|
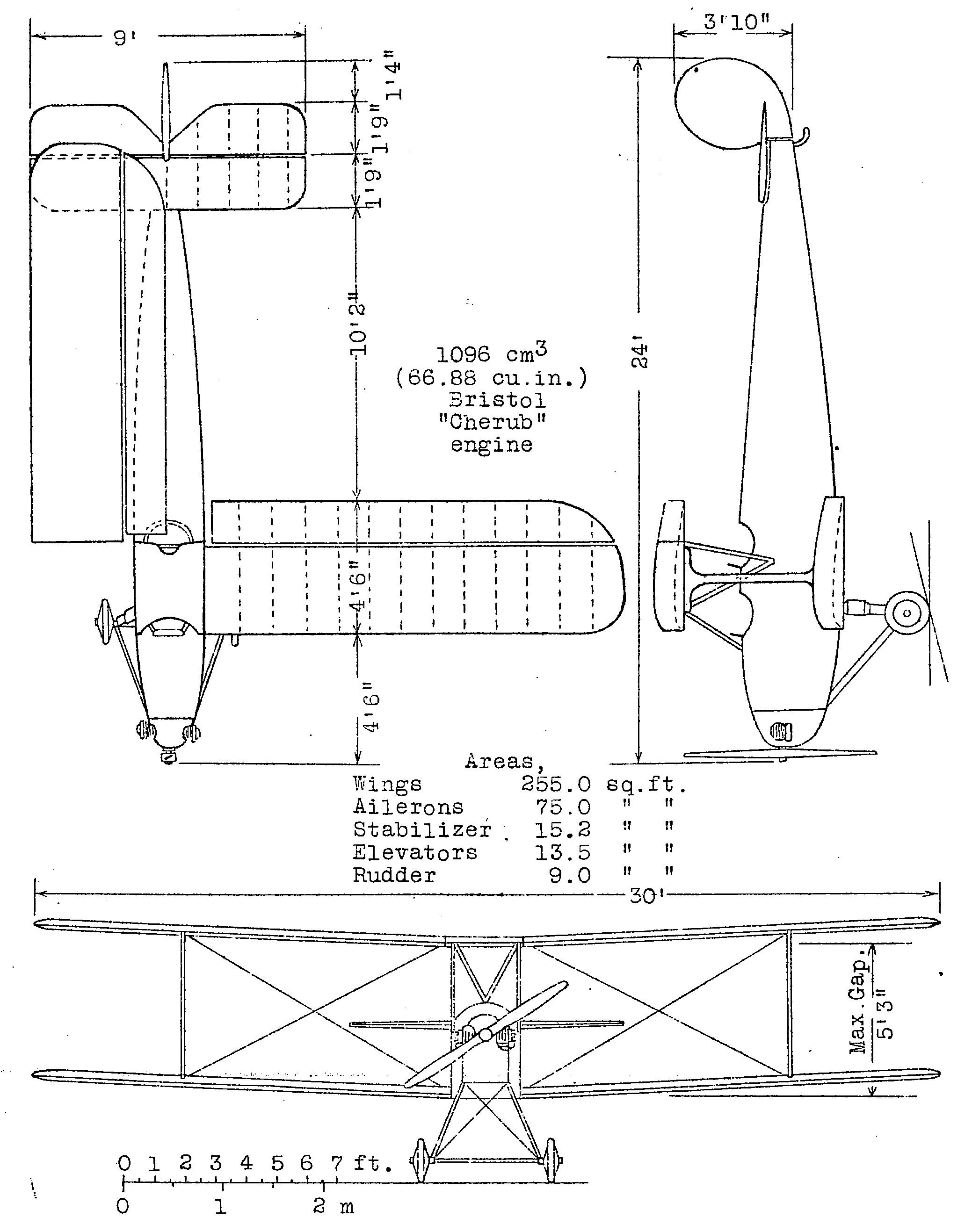
Bristol Brownie
The Bristol Type 91 Brownie was a light sports aircraft produced in the United Kingdom by the Bristol Aeroplane Company in 1924. It was a low-wing cantilever monoplane aircraft of conventional configuration with fixed tailskid undercarriage. The pilot and passenger sat in tandem open cockpits. It won the £1,000 pound prize for second place at the Lympne light aircraft trials in October 1924. Design Bristol had not built an aircraft to compete in the 1923 Lympne light aircraft trials, which had been for aircraft with engines of 750 cc or less, making use of Bristol's Cherub engine impossible. The rules were changed for the 1924 trials, permitting engines of up to 1,100 cc to be used, and accordingly Frank Barnwell started design work on a competitor early in 1924. He produced studies for alternative wood and metal aircraft, and after consideration of these the Board of Bristol Aircraft authorised the production of two aircraft on 4 February, adding a third on 5 May. All three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avro Avis
The Avro 562 Avis was a two-seat light biplane designed and built by the A.V.Roe and Company Limited at Hamble for the 1924 Lympne Light Aeroplane Trials. Design and development The Avis was a single-bay unstaggered biplane with full-span ailerons on both upper and lower wings. It had a fixed landing gear with a tailskid and could be powered by a nose-mounted 32 hp Bristol Cherub II engine or a 35 hp Blackburne Thrush radial piston engine.Jackson 1990, p. 222. It had tandem open cockpits. First flown with the Thrush engine prior to the trials, it was refitted with the Cherub, and first flown with this engine by Bert Hinkler at Lympne on 30 September 1924. On the next day it won the Grosvenor Cup at a speed of 65.87 mph.Jackson 1990, pp. 222–223. For the 1926 trials it was re-engined with a 38 hp Blackburne Thrush, being eliminated after a forced landing. In 1927, it was re-engined again with a Bristol Cherub I and passed into private ownership until it w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-wing Aircraft
A monoplane is a fixed-wing aircraft configuration with a single mainplane, in contrast to a biplane or other types of multiplanes, which have multiple planes. A monoplane has inherently the highest efficiency and lowest drag of any wing configuration and is the simplest to build. However, during the early years of flight, these advantages were offset by its greater weight and lower manoeuvrability, making it relatively rare until the 1930s. Since then, the monoplane has been the most common form for a fixed-wing aircraft. Characteristics Support and weight The inherent efficiency of the monoplane is best achieved in the cantilever wing, which carries all structural forces internally. However, to fly at practical speeds the wing must be made thin, which requires a heavy structure to make it strong and stiff enough. External bracing can be used to improve structural efficiency, reducing weight and cost. For a wing of a given size, the weight reduction allows it to fly slower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol Aeroplane Company Aircraft
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in South West England. The wider Bristol Built-up Area is the eleventh most populous urban area in the United Kingdom. Iron Age hillforts and Roman villas were built near the confluence of the rivers Frome and Avon. Around the beginning of the 11th century, the settlement was known as (Old English: 'the place at the bridge'). Bristol received a royal charter in 1155 and was historically divided between Gloucestershire and Somerset until 1373 when it became a county corporate. From the 13th to the 18th century, Bristol was among the top three English cities, after London, in tax receipts. A major port, Bristol was a starting place for early voyages of exploration to the New World. On a ship out of Bristol in 1497, John Cabot, a Venetian, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1920s British Sport Aircraft
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20 * one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album ''63/19'' by Kool A.D. * ''Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle. * "Nineteen", a song by Bad4Good from the 1992 album ''Refugee'' * "Nineteen", a song by Karma to Burn from the 2001 album ''Almost Heathen''. * "Nineteen" (song), a 2007 song by American singer Billy Ray Cyrus. * "Nineteen", a song by Tegan and Sara from the 2007 album '' The Con''. * "XIX" (song), a 2014 song by Slipkno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westland Woodpigeon
__NOTOC__ The Westland Woodpigeon was a British two-seat light biplane designed to compete in the 1924 Lympne light aircraft trials. Design and development The Woodpigeon was a conventional wooden biplane powered by a 32 hp (24 kW) Bristol Cherub III engine. Two aircraft were built. The first made its first flight on 14 September 1924;James, Derek M. ''Westland Aircraft since 1915''. London: Putnam, 1991. , p. 111 the second aircraft, registered ''G-EBJV'', flew in trials but was not successful. The second aircraft was re-engined with a 30 hp (22 kW) ABC Scorpion and increased wingspan in 1926 for the 1926 Lympne trials but again was not successful. In 1927 the two aircraft were re-engined with 60 hp (45 kW) Anzani 6 radials and redesignated Woodpigeon IIs Jackson 1974, page 332 Variants ;Woodpigeon I : Bristol Cherub III-powered variant, two built. ;Woodpigeon II :Two Woodpigeon Is re-engined with Anzani engines. Specifications (Woodpigeon I) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vickers Vagabond
The Vickers Vagabond was Vickers' entrant for the second Lympne light aircraft competition, held in 1924. It was a conventional small biplane, with a very unusual method of trimming. It was eliminated from the trials at an early stage and only one was built. Development Following the first Lympne trials held in 1923 for single-seat motor-gliders, the Air Ministry organised a similar event in 1924, this time for low-powered two-seat aircraft. The engine capacity limit was set at 1,100 cc. and, as before, the wings had to fold for easy transport and storage. The trials took place between 29 September and 4 October. Several companies built aircraft for them, including the Blackburn Bluebird, Hawker Cygnet, Supermarine Sparrow and two from Westland, the Woodpigeon and Widgeon. The Type 98 Vagabond was Vickers' entry. It was a single-bay, wire-braced biplane with wings of constant chord except towards the rounded trailing tips. The wings had equal span and carried marke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supermarine Sparrow
The Supermarine Sparrow (later called the Sparrow I) was a British two-seat light biplane designed by R.J. Mitchell and built at Supermarine's works at Woolston, Southampton. It first flew on 11 September 1924. After being rebuilt in 1926 as a parasol monoplane, it was re-designated Sparrow II. The Sparrow was Supermarine's earliest landplane. It was a wooden two-seat sesquiplane powered by a Blackburne Thrush. It had foldable wings with different cross sections; to allow the aircraft to take-off and land over short distances, Mitchell gave the wings had a high angle of attack. The Sparrow behaved erratically during tests. It was entered for the 1924 Two-Seater Light Aeroplane Competition but suffered engine failure during the competition. A substitute engine failed during the race, forcing the pilot to land at short notice, and the plane was eliminated. Sparrow II was heavier and slower than its predecessor. It was entered for the 1926 competition at Lympne but, having m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parnall Pixie
The Parnall Pixie was a low powered British single-seat monoplane light aircraft originally designed to compete in the Lympne, UK trials for motor-gliders in 1923, where it was flown successfully by Norman Macmillan. It had two sets of wings, one for cross-country flights and the other for speed; it later appeared as a biplane which could be converted into a monoplane. Design and development Though only three Parnall Pixies were built, they appeared with a remarkable variety of wings; a normal span monoplane (Pixie I); a short span monoplane (Pixie II); a biplane readily convertible to a monoplane (Pixie IIIA); and a non-convertible monoplane version of the latter, with a greater span than the Pixie I. The first Pixie was designed to compete in the Lympne Light Aeroplane Trials of 1923, organised by the Royal Aero Club for what they described as single-seat motor-gliders. The intention was to develop economical private aviation, so the engine size was limited to 750 cc with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawker Cygnet
The Hawker Cygnet was a British ultralight biplane aircraft of the 1920s. Background In 1924, the Royal Aero Club organized a Light Aircraft Competition. £3000 was offered in prizes. An entry was made by Hawker Aircraft, which was a design by Sydney Camm, the Cygnet. Camm had joined Hawker the previous year. Two aircraft were built (''G-EBMB'' and ''G-EBJH'') and were entered in the competition, held in 1924 at Lympne Aerodrome, by T. O. M. Sopwith and Fred Sigrist. The aircraft were flown by Longton and Raynham and came in 4th and 3rd places respectively. In 1925, ''G-EBMB'' was entered again in the 100 mi (161 km) International Handicap Race, this time flown by George Bulman, who won at a speed of 75.6 mph (121.7 km/h). At the same meeting, the Cygnet came in 2nd in the 50 mi (80 km) Light Aeroplane Race. In 1926, both aircraft were entered in the competition piloted by Bulman and Flying Officer Ragg, taking first and second place respect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnosspelius Gull
__NOTOC__ The Gnosspelius Gull was a 1920s British experimental ultra-light monoplane designed by Major O.T. Gnosspelius and built by Short Brothers at Rochester for the 1923 Lympne light aircraft trials.Jackson 1974, page 315 Development Gnosspelius was head of the research department of Short Brothers, for whom he had devised an ingenious mechanism for testing aerofoil sections, the Gnosspelius Aerodynamic Pendulum. 21 December 1921 Tests using this had indicated that incorporating a small step into the upper surface of the wing at the point of its greatest thickness would reduce [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gloster Gannet
The Gloster Gannet was a single-seat single-engined light aircraft built by the Gloucestershire Aircraft Company Limited of Cheltenham, United Kingdom, to compete in the 1923 Lympne Trials. Engine development problems prevented it from taking part. Development In 1923 the Royal Aero Club (RAeC) organised what became known as the Lympne light aircraft trials after the airfield where they were based, though the RAeC referred to the competing aircraft as ''motor-gliders''. The intention was to develop economical private aviation, so the engine size was limited to 750 cc with immediate consequences for aircraft size and weight. Various sponsors provided attractive prizes, particularly the total of £1500 jointly from the Duke of Sutherland and the Daily Mail. The event took place from 8–13 October 1923. The Gannet was Gloster's intended entry. It was a small, single-bay biplane, one of the smallest aircraft built in Britain. It was powered by a specially designed Card ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |