|
Brook Rearrangement
In organic chemistry the Brook rearrangement refers to any [1,''n''] carbon to oxygen silyl migration. The Rearrangement reaction, rearrangement was first observed in the late 1950s by Canadian chemist Adrian Gibbs Brook (1924–2013), after which the reaction is named. These migrations can be promoted in a number of different ways, including thermally, photolytically or under basic/acidic conditions. In the forward direction, these silyl migrations produce silyl ethers as products which is driven by the stability of the oxygen-silicon bond. The silyl substituents can be Aliphatic compound, aliphatic or Aromatic compound, aromatic, and if the silicon is a center of Chirality (chemistry), chirality, the migration occurs with retention at this center. This migration occurs through a transition state where silicon is penta-Coordination complex, coordinate and bears a partial negative charge. If a center of chirality is present at the carbon center to which the silyl group is attached ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2012) ''Organic Chemistry''. Oxford University Press. pp. 1–15. . Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical ( in silico) study. The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but also containing other elements, especially oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus (included in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
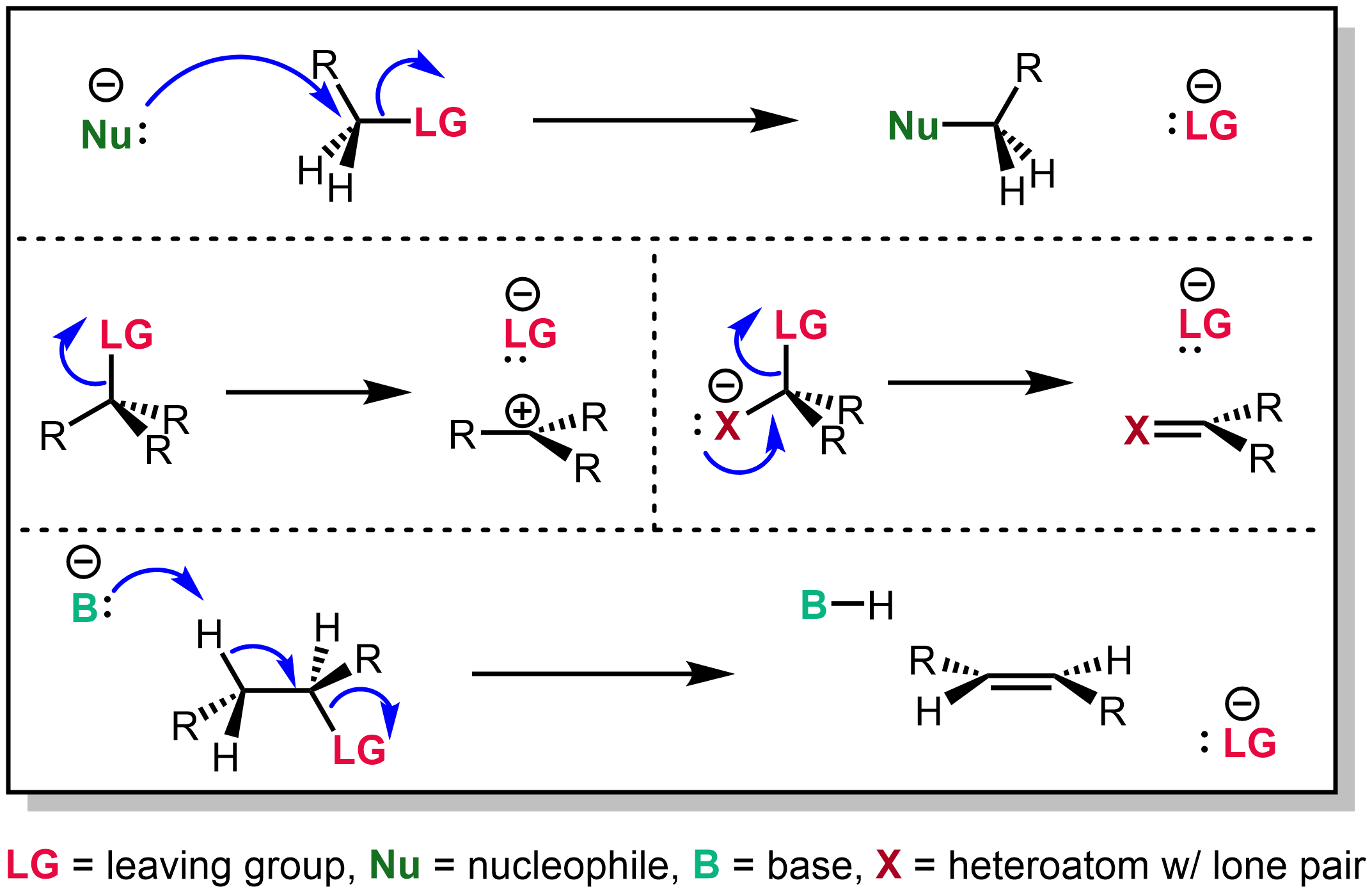
Leaving Group
In chemistry, a leaving group is defined by the IUPAC as an atom or group of atoms that detaches from the main or residual part of a substrate during a reaction or elementary step of a reaction. However, in common usage, the term is often limited to a fragment that departs with a pair of electrons in heterolytic bond cleavage. In this usage, a leaving group is a less formal but more commonly used synonym of the term '' nucleofuge''. In this context, leaving groups are generally anions or neutral species, departing from a neutral or cationic substrates, respectively, though in rare cases, cations leaving from a dicationic substrate are also known. A species' ability to serve as a leaving group depends on its ability to stabilize the additional electron density that results from bond heterolysis. Common anionic leaving groups are halides such as Cl−, Br−, and I−, and sulfonate esters such as tosylate (TsO−), while water (H2O), alcohols (HOR), and amines (R3N) are common neutr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acylsilane
Acylsilanes are a group of chemical compounds sharing a common functional group with the general structure R(CO)-SiR3. Acylsilanes are starting compounds in the Brook rearrangement with vinyl lithium compounds to silyl enol ethers. Synthesis Acylsilanes can be synthesized using the following procedures: Starting with the 1,3-dithiane, substituting with the silyl group, then removing the dithioacetal group with mercury(II) chloride Mercury(II) chloride (or mercury bichloride, mercury dichloride), historically also known as sulema or corrosive sublimate, is the inorganic chemical compound of mercury and chlorine with the formula HgCl2. It is white crystalline solid and is ... and hydrolysis. This method also can make acylgermanes using the appropriate halogermane reagents. Another method was reported by Kuwajima ''et al.'' using 1,1-bis(trimethylsilyl)alkan-1-ols. ''t''-Butyl hypochlorite converts the starting material to the acylsilane. References {{Reflist Function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wittig Reaction
The Wittig reaction or Wittig olefination is a chemical reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a triphenyl phosphonium ylide called a Wittig reagent. Wittig reactions are most commonly used to convert aldehydes and ketones to alkenes. Most often, the Wittig reaction is used to introduce a methylene group using methylenetriphenylphosphorane (Ph3P=CH2). Using this reagent, even a sterically hindered ketone such as camphor can be converted to its methylene derivative. Stereochemistry For the reaction with aldehydes, the double bond geometry is readily predicted based on the nature of the ylide. With unstabilised ylides (R3 = alkyl) this results in (''Z'')-alkene product with moderate to high selectivity. With stabilized ylides (R3 = ester or ketone), the (''E'')-alkene is formed with high selectivity. The (''E'')/(''Z'') selectivity is often poor with semistabilized ylides (R3 = aryl). To obtain the (''E'')-alkene for unstabilized ylides, the Schlosser modification of the W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intramolecular Reaction
Intramolecular in chemistry describes a process or characteristic limited within the structure of a single molecule, a property or phenomenon limited to the extent of a single molecule. Examples * intramolecular hydride transfer (transfer of a hydride ion from one part to another within the same molecule) * intramolecular hydrogen bond (a hydrogen bond formed between two functional groups of the same molecule) *cyclization of ω-haloalkylamines and alcohols to form the corresponding saturated nitrogen and oxygen heterocycles, respectively (an SN2 reaction within the same molecule) In intramolecular organic reactions, two reaction sites are contained within a single molecule. This creates a very high effective concentration (resulting in high reaction rates), and, therefore, many intramolecular reactions that would not occur as an intermolecular reaction between two compounds take place. Examples of intramolecular reactions are the Smiles rearrangement, the Dieckmann condensation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sp2 Hybridization
In chemistry, orbital hybridisation (or hybridization) is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new ''hybrid orbitals'' (with different energies, shapes, etc., than the component atomic orbitals) suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theory. For example, in a carbon atom which forms four single bonds the valence-shell s orbital combines with three valence-shell p orbitals to form four equivalent sp3 mixtures in a tetrahedral arrangement around the carbon to bond to four different atoms. Hybrid orbitals are useful in the explanation of molecular geometry and atomic bonding properties and are symmetrically disposed in space. Usually hybrid orbitals are formed by mixing atomic orbitals of comparable energies. History and uses Chemist Linus Pauling first developed the hybridisation theory in 1931 to explain the structure of simple molecules such as methane (CH4) using atomic orbitals. Pauling pointed out that a carbon atom forms fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigonal Bipyramid
In geometry, the triangular bipyramid (or dipyramid) is a type of hexahedron, being the first in the infinite set of face-transitive bipyramids. It is the dual of the triangular prism with 6 isosceles triangle faces. As the name suggests, it can be constructed by joining two tetrahedra along one face. Although all its faces are congruent and the solid is face-transitive, it is not a Platonic solid because some vertices adjoin three faces and others adjoin four. The bipyramid whose six faces are all equilateral triangles is one of the Johnson solids, (). As a Johnson solid with all faces equilateral triangles, it is also a deltahedron. Formulae The following formulae for the height (H), surface area (A) and volume (V) can be used if all faces are regular, with edge length L: :H = L\cdot \frac \approx L\cdot 1.632993162 :A = L^2 \cdot \frac \approx L^2\cdot 2.598076211 :V = L^3 \cdot \frac \approx L^3\cdot 0.235702260 Dual polyhedron The dual polyhedron of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walden Cycle
Walden inversion is the inversion of a stereogenic center in a chiral molecule in a chemical reaction. Since a molecule can form two enantiomers around a stereogenic center, the Walden inversion converts the configuration of the molecule from one enantiomeric form to the other. For example, in an SN2 reaction, Walden inversion occurs at a tetrahedral carbon atom. It can be visualized by imagining an umbrella turned inside-out in a gale. In the Walden inversion, the backside attack by the nucleophile in an SN2 reaction gives rise to a product whose configuration is opposite to the reactant. Therefore, during SN2 reaction, 100% inversion of product takes place. This is known as Walden inversion. It was first observed by chemist Paul Walden in 1896. He was able to convert one enantiomer of a chemical compound into the other enantiomer and back again in a so-called Walden cycle which went like this: (+) chlorosuccinic acid (1 in the illustration) was converted to (+) malic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground State
The ground state of a quantum-mechanical system is its stationary state of lowest energy; the energy of the ground state is known as the zero-point energy of the system. An excited state is any state with energy greater than the ground state. In quantum field theory, the ground state is usually called the vacuum state or the vacuum. If more than one ground state exists, they are said to be degenerate. Many systems have degenerate ground states. Degeneracy occurs whenever there exists a unitary operator that acts non-trivially on a ground state and commutes with the Hamiltonian of the system. According to the third law of thermodynamics, a system at absolute zero temperature exists in its ground state; thus, its entropy is determined by the degeneracy of the ground state. Many systems, such as a perfect crystal lattice, have a unique ground state and therefore have zero entropy at absolute zero. It is also possible for the highest excited state to have absolute zero temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy Of Activation
In chemical kinetics, the entropy of activation of a reaction is one of the two parameters (along with the enthalpy of activation) which are typically obtained from the temperature dependence of a reaction rate constant, when these data are analyzed using the Eyring equation of the transition state theory. The standard entropy of activation is symbolized and equals the change in entropy when the reactants change from their initial state to the activated complex or transition state ( = change, = entropy, = activation). It determines the preexponential factor of the Arrhenius equation for temperature dependence of reaction rates. The relationship depends on the molecularity of the reaction: for reactions in solution and unimolecular gas reactions , while for bimolecular gas reactions . In these equations is the base of natural logarithms, is the Planck constant, is the Boltzmann constant and the absolute temperature. ' is the ideal gas constant in units of (bar·L)/(mol·K). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activation Energy
In chemistry and physics, activation energy is the minimum amount of energy that must be provided for compounds to result in a chemical reaction. The activation energy (''E''a) of a reaction is measured in joules per mole (J/mol), kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) or kilocalories per mole (kcal/mol). Activation energy can be thought of as the magnitude of the potential barrier (sometimes called the energy barrier) separating minima of the potential energy surface pertaining to the initial and final thermodynamic state. For a chemical reaction to proceed at a reasonable rate, the temperature of the system should be high enough such that there exists an appreciable number of molecules with translational energy equal to or greater than the activation energy. The term "activation energy" was introduced in 1889 by the Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius. Other uses Although less commonly used, activation energy also applies to nuclear reactions and various other physical phenomena. Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammett Equation
The Hammett equation in organic chemistry describes a linear free-energy relationship relating reaction rates and equilibrium constants for many reactions involving benzoic acid derivatives with meta- and para-substituents to each other with just two parameters: a substituent constant and a reaction constant. This equation was developed and published by Louis Plack Hammett in 1937 as a follow-up to qualitative observations in a 1935 publication. The basic idea is that for any two reactions with two aromatic reactants only differing in the type of substituent, the change in free energy of activation is proportional to the change in Gibbs free energy.''Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A'' Second Edition F.A. Carey, R.J. Sundberg Plenum Press This notion does not follow from elemental thermochemistry or chemical kinetics and was introduced by Hammett intuitively. The basic equation is: :\log \frac = \sigma\rho relating the equilibrium constant, ''K'', for a given equilibrium re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |