|
Brookhart's Acid
Brookhart's acid is the salt of the diethyl ether oxonium ion and tetrakis ,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenylorate (BAr′4). It is a colorless solid, used as a strong acid. The compound was first reported by Volpe, Grant, and Brookhart in 1992. Preparation This compound is prepared by treatment of NaBAr′4 in diethyl ether (Et2O) with hydrogen chloride: : NaBAr′4 + HCl + 2 Et2O → (OEt2)2sup>+ + NaCl NaBAr′4 is soluble in diethyl ether, whereas sodium chloride is not. Precipitation of sodium chloride thus drives the formation of the oxonium acid compound, which is isolable as a solid. Structure and properties The acid crystallizes as a white, hygroscopic crystalline solid. NMR and elemental analysis showed that the crystal contains two equivalents of diethyl ether. In solution, the compound slowly degrades to ''m''-C6H3(CF3)2 and BAr′3. (OEt2)2B(C6F5)4] is a related compound with a slightly different weakly coordinating anion; it was first reported in 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diethyl Ether
Diethyl ether, or simply ether, is an organic compound in the ether class with the formula , sometimes abbreviated as (see Pseudoelement symbols). It is a colourless, highly volatile, sweet-smelling ("ethereal odour"), extremely flammable liquid. It is commonly used as a solvent in laboratories and as a starting fluid for some engines. It was formerly used as a general anesthetic, until non-flammable drugs were developed, such as halothane. It has been used as a recreational drug to cause intoxication. Production Most diethyl ether is produced as a byproduct of the vapor-phase hydration of ethylene to make ethanol. This process uses solid-supported phosphoric acid catalysts and can be adjusted to make more ether if the need arises. Vapor-phase dehydration of ethanol over some alumina catalysts can give diethyl ether yields of up to 95%. Diethyl ether can be prepared both in laboratories and on an industrial scale by the acid ether synthesis. Ethanol is mixed with a stro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetonitrile
Acetonitrile, often abbreviated MeCN (methyl cyanide), is the chemical compound with the formula and structure . This colourless liquid is the simplest organic nitrile (hydrogen cyanide is a simpler nitrile, but the cyanide anion is not classed as organic). It is produced mainly as a byproduct of acrylonitrile manufacture. It is used as a polar aprotic solvent in organic synthesis and in the purification of butadiene. The skeleton is linear with a short distance of 1.16 Å. Acetonitrile was first prepared in 1847 by the French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas. Applications Acetonitrile is used mainly as a solvent in the purification of butadiene in refineries. Specifically, acetonitrile is fed into the top of a distillation column filled with hydrocarbons including butadiene, and as the acetonitrile falls down through the column, it absorbs the butadiene which is then sent from the bottom of the tower to a second separating tower. Heat is then employed in the separatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2,2'-bipyridine
The comma is a punctuation mark that appears in several variants in different languages. It has the same shape as an apostrophe or single closing quotation mark () in many typefaces, but it differs from them in being placed on the baseline of the text. Some typefaces render it as a small line, slightly curved or straight, but inclined from the vertical. Other fonts give it the appearance of a miniature filled-in figure on the baseline. The comma is used in many contexts and languages, mainly to separate parts of a sentence such as clauses, and items in lists mainly when there are three or more items listed. The word ''comma'' comes from the Greek (), which originally meant a cut-off piece, specifically in grammar, a short clause. A comma-shaped mark is used as a diacritic in several writing systems and is considered distinct from the cedilla. In Byzantine and modern copies of Ancient Greek, the " rough" and "smooth breathings" () appear above the letter. In Latvian, R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usually gaseous or liquid) as the reactant, or heterogeneous, whose components are not in the same phase. Enzymes and other biocatalysts are often considered as a third category. Catalysis is ubiquitous in chemical industry of all kinds. Estimates are that 90% of all commercially produced chemical products involve catalysts at some s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propylene
Propylene, also known as propene, is an unsaturated organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CH=CH2. It has one double bond, and is the second simplest member of the alkene class of hydrocarbons. It is a colorless gas with a faint petroleum-like odor. Production Steam cracking The dominant technology for producing propylene is steam cracking. The same technology is applied to ethane to ethylene. These two conversions are the #2 and #1 processes in the chemical industry, as judged by their scale. In this process, propane undergoes dehydrogenation. The by-product is hydrogen: :CH3CH2CH3 → CH3CH=CH2 + H2 The yield of propene is about 85 m%. By-products are usually used as fuel for the propane dehydrogenation reaction. Steam cracking is one of the most energy-intensive industrial processes. The feedstock is naphtha or propane, especially in the Middle East, where there is an abundance of propane from oil/gas operations. Propene can be separated by fractional distilla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds). Ethylene is widely used in the chemical industry, and its worldwide production (over 150 million tonnes in 2016) exceeds that of any other organic compound. Much of this production goes toward polyethylene, a widely used plastic containing polymer chains of ethylene units in various chain lengths. Ethylene is also an important natural plant hormone and is used in agriculture to force the ripening of fruits. The hydrate of ethylene is ethanol. Structure and properties This hydrocarbon has four hydrogen atoms bound to a pair of carbon atoms that are connected by a double bond. All six atoms that comprise ethylene are coplanar. The H-C-H angle is 117.4°, close to the 120° for ideal sp² hybridized carbon. The molecule is also relatively weak: rota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry'. 1232 pages. Two general types of monoalkenes are distinguished: terminal and internal. Also called α-olefins, terminal alkenes are more useful. However, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) recommends using the name "alkene" only for acyclic hydrocarbons with just one double bond; alkadiene, alkatriene, etc., or polyene for acyclic hydrocarbons with two or more double bonds; cycloalkene, cycloalkadiene, etc. for cyclic ones; and "olefin" for the general class – cyclic or acyclic, with one or more double bonds. Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups (also known as mono-enes) form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula with '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copolymerisation
In polymer chemistry, a copolymer is a polymer derived from more than one species of monomer. The polymerization of monomers into copolymers is called copolymerization. Copolymers obtained from the copolymerization of two monomer species are sometimes called ''bipolymers''. Those obtained from three and four monomers are called ''terpolymers'' and ''quaterpolymers'', respectively. Copolymers can be characterized by a variety of techniques such as NMR spectroscopy and size-exclusion chromatography to determine the molecular size, weight, properties, and composition of the material. Commercial copolymers include acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), styrene/butadiene co-polymer (SBR), nitrile rubber, styrene-acrylonitrile, styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) and ethylene-vinyl acetate, all of which are formed by chain-growth polymerization. Another production mechanism is step-growth polymerization, which is used to produce the nylon-12/6/66 copolymer of nylon 12, nylon 6 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coord
In geometry, a coordinate system is a system that uses one or more numbers, or coordinates, to uniquely determine the position of the points or other geometric elements on a manifold such as Euclidean space. The order of the coordinates is significant, and they are sometimes identified by their position in an ordered tuple and sometimes by a letter, as in "the ''x''-coordinate". The coordinates are taken to be real numbers in elementary mathematics, but may be complex numbers or elements of a more abstract system such as a commutative ring. The use of a coordinate system allows problems in geometry to be translated into problems about numbers and ''vice versa''; this is the basis of analytic geometry. Common coordinate systems Number line The simplest example of a coordinate system is the identification of points on a line with real numbers using the ''number line''. In this system, an arbitrary point ''O'' (the ''origin'') is chosen on a given line. The coordinate of a poi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part") is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals. The term "polymer" derives from the Greek word πολύς (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and μέρος (''meros'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
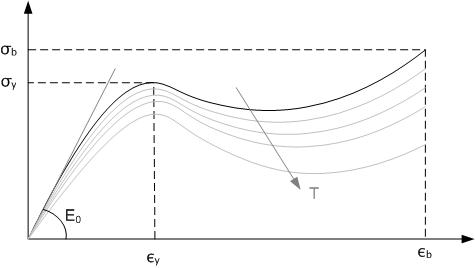
Thermoplastic
A thermoplastic, or thermosoft plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling. Most thermoplastics have a high molecular weight. The polymer chains associate by intermolecular forces, which weaken rapidly with increased temperature, yielding a viscous liquid. In this state, thermoplastics may be reshaped and are typically used to produce parts by various polymer processing techniques such as injection molding, compression molding, calendering, and extrusion. Thermoplastics differ from thermosetting polymers (or "thermosets"), which form irreversible chemical bonds during the curing process. Thermosets do not melt when heated, but typically decompose and do not reform upon cooling. Above its glass transition temperature and below its melting point, the physical properties of a thermoplastic change drastically without an associated phase change. Some thermoplastics do not fully crystallize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |