|
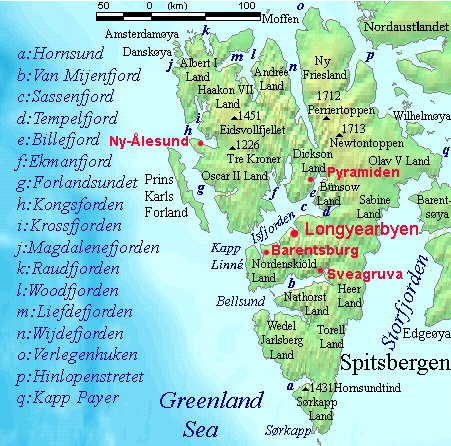
Brøggerhalvøya
Brøggerhalvøya is a peninsula in Oscar II Land on the west coast of the island of Spitsbergen in Svalbard, Norway. It is long and wide and borders Kongsfjorden to the north and Forlandsundet to the west. Ny-Ålesund, the world's northernmost permanent settlement, is located on the peninsula, which is named for Waldemar Christopher Brøgger. The Norwegian Polar Institute placed reindeer on the peninsula in 1978. Their grazing had a negative impact on the frail but biologically rich area, reducing the biodiversity. The peninsula has a similar geology to Ny-Ålesund, Carboniferous and Permian The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleoz ..., but is unaffected by coal wastes, which made the peninsula act as a control area. Melting ice since the last glacial period has resulted i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ny-Ålesund
Ny-Ålesund ("New Ålesund") is a small town in Oscar II Land on the island of Spitsbergen in Svalbard, Norway. It is situated on the Brøgger peninsula ( Brøggerhalvøya) and on the shore of the bay of Kongsfjorden. The company town is owned and operated by Kings Bay, which provides facilities for permanent research activities by 19 institutions from 11 countries. The town is ultimately owned by the Ministry of Climate and Environment and is not incorporated (i.e. is not recognised as a town by the Norwegian government). Ny-Ålesund has an all-year permanent population of 30 to 35, with the summer population reaching 114. Its facilities include Ny-Ålesund Airport, Hamnerabben, Svalbard Rocket Range, a port and Ny-Ålesund Town and Mine Museum, as well as a number of buildings dedicated to research and environmental monitoring activities. It is the northernmost functional civilian settlement in the world. The town was founded in 1917 by Peter Brandal and his mining company, Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
08 Ny Alesund Prn
8 (eight) is the natural number following 7 and preceding 9. In mathematics 8 is: * a composite number, its proper divisors being , , and . It is twice 4 or four times 2. * a power of two, being 2 (two cubed), and is the first number of the form , being an integer greater than 1. * the first number which is neither prime nor semiprime. * the base of the octal number system, which is mostly used with computers. In octal, one digit represents three bits. In modern computers, a byte is a grouping of eight bits, also called an octet. * a Fibonacci number, being plus . The next Fibonacci number is . 8 is the only positive Fibonacci number, aside from 1, that is a perfect cube. * the only nonzero perfect power that is one less than another perfect power, by Mihăilescu's Theorem. * the order of the smallest non-abelian group all of whose subgroups are normal. * the dimension of the octonions and is the highest possible dimension of a normed division algebra. * the first number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peninsula
A peninsula (; ) is a landform that extends from a mainland and is surrounded by water on most, but not all of its borders. A peninsula is also sometimes defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. Peninsulas exist on all continents. The size of a peninsula can range from tiny to very large. The largest peninsula in the world is the Arabian Peninsula. Peninsulas form due to a variety of causes. Etymology Peninsula derives , which is translated as 'peninsula'. itself was derived , or together, 'almost an island'. The word entered English in the 16th century. Definitions A peninsula is usually defined as a piece of land surrounded on most, but not all sides, but is sometimes instead defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. A peninsula may be bordered by more than one body of water, and the body of water does not have to be an ocean or a sea. A piece of land on a very tight river bend or one between two rivers is sometimes s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oscar II Land
Oscar II Land is the land area between Isfjorden and Kongsfjorden on Spitsbergen, Svalbard. The long glacier Sveabreen divides Oscar II Land from James I Land. The area is named after Oscar II of Sweden Oscar II (Oscar Fredrik; 21 January 1829 – 8 December 1907) was King of Sweden from 1872 until his death in 1907 and King of Norway from 1872 to 1905. Oscar was the son of King Oscar I and Queen Josephine. He inherited the Swedish and Norwe .... Older name variants are ''Oscar II's Land'' and ''Terre Oscar II''. The Hofgaardtoppen mountain is the highest peak in Oscar II Land. References Geography of Svalbard Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spitsbergen
Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Norway. Constituting the westernmost bulk of the archipelago, it borders the Arctic Ocean, the Norwegian Sea, and the Greenland Sea. Spitsbergen covers an area of , making it the largest island in Norway and the 36th-largest in the world. The administrative centre is Longyearbyen. Other settlements, in addition to research outposts, are the Russian mining community of Barentsburg, the research community of Ny-Ålesund, and the mining outpost of Sveagruva. Spitsbergen was covered in of ice in 1999, which was approximately 58.5% of the island's total area. The island was first used as a whaling base in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which it was abandoned. Coal mining started at the end of the 19th century, and several permanent commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74° to 81° north latitude, and from 10° to 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed by Nordaustlandet and . The largest settlement is Longyearbyen. The islands were first used as a base by the whalers who sailed far north in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which they were abandoned. Coal mining started at the beginning of the 20th century, and several permanent communities were established. The Svalbard Treaty of 1920 recognizes Norwegian sovereignty, and the 1925 Svalbard Act made Svalbard a full part of the Kingdom of Norway. They also established Svalbard as a free economic zone and a demilitarized zone. The Norwegian Store Norske and the Russian remain the only mining companies in place. Res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of Norway. Bouvet Island, located in the Subantarctic, is a dependency of Norway; it also lays claims to the Antarctic territories of Peter I Island and Queen Maud Land. The capital and largest city in Norway is Oslo. Norway has a total area of and had a population of 5,425,270 in January 2022. The country shares a long eastern border with Sweden at a length of . It is bordered by Finland and Russia to the northeast and the Skagerrak strait to the south, on the other side of which are Denmark and the United Kingdom. Norway has an extensive coastline, facing the North Atlantic Ocean and the Barents Sea. The maritime influence dominates Norway's climate, with mild lowland temperatures on the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kongsfjorden
Kongsfjorden as seen from Blomstrandhalvøya Kongsfjorden (Kongs Fjord or Kings Bay) is an inlet on the west coast of Spitsbergen, an island which is part of the Svalbard archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. The inlet is long and ranges in width from 6 to 14 km (4 to 9 miles). Two glaciers, Kronebreen and Kongsvegen, head the fjord. The coal-mining town of Ny-Ålesund is located on its southern shore and is one of the few permanent settlements on Spitsbergen. It is also a popular shore break for cruise ships, although local scientists who monitor levels as part of their climate change research have voiced concerns that the excessive pollution generated by cruise ships is interfering with their measurements. Kongsfjorden was originally named ''Deer Sound'' by Jonas Poole (1610), and was known as such by the English whalers until at least 1658. Giles and Rep (c. 1710) were the first to name it ''Koninks Bay''. William Scoresby William Scoresby (5 October 178921 March 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forlandsundet
Forlandsundet is an 88 km long sound separating Prins Karls Forland and Spitsbergen. Its northern limits are Fuglehuken to the west and Kvadehuken to the east. Its southern limits are Salpynten to the west and Daudmannsodden to the east. References * Norwegian Polar InstitutPlace names in Norwegian polar areas Straits of Svalbard Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waldemar Christofer Brøgger (geologist)
Waldemar Christofer Brøgger FRSE (10 November 185117 February 1940) was a Norwegian geologist and mineralogist. His research on Permian igneous rocks (286 to 245 million years ago) of the Oslo district greatly advanced petrologic theory on the formation of rocks. Biography He was born in Christiania (now Oslo), Norway. He was the son of Anton Wilhelm Brøgger (1820–82) and Oline (“Lina”) Marie Bjerring (1826–1905). He attended Oslo Cathedral School and graduated in 1870. He studied science and zoology under Theodor Kjerulf at University of Christiania (now University of Oslo). He was Cand. filos. (1870) and delivered his dissertation in 1875. Brøgger was then immediately employed in the Norwegian Geological Survey as an assistant. In the winter of 1875–76, he made a study trip together with fellow student Hans Reusch (1852–1922) to Corsica and Elba. The two jointly published an illustrated work, ''Jættegryder ved Christiania'' (Copenhagen. 1874) which was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Polar Institute
The Norwegian Polar Institute (NPI; no, Norsk Polarinstitutt) is Norway's central governmental institution for scientific research, mapping and environmental monitoring in the Arctic and the Antarctic. The NPI is a directorate under Norway's Ministry of Climate and Environment. The institute advises Norwegian authorities on matters concerning polar environmental management and is the official environmental management body for Norwegian activities in Antarctica. Activities The institute's activities are focused on environmental research and management in the polar regions. The NPI's researchers investigate biodiversity, climate and environmental toxins in the Arctic and Antarctic, and in this context the institute equips and organizes large-scale expeditions to both polar regions. The institute contributes to national and international climate work, and is an active contact point for the international scientific community. The institute collects and analyses data on the environm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reindeer
Reindeer (in North American English, known as caribou if wild and ''reindeer'' if domesticated) are deer in the genus ''Rangifer''. For the last few decades, reindeer were assigned to one species, ''Rangifer tarandus'', with about 10 subspecies. A 2022 revision of the genus elevated five of the subspecies to species (see Taxonomy below). They have a circumpolar distribution and are native to the Arctic, sub-Arctic, tundra, boreal forest, and mountainous regions of northern Europe, Siberia, and North America. Reindeer occur in both migratory and sedentary populations, and their herd sizes vary greatly in different regions. The tundra subspecies are adapted for extreme cold, and some are adapted for long-distance migration. Reindeer vary greatly in size and color from the smallest species, the Svalbard reindeer (''R. t. platyrhynchus''), to the largest subspecies, Osborn's caribou (''R. t. osborni''). Although reindeer are quite numerous, some species and subspecies are in d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)