|
Brønnøy Dialect
The Brønnøy dialect ( no, Brønnøymål or ''Sørvest-helgelandsk'') is a dialect of Norwegian used in Brønnøy Brønnøy is a municipality in Nordland county, Norway. It is part of the Helgeland region. The administrative centre and commercial centre of the municipality is the town of Brønnøysund. A secondary centre is the village of Hommelstø. Ot .... Phonology Tonemes Unlike most Norwegian dialects, the Brønnøy dialect lacks tonal accents. References Bibliography * Culture in Nordland Norwegian dialects City colloquials {{norway-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brønnøy
Brønnøy is a municipality in Nordland county, Norway. It is part of the Helgeland region. The administrative centre and commercial centre of the municipality is the town of Brønnøysund. A secondary centre is the village of Hommelstø. Other villages include Tosbotn, Lande, Trælnes, and Indreskomo. The Brønnøysund Register Centre is an important employer in Brønnøy. Also, one of the largest limestone mines in Northern Europe is located in the municipality. Brønnøysund Airport, Brønnøy is located near the town of Brønnøysund. The municipality is the 107th largest by area out of the 356 municipalities in Norway. Brønnøy is the 132nd most populous municipality in Norway with a population of 7,777. The municipality's population density is and its population has increased by 0% over the previous 10-year period. General information The municipality of Brønnøy was established on 1 January 1838 (see formannskapsdistrikt law). On 1 October 1875 the eastern d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, English, is also the world's most widely spoken language with an estimated 2 billion speakers. All Germanic languages are derived from Proto-Germanic, spoken in Iron Age Scandinavia. The West Germanic languages include the three most widely spoken Germanic languages: English with around 360–400 million native speakers; German language, German, with over 100 million native speakers; and Dutch language, Dutch, with 24 million native speakers. Other West Germanic languages include Afrikaans, an offshoot of Dutch, with over 7.1 million native speakers; Low German, considered a separate collection of Standard language, unstandardized dialects, with roughly 4.35–7.15 million native speakers and probably 6.7–10 million people who can understand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Germanic
Northwest Germanic is a proposed grouping of the Germanic languages, representing the current consensus among Germanic historical linguists. It does not challenge the late 19th-century tri-partite division of the Germanic dialects into North Germanic, West Germanic and East Germanic, but proposes additionally that North and West Germanic (i.e. all surviving Germanic languages today) remained as a subgroup after the southward migration of the East Germanic tribes, only splitting into North and West Germanic later. Whether this subgroup constituted a unified proto-language, or simply represents a group of dialects that remained in contact and close geographical proximity, is a matter of debate, but the formulation of Ringe and Taylor probably enjoys widespread support: There is some evidence that North and West Germanic developed as a single language, Proto-Northwest Germanic, after East Germanic had begun to diverge. However, changes unproblematically datable to the PNWGmc period a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glottolog
''Glottolog'' is a bibliographic database of the world's lesser-known languages, developed and maintained first at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany (between 2015 and 2020 at the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History in Jena, Germany). Its main curators include Harald Hammarström and Martin Haspelmath. Overview Sebastian Nordhoff and Harald Hammarström created the Glottolog/Langdoc project in 2011. The creation of ''Glottolog'' was partly motivated by the lack of a comprehensive language bibliography, especially in ''Ethnologue''. Glottolog provides a catalogue of the world's languages and language families and a bibliography on the world's less-spoken languages. It differs from the similar catalogue '' Ethnologue'' in several respects: * It tries to accept only those languages that the editors have been able to confirm both exist and are distinct. Varieties that have not been confirmed, but are inherited from anothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Planck Institute For Evolutionary Anthropology
The Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology (german: Max-Planck-Institut für evolutionäre Anthropologie, shortened to MPI EVA) is a research institute based in Leipzig, Germany, that was founded in 1997. It is part of the Max Planck Society network. Well-known scientists currently based at the institute include founding director Svante Pääbo and Johannes Krause (genetics), Christophe Boesch (primatology), Jean-Jacques Hublin (human evolution), Richard McElreath ( evolutionary ecology), and Russell Gray (linguistic and cultural evolution). Departments The institute comprises six departments, several Research Groups, and The Leipzig School of Human Origins. Currently, approximately 375 people are employed at the institute. The former department of Linguistics, which existed from 1998 to 2015, was closed in May 2015, upon the retirement of its director, Bernard Comrie. The former department of Developmental and Comparative Psychology operated from 1998 to 2018 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Germanic Languages
The North Germanic languages make up one of the three branches of the Germanic languages—a sub-family of the Indo-European languages—along with the West Germanic languages and the extinct East Germanic languages. The language group is also referred to as the Nordic languages, a direct translation of the most common term used among Danish, Faroese, Icelandic,Elfdalian,Norwegian, Gutnish, and Swedish scholars and people. The term ''North Germanic languages'' is used in comparative linguistics, whereas the term Scandinavian languages appears in studies of the modern standard languages and the dialect continuum of Scandinavia. Danish, Norwegian and Swedish are close enough to form a strong mutual intelligibility where cross-border communication in native languages is very common. Approximately 20 million people in the Nordic countries speak a Scandinavian language as their native language,Holmberg, Anders and Christer Platzack (2005). "The Scandinavian languages". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Scandinavian
The North Germanic languages make up one of the three branches of the Germanic languages—a sub-family of the Indo-European languages—along with the West Germanic languages and the extinct East Germanic languages. The language group is also referred to as the Nordic languages, a direct translation of the most common term used among Danish, Faroese, Icelandic,Elfdalian,Norwegian, Gutnish, and Swedish scholars and people. The term ''North Germanic languages'' is used in comparative linguistics, whereas the term Scandinavian languages appears in studies of the modern standard languages and the dialect continuum of Scandinavia. Danish, Norwegian and Swedish are close enough to form a strong mutual intelligibility where cross-border communication in native languages is very common. Approximately 20 million people in the Nordic countries speak a Scandinavian language as their native language,Holmberg, Anders and Christer Platzack (2005). "The Scandinavian languages". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Language
Norwegian ( no, norsk, links=no ) is a North Germanic language spoken mainly in Norway, where it is an official language. Along with Swedish and Danish, Norwegian forms a dialect continuum of more or less mutually intelligible local and regional varieties; some Norwegian and Swedish dialects, in particular, are very close. These Scandinavian languages, together with Faroese and Icelandic as well as some extinct languages, constitute the North Germanic languages. Faroese and Icelandic are not mutually intelligible with Norwegian in their spoken form because continental Scandinavian has diverged from them. While the two Germanic languages with the greatest numbers of speakers, English and German, have close similarities with Norwegian, neither is mutually intelligible with it. Norwegian is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples living in Scandinavia during the Viking Age. Today there are two official forms of ''written'' Norwegian, (literally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture In Nordland
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tylor, Edward. (1871). Primitive Culture. Vol 1. New York: J.P. Putnam's Son Culture is often originated from or attributed to a specific region or location. Humans acquire culture through the learning processes of enculturation and socialization, which is shown by the diversity of cultures across societies. A cultural norm codifies acceptable conduct in society; it serves as a guideline for behavior, dress, language, and demeanor in a situation, which serves as a template for expectations in a social group. Accepting only a monoculture in a social group can bear risks, just as a single species can wither in the face of environmental change, for lack of functional responses to the change. Thus in military culture, valor is counted a typical be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
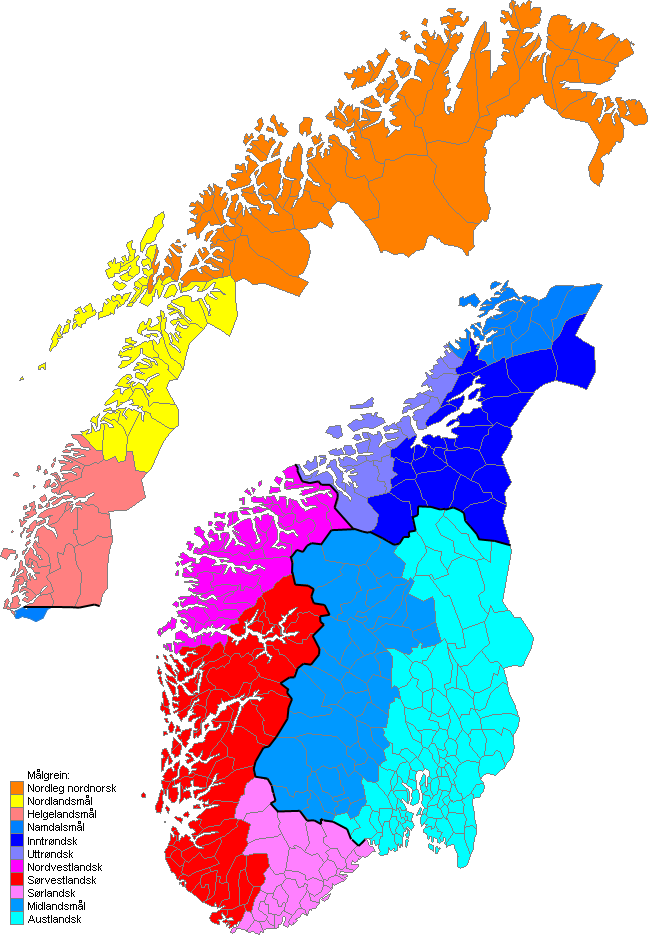
Norwegian Dialects
Norwegian dialects (''dialekter'') are commonly divided into four main groups, 'Northern Norwegian' (), 'Central Norwegian' (''trøndersk''), 'Western Norwegian' (''vestlandsk''), and 'Eastern Norwegian' (). Sometimes 'Midland Norwegian' () and/or 'South Norwegian' () are considered fifth or sixth groups. The dialects are generally Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible, but differ significantly with regard to Accent (dialect), accent, grammar, syntax, and vocabulary. If not accustomed to a particular dialect, even a native Norwegian speaker may have difficulty understanding it. Dialects can be as local as farm clusters, but many linguists note an ongoing regionalization, diminishing or even elimination of local variations. Normalized speech, following the written languages ''Bokmål'' and ''Nynorsk'' or the more conservative (language), conservative ''Riksmål'' and ''Høgnorsk'', is not in common use, except in parts of Finnmark (where the original Sami people, Sami pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |