|
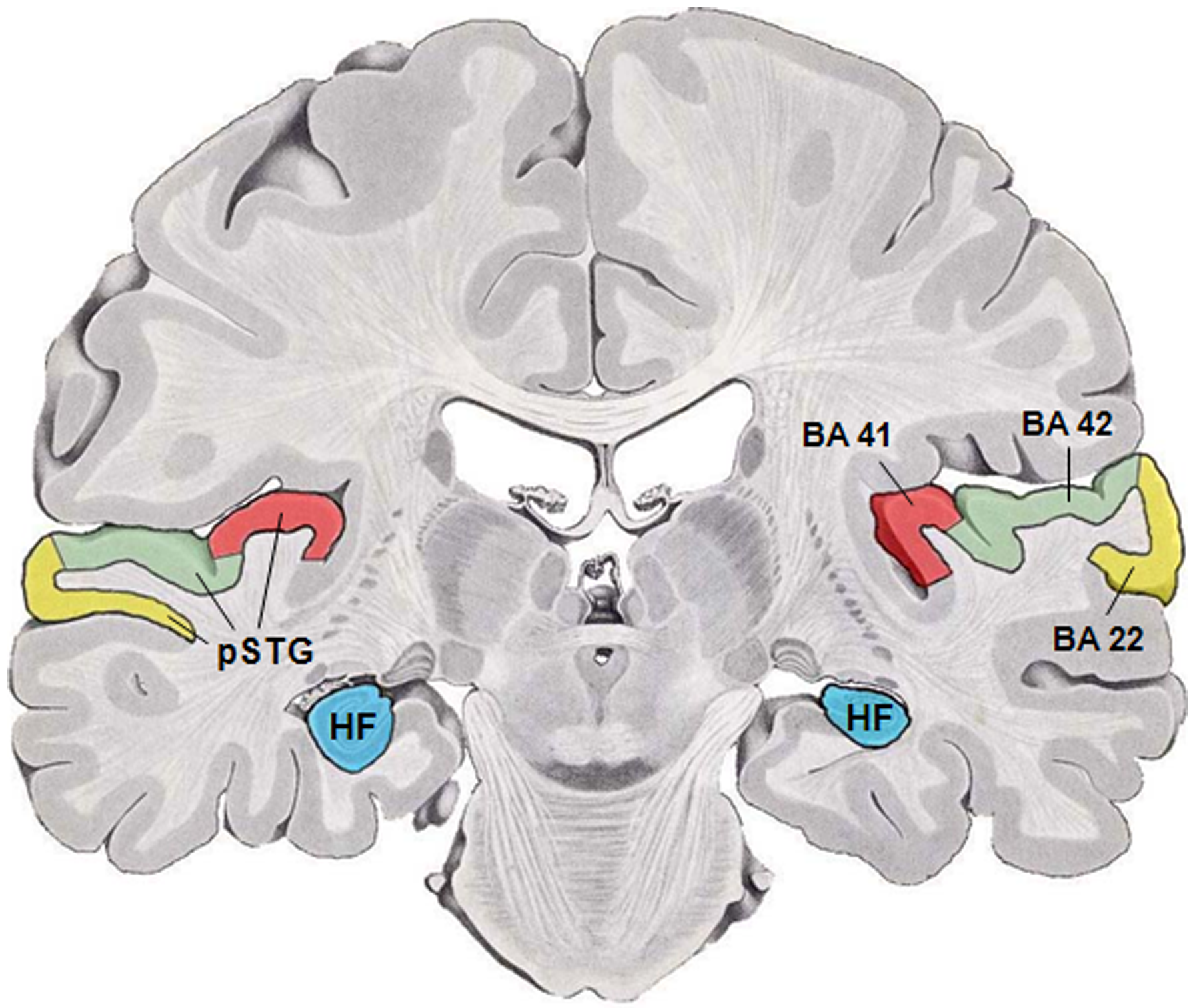
Brodmann Area 22
Brodmann area 22 is a Brodmann's area that is cytoarchitecturally located in the posterior superior temporal gyrus of the brain. In the left cerebral hemisphere, it is one portion of Wernicke's area. The left hemisphere BA22 helps with generation and understanding of individual words. On the right side of the brain, BA22 helps to discriminate pitch and sound intensity, both of which are necessary to perceive melody and prosody. Wernicke's area is active in processing language and consists of the left Brodmann area 22 and Brodmann area 40, the supramarginal gyrus. It is bounded rostrally by Brodmann area 38, medially by Brodmann area 42, ventrocaudally by Brodmann area 21, and dorsocaudally by Brodmann area 40, and Brodmann area 39. These cortical regions surround the lower left posterior Sylvian fissure. Language The Brodmann areas that are relevant to language include Broca's area (BA 44/45) and Wernicke's area (BA 42/22), where Broca's area is responsible for langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronal Section
The coronal plane (also known as the frontal plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into Anatomical terms of location#Dorsal and ventral, dorsal and ventral sections. It is perpendicular to the sagittal plane, sagittal and transverse plane, transverse planes. Details The coronal plane is an example of a Anatomical terms of location#General usage, longitudinal plane. For a human, the mid-coronal plane would transect a standing body into two halves (front and back, or anterior and posterior) in an imaginary line that cuts through both shoulders. The description of the coronal plane applies to most animals as well as humans even though humans walk upright and the various planes are usually shown in the vertical orientation. The sternal plane (''planum sternale'') is a coronal plane which transects the front of the Human sternum, sternum. Etymology The term is derived from Latin ''corona'' ('garland, crown'), from Ancient Greek κορώνη (''korōnē'', 'garland, wrea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brodmann Area 21
Brodmann area 21, or BA21, is part of the temporal cortex in the human brain. The region encompasses most of the lateral temporal cortex and is also known as middle temporal area 21. In the human it corresponds approximately to the middle temporal gyrus. Function BA 21 is a higher-order visual association cortex with medium myelin content. As a lateral temporal region, it is likely to play a part in auditory processing and language. Language function is left lateralized in most individuals. Location BA21 is a subdivision of the cytoarchitecturally defined temporal region of the cerebral cortex. BA21 is superior to BA20 and inferior to BA40 and BA41. It is bounded rostrally by the temporopolar area 38 (H), ventrally by the inferior temporal area 20, caudally by the occipitotemporal area 37 (H), and dorsally by the superior temporal area 22 (Brodmann-1909). Guenon Brodmann area 21 is a subdivision of the cerebral cortex of the guenon defined on the basis of cytoarchitectur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Sulcus
In neuroanatomy, the lateral sulcus (also called Sylvian fissure, after Franciscus Sylvius, or lateral fissure) is one of the most prominent features of the human brain. The lateral sulcus is a deep fissure in each hemisphere that separates the frontal and parietal lobes from the temporal lobe. The insular cortex lies deep within the lateral sulcus. Anatomy The lateral sulcus divides both the frontal lobe and parietal lobe above from the temporal lobe below. It is in both hemispheres of the brain. The lateral sulcus is one of the earliest-developing sulci of the human brain. It first appears around the fourteenth gestational week. The insular cortex lies deep within the lateral sulcus. The lateral sulcus has a number of side branches. Two of the most prominent and most regularly found are the ascending (also called vertical) ramus and the horizontal ramus of the lateral fissure, which subdivide the inferior frontal gyrus. The lateral sulcus also contains the transverse tempor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brodmann Areas
A Brodmann area is a region of the cerebral cortex, in the human or other primate brain, defined by its cytoarchitecture, or histological structure and organization of cells. History Brodmann areas were originally defined and numbered by the German anatomist Korbinian Brodmann based on the cytoarchitectural organization of neurons he observed in the cerebral cortex using the Nissl method of cell staining. Brodmann published his maps of cortical areas in humans, monkeys, and other species in 1909, along with many other findings and observations regarding the general cell types and laminar organization of the mammalian cortex. The same Brodmann area number in different species does not necessarily indicate homologous areas. A similar, but more detailed cortical map was published by Constantin von Economo and Georg N. Koskinas in 1925. Present importance Brodmann areas have been discussed, debated, refined, and renamed exhaustively for nearly a century and remain the most wid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from CT and PET scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft-tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, though "Open" MRI designs mostly relieve this. Additionally, implants and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area of the brain is in use, blood flow to that region also increases. The primary form of fMRI uses the blood-oxygen-level dependent (BOLD) contrast, discovered by Seiji Ogawa in 1990. This is a type of specialized brain and body scan used to map neuron, neural activity in the brain or spinal cord of humans or other animals by imaging the change in blood flow (hemodynamic response) related to energy use by brain cells. Since the early 1990s, fMRI has come to dominate brain mapping research because it does not involve the use of injections, surgery, the ingestion of substances, or exposure to ionizing radiation. This measure is frequently corrupted by noise from various sources; hence, statistical procedures are used to extract the underlying si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexicon
A lexicon is the vocabulary of a language or branch of knowledge (such as nautical or medical). In linguistics, a lexicon is a language's inventory of lexemes. The word ''lexicon'' derives from Koine Greek language, Greek word (), neuter of () meaning 'of or for words'. Linguistic theories generally regard human languages as consisting of two parts: a lexicon, essentially a catalogue of a language's words (its wordstock); and a grammar, a system of rules which allow for the combination of those words into meaningful sentences. The lexicon is also thought to include bound morphemes, which cannot stand alone as words (such as most affixes). In some analyses, compound words and certain classes of idiomatic expressions, collocations and other phrases are also considered to be part of the lexicon. Dictionary, Dictionaries are lists of the lexicon, in alphabetical order, of a given language; usually, however, bound morphemes are not included. Size and organization Items in the le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptive Aphasia
Wernicke's aphasia, also known as receptive aphasia, sensory aphasia or posterior aphasia, is a type of aphasia in which individuals have difficulty understanding written and spoken language. Patients with Wernicke's aphasia demonstrate fluent speech, which is characterized by typical speech rate, intact syntactic abilities and effortless speech output. Writing often reflects speech in that it tends to lack content or meaning. In most cases, motor deficits (i.e. hemiparesis) do not occur in individuals with Wernicke's aphasia. Therefore, they may produce a large amount of speech without much meaning. Individuals with Wernicke's aphasia are typically unaware of their errors in speech and do not realize their speech may lack meaning. They typically remain unaware of even their most profound language deficits. Like many acquired language disorders, Wernicke's aphasia can be experienced in many different ways and to many different degrees. Patients diagnosed with Wernicke's aphasia c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auditory Cortex
The auditory cortex is the part of the temporal lobe that processes auditory information in humans and many other vertebrates. It is a part of the auditory system, performing basic and higher functions in hearing, such as possible relations to language switching.Cf. Pickles, James O. (2012). ''An Introduction to the Physiology of Hearing'' (4th ed.). Bingley, UK: Emerald Group Publishing Limited, p. 238. It is located bilaterally, roughly at the upper sides of the temporal lobes – in humans, curving down and onto the medial surface, on the superior temporal plane, within the lateral sulcus and comprising parts of the transverse temporal gyri, and the superior temporal gyrus, including the planum polare and planum temporale (roughly Brodmann areas 41 and 42, and partially 22). The auditory cortex takes part in the spectrotemporal, meaning involving time and frequency, analysis of the inputs passed on from the ear. The cortex then filters and passes on the information to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexical Semantics
Lexical semantics (also known as lexicosemantics), as a subfield of linguistic semantics, is the study of word meanings.Pustejovsky, J. (2005) Lexical Semantics: Overview' in Encyclopedia of Language and Linguistics, second edition, Volumes 1-14Taylor, J. (2017) Lexical Semantics'. In B. Dancygier (Ed.), The Cambridge Handbook of Cognitive Linguistics (Cambridge Handbooks in Language and Linguistics, pp. 246-261). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. It includes the study of how words structure their meaning, how they act in grammar and compositionality, and the relationships between the distinct senses and uses of a word. The units of analysis in lexical semantics are lexical units which include not only words but also sub-words or sub-units such as affixes and even compound words and phrases. Lexical units include the catalogue of words in a language, the lexicon. Lexical semantics looks at how the meaning of the lexical units correlates with the structure of the language or s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Lobe
The temporal lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain. The temporal lobe is involved in processing sensory input into derived meanings for the appropriate retention of visual memory, language comprehension, and emotion association. ''Temporal'' refers to the head's Temple (anatomy), temples. Structure The Temple (anatomy)#Etymology, temporal Lobe (anatomy), lobe consists of structures that are vital for declarative or long-term memory. Declarative memory, Declarative (denotative) or Explicit memory, explicit memory is conscious memory divided into semantic memory (facts) and episodic memory (events). Medial temporal lobe structures that are critical for long-term memory include the hippocampus, along with the surrounding Hippocampal formation, hippocampal region consisting of the Perirhinal cortex, perirhinal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sylvian Fissure
In neuroanatomy, the lateral sulcus (also called Sylvian fissure, after Franciscus Sylvius, or lateral fissure) is one of the most prominent features of the human brain. The lateral sulcus is a deep fissure in each hemisphere that separates the frontal and parietal lobes from the temporal lobe. The insular cortex lies deep within the lateral sulcus. Anatomy The lateral sulcus divides both the frontal lobe and parietal lobe above from the temporal lobe below. It is in both hemispheres of the brain. The lateral sulcus is one of the earliest-developing sulci of the human brain. It first appears around the fourteenth gestational week. The insular cortex lies deep within the lateral sulcus. The lateral sulcus has a number of side branches. Two of the most prominent and most regularly found are the ascending (also called vertical) ramus and the horizontal ramus of the lateral fissure, which subdivide the inferior frontal gyrus. The lateral sulcus also contains the transverse tempor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |