼ør─ümaß╣ćera or ┼ør─ümaß╣ć─ōr─½. Definition ''Bhikkhu'' literally means "beggar" or "one who lives by alms". The historical Buddha, Prince Siddhartha, having abandoned a life of pleasure and status, lived as an alms mendicant as part of his ┼øramaß╣ća lifestyle. Those of his more serious students who renounced their lives as householders and came to study full-time under his supervision also adopted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soma Thera
Kotahene Soma Maha Thera (December 23, 1898 - February 23, 1960), born as Victor Emmanuel Perera Pulle in Kotahena, Colombo,The Path Of Freedom (Vimuttimagga) of Arahant Upatissa' Translated from the Chinese by Rev. N. R. M. Ehara, Soma Thera, Kheminda Thera. Buddhist Publication Society. Kandy, Ceylon, page IX was a Theravada Buddhist monk, translator and missionary. Childhood Soma Thera was raised as a Sinhalese Catholic and received his education at the Catholic St. Benedict's College in Kotahena, but became a Buddhist in his teenage years after reading the Dhammapada. Ordination and Travels In 1934, he went to Japan with his friend G.S. Prelis (later ordained as Kheminda Thera) and translated the Chinese version of the Vimuttimagga into English, which was published as ''The Path of Freedom''. In 1936, both Victor Perera and Prelis went to Burma and received the higher ordination as Theravada Buddhist monks A ''bhikkhu'' ( Pali: ÓżŁÓż┐ÓżĢÓźŹÓż¢Óźü, Sanskrit: ÓżŁÓż┐Óż ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |