|
British Columbia Highway 14
British Columbia Highway 14, named the West Coast (Sooke) Highway is the southernmost numbered route in the province of British Columbia. An east-west highway on the southwestern coast of Vancouver Island in the Capital Regional District, it is sometimes known as the ''Juan de Fuca Highway'', as well as ''Sooke Road'', Sooke being one of the largest communities that the highway passes through. Highway 14 first opened in 1953, extending west from Colwood, a suburb of Victoria, to the coastal community of Jordan River, and was extended all the way west to the remote community of Port Renfrew by 1975. The highway's eastern terminus was relocated to northern Langford in 2002. Outside of urban areas the route has exceptionally winding, curving and hilly stretches. Some of the sharper corners have oversized, freeway-style, jersey barriers instead of the more typical steel crash rails, mostly to prevent an out-of-control vehicle from falling off a cliff into the Strait of Juan de F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langford, British Columbia
Langford is a city on southern Vancouver Island in the province of British Columbia, Canada. Langford is one of the 13 component municipalities of Greater Victoria and is within the Capital Regional District. Langford was incorporated in 1992 and has a population of over 40,000 people. Its municipal neighbours are Colwood to the southeast, Highlands to the north, Metchosin to the southwest, and View Royal to the northeast. History The City of Langford was incorporated on December 8, 1992. Langford's history of European settlement dates back to 1851, when Captain Edward Langford established one of the four Hudson's Bay Company farms in the Victoria area. In the early 1860s, the region of Langford experienced a short-lived gold rush in what is now Goldstream Provincial Park. The area was once a favourite recreation destination for thousands of Victorians in the late 1800s: day-trippers travelled via railway to the popular country resort Goldstream House Hotel; hunters built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strait Of Juan De Fuca
The Strait of Juan de Fuca (officially named Juan de Fuca Strait in Canada) is a body of water about long that is the Salish Sea's outlet to the Pacific Ocean. The international boundary between Canada and the United States runs down the centre of the Strait. It was named in 1787 by the maritime fur trader Charles William Barkley, captain of '' Imperial Eagle'', for Juan de Fuca, the Greek navigator who sailed in a Spanish expedition in 1592 to seek the fabled Strait of Anián. Barkley was the first non-indigenous person to find the strait, unless Juan de Fuca's story was true. The strait was explored in detail between 1789 and 1791 by Manuel Quimper, José María Narváez, Juan Carrasco, Gonzalo López de Haro, and Francisco de Eliza. Definition The United States Geological Survey defines the Strait of Juan de Fuca as a channel. It extends east from the Pacific Ocean between Vancouver Island, British Columbia, and the Olympic Peninsula, Washington, to Haro Strait, Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Marine Circle Route
The Pacific Marine Circle Route is a marked scenic loop road through southern Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada. The route is composed of Highway 14, Pacific Marine Road, Shore Road, Highway 18, and a segment of the Trans-Canada Highway. The Pacific Marine Circle Route was established by the British Columbia Ministry of Tourism, Arts and Culture with the promise of an increase in tourist travel in southern Vancouver Island. It is one of British Columbia's 12 Circle Routes scattered throughout the province. Route Clockwise, the route heads south from Malahat, passes through Goldstream Provincial Park then briefly east to Langford, south and west to Sooke, west to Port Renfrew, north and east to Lake Cowichan, east and south to Duncan, southeast to Mill Bay, then south back to Malahat. The route can also be travelled in the opposite direction and started or finished at any points. Points of Interest * Cowichan Lake * French Beach Provincial Park * Gold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of Fisheries And Oceans
Fisheries and Oceans Canada (DFO; french: Pêches et Océans Canada, MPO), is a department of the Government of Canada that is responsible for developing and implementing policies and programs in support of Canada's economic, ecological and scientific interests in oceans and inland waters. Its mandate includes responsibility for the conservation and sustainable use of Canada's fisheries resources while continuing to provide safe, effective and environmentally sound marine services that are responsive to the needs of Canadians in a global economy. The federal government is constitutionally mandated for conservation and protection of fisheries resources in all Canadian fisheries waters. However, the department is largely focused on the conservation and allotment of harvests of salt water fisheries on the Atlantic, Pacific and Arctic coasts of Canada. The department works toward conservation and protection of inland freshwater fisheries, such as on the Great Lakes and Lake Winn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Helmcken
Mount Helmcken is a large hill in Metchosin, east of Sooke, in British Columbia, Canada. It is also just west of Colwood. The mountain is accessed via Neild Road which runs all the way to the top where it joins Zanita Heights. The mountain is named for John S. Helmcken, a surgeon for the Hudson's Bay Company who opposed the province's entry into Confederation, preferring annexation by the United States. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Helmcken Mountains of British Columbia under 1000 metres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metchosin, British Columbia
The District of Metchosin is a municipality and community in Greater Victoria on the southern tip of Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada. It is a coastal community adjacent to the Strait of Juan de Fuca. Metchosin is part of the Western Communities and one of the 13 regional municipalities. Climate Metchosin has a warm-summer Mediterranean climate (Köppen: ''Csb'') in parts caused by the rain shadow and to the east of the strait of the Strait of Juan de Fuca, but keeping some oceanic characteristics (''Cfb''). Sligo, Ireland has very close temperatures with only a slightly warmer summer. The biggest difference is in the summer drying, common of the Pacific Northwest. Demographics In the 2021 Census of Population conducted by Statistics Canada, Metchosin had a population of 5,067 living in 1,856 of its 1,938 total private dwellings, a change of from its 2016 population of 4,708. With a land area of , it had a population density of in 2021. Religion According to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans-Canada Highway
The Trans-Canada Highway (French: ; abbreviated as the TCH or T-Can) is a transcontinental federal–provincial highway system that travels through all ten provinces of Canada, from the Pacific Ocean on the west coast to the Atlantic Ocean on the east coast. The main route spans across the country, one of the longest routes of its type in the world. The highway system is recognizable by its distinctive white-on-green maple leaf route markers, although there are small variations in the markers in some provinces. While by definition the Trans-Canada Highway is a highway ''system'' that has several parallel routes throughout most of the country, the term "Trans-Canada Highway" often refers to the main route that consists of Highway 1 (British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba), Highways 17 and 417 (Ontario), Autoroutes 40, 20 and 85 (Quebec), Highway 2 (New Brunswick), Highways 104 and 105 (Nova Scotia) and Highway 1 (Newfoundland). This mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BC Highway 14 - Cyclist In The Mist
BC most often refers to: * Before Christ, a calendar era based on the traditionally reckoned year of the birth of Jesus of Nazareth * British Columbia, the westernmost province of Canada * Baja California, a state of Mexico BC may also refer to: Arts and entertainment * "B.C.", a song by Sparks from the 1974 album ''Propaganda'' * ''B.C.'' (comic strip) by Johnny Hart, and one of its characters * ''BC'' (video game) by Lionhead Studios * ''BC The Archaeology of the Bible Lands'', a BBC television series * Bullet Club, a professional wrestling stable Businesses and organizations * Basilian Chouerite Order of Saint John the Baptist, an order of the Greek Catholic Church * BC Card, a Korean credit card company * Bella Center, a conference center in Copenhagen, Denmark * Brasseries du Cameroun, a brewery in Cameroon (also known as ''SABC'') * Brunswick Corporation (NYSE ticker symbol BC) Education United States * Bakersfield College, a college in Bakersfield, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
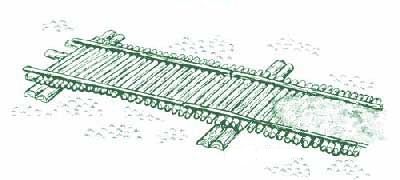
Corduroy Road
A corduroy road or log road is a type of road or timber trackway made by placing logs, perpendicular to the direction of the road over a low or swampy area. The result is an improvement over impassable mud or dirt roads, yet rough in the best of conditions and a hazard to horses due to shifting loose logs. Corduroy roads can also be built as a foundation for other surfacing. If the logs are buried in wet, acidic, anaerobic soils such as peat or muskeg, they decay very slowly. A few corduroy road foundations that date back to the early 20th century still exist in North America. One example is the Alaska Highway between Burwash Landing and Koidern, Yukon, Canada, which was rebuilt in 1943, less than a year after the original route was graded on thin soil and vegetation over permafrost, by using corduroy, then building a gravel road on top. During the 1980s, the gravel was covered with a chip-seal. The late 1990s saw replacement of this road with modern road construction, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jersey Barrier
A Jersey barrier, Jersey wall, or Jersey bump is a modular concrete or plastic barrier employed to separate lanes of traffic. It is designed to minimize vehicle damage in cases of incidental contact while still preventing vehicle crossovers resulting in a likely head-on collision. Jersey barriers are also used to reroute traffic and protect pedestrians and workers during highway construction. They are named after the U.S. state of New Jersey which first started using the barriers as separators between lanes of a highway in the 1950s. The barriers are also known as a K-rail, a term stipulated in the California Department of Transportation specification for temporary concrete traffic barriers which first started using concrete median barriers in the mid-1940s. Over time, different variants were created. Taller variants, such as the Ontario Tall Wall, proved more effective at stopping vehicles and had the added advantage of blocking most oncoming headlights. More modular varian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Renfrew, British Columbia
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Hamburg, Manchester and Duluth; these access the sea via rivers or canals. Because of their roles as ports of entry for immigrants as well as soldiers in wartime, many port cities have experienced dramatic multi-ethnic and multicultural changes throughout their histories. Ports are extremely important to the global economy; 70% of global merchandise trade by value passes through a port. For this reason, ports are also often densely populated settlements that provide the labor for processing and handling goods and related services for the ports. Today by far the greatest growth in port development is in Asia, the continent with some of the world's largest and busiest ports, such as Singapore and the Chinese ports of Shanghai and Ningbo-Zhou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jordan River, British Columbia
Jordan River, founded as and still officially gazetted as River Jordan, is a small settlement on the west coast of Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada, located approximately west of Victoria. Established as a logging camp in the late 19th century, Jordan River has Vancouver Island's second hydroelectric power plant. It is popular amongst winter surfers. The eastern terminus of the Juan de Fuca Trail is at China Beach, west of Jordan River. History In 1790, the Spanish navigator and explorer Lieutenant Francisco de Eliza rebuilt a Spanish fort at Nootka Sound and subsequently explored the area between Nootka Sound and present day Victoria, BC. Originally named Rio Hermoso by his Sub-Lieutenant Manuel Quimper on June 14, 1790, the name was changed later that year to Rio Jordan when the Carta Reducida was made by Gonzalo López de Haro. The name change from Rio Hermoso to Rio Jordan is attributed to Francisco de Eliza's chaplain, Alejandro Jordan. Subsequent char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)