|
Brienner Straße (Munich)
The neoclassical Brienner Straße in Munich is one of four royal avenues next to the Ludwigstraße, the Maximilianstraße and the Prinzregentenstraße. The boulevard was constructed from 1812 onwards, during the reigns of Maximilian I Joseph of Bavaria and his successor Ludwig I, in accordance with a plan by Karl von Fischer and Friedrich Ludwig von Sckell. The avenue is named after the Battle of Brienne. Architecture The Brienner Straße starts at ''Odeonsplatz'' on the northern fringe of the Old Town close to the Residenz, and runs from east to west passing ''Wittelsbacher Platz'' and the circular ''Karolinenplatz'' and finally opens into the impressive '' Königsplatz'', designed with the " Doric" ''Propylaea'', the " Ionic" ''Glyptothek'' and the " Corinthian" '' State Museum of Classical Art'', behind which St. Boniface's Abbey was erected. In the westernmost part of the Brienner Straße, between Königsplatz and Stiglmeierplatz, the Munich ''Volkstheater'' (People's T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassical Architecture
Neoclassical architecture is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy and France. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing styles of architecture in most of Europe for the previous two centuries, Renaissance architecture and Baroque architecture, already represented partial revivals of the Classical architecture of ancient Rome and (much less) ancient Greek architecture, but the Neoclassical movement aimed to strip away the excesses of Late Baroque and return to a purer and more authentic classical style, adapted to modern purposes. The development of archaeology and published accurate records of surviving classical buildings was crucial in the emergence of Neoclassical architecture. In many countries, there was an initial wave essentially drawing on Roman architecture, followed, from about the start of the 19th century, by a second wave of Greek Revival archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
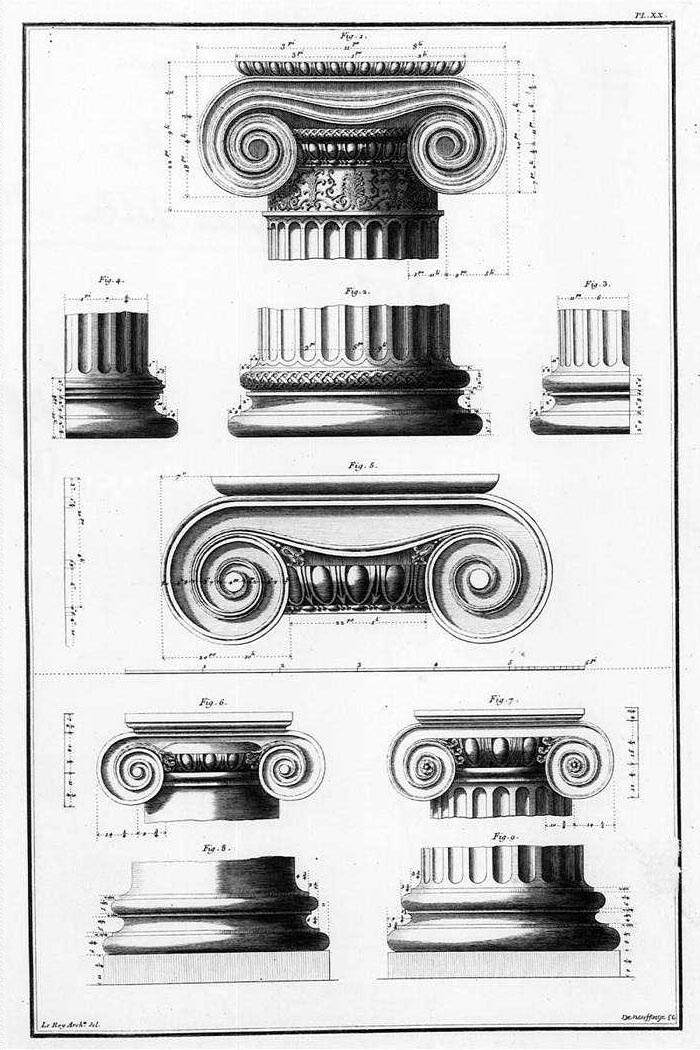
Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. The Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital, which have been the subject of much theoretical and practical discourse, based on a brief and obscure p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Navarino
The Battle of Navarino was a naval battle fought on 20 October (O. S. 8 October) 1827, during the Greek War of Independence (1821–29), in Navarino Bay (modern Pylos), on the west coast of the Peloponnese peninsula, in the Ionian Sea. Allied forces from Britain, France, and Russia decisively defeated Ottoman and Egyptian forces which were trying to suppress the Greeks, thereby making Greek independence much more likely. An Ottoman armada which, in addition to Imperial warships, included squadrons from the ''eyalets'' (provinces) of Egypt and Tunis, was destroyed by an Allied force of British, French and Russian warships. It was the last major naval battle in history to be fought entirely with sailing ships, although most ships fought at anchor. The Allies' victory was achieved through superior firepower and gunnery. The context of the three Great Powers' intervention in the Greek conflict was the Russian Empire's long-running expansion at the expense of the decaying Ottom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Invasion Of Russia
The French invasion of Russia, also known as the Russian campaign, the Second Polish War, the Army of Twenty nations, and the Patriotic War of 1812 was launched by Napoleon Bonaparte to force the Russian Empire back into the continental blockade of the United Kingdom. Napoleon's invasion of Russia is one of the best studied military campaigns in history and is listed among the most lethal military operations in world history. It is characterized by the massive toll on human life: in less than six months nearly a million soldiers and civilians died. On 24 June 1812 and the following days, the first wave of the multinational crossed the Niemen into Russia. Through a series of long forced marches, Napoleon pushed his army of almost half a million people rapidly through Western Russia, now Belarus, in an attempt to destroy the separated Russian armies of Barclay de Tolly and Pyotr Bagration who amounted to around 180,000–220,000 at this time. Within six weeks, Napoleon lost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
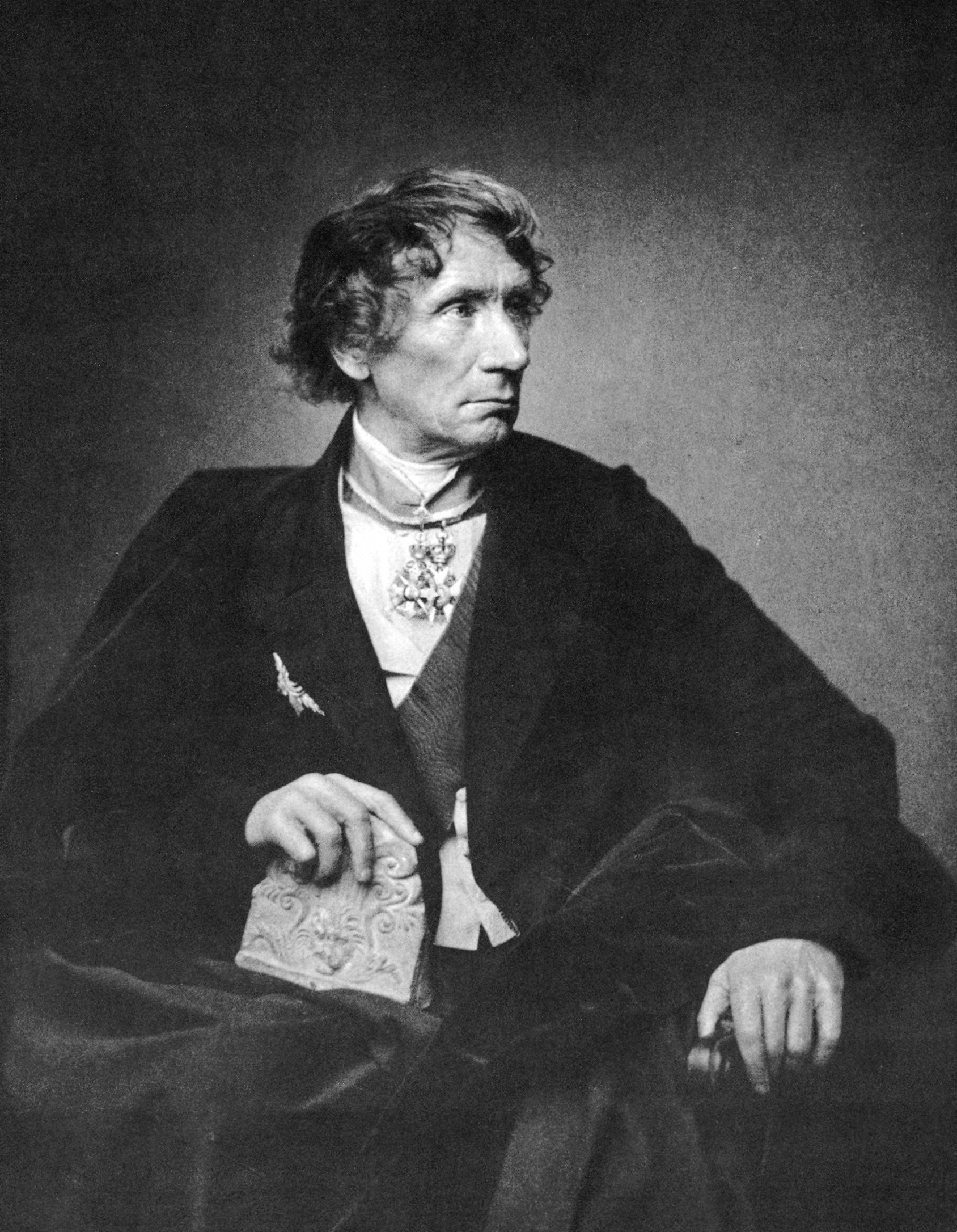
Leo Von Klenze
Leo von Klenze (Franz Karl Leopold von Klenze; 29 February 1784, Buchladen (Bockelah / Bocla) near Schladen – 26 January 1864, Munich) was a German neoclassicist architect, painter and writer. Court architect of Bavarian King Ludwig I, Leo von Klenze was one of the most prominent representatives of Greek revival style. Biography Von Klenze studied architecture and public building finance under Friedrich Gilly in Berlin, and worked as an apprentice to Charles Percier and Pierre François Léonard Fontaine in Paris. Between 1808 and 1813 he was a court architect of Jérôme Bonaparte, King of Westphalia. Later he moved to Bavaria and in 1816 began to work as court architect of Ludwig I. The King's passion for Hellenism shaped the architectural style of von Klenze. He built many neoclassical buildings in Munich, including the Ruhmeshalle and Monopteros temple. On Königsplatz he designed probably the best known modern Hellenistic architectural ensemble. Near Reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lenbachhaus
The Lenbachhaus () is a building housing an art museum in Munich's ''Kunstareal''. The building The Lenbachhaus was built as a Florentine-style villa for the painter Franz von Lenbach between 1887 and 1891 by Gabriel von Seidl and was expanded 1927–1929 by Hans Grässel and again 1969–1972 by Heinrich Volbehr and Rudolf Thönnessen. Some of the rooms have kept their original design. The city of Munich acquired the building in 1924 and opened a museum there in 1929. The latest wing was closed to the public in 2009 to allow the expansion and restoration of the Lenbachhaus by Norman Foster; the 1972 extension was demolished to make way for the new building. The museum reopened in May 2013. The architect placed the new main entrance on Museumsplatz in front of the Propylaea. The new facade, clad in metal tubes made of an alloy of copper and aluminum, will weather with time. The gallery The gallery contains a variety of works by Munich painters and contemporary artists, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinakothek Der Moderne
The Pinakothek der Moderne (, ''Pinakothek of the Modern'') is a modern art museum, situated in central Munich's ''Kunstareal''. Locals sometimes refer to it as the ''Dritte'' ("third") ''Pinakothek'' after the Old and New. It is one of the world's largest museums for modern and contemporary art. The building Designed by German architect Stephan Braunfels, the Pinakothek der Moderne was inaugurated in September 2002 after seven years of construction. The $120 million, 22,000-square-meter building took a decade to finish because of bureaucratic objections to design and cost, which were ultimately bridged by private initiative and financing. The rectilinear facade, dominated by white and grey concrete, is interrupted by large windows and high rise columns, the latter supporting the extensive canopied roof. Each of the four corners of the building, connected by a central domed rotunda, is dedicated to a special collection. The Museum is thus divided into Art (Kunst), Architecture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neue Pinakothek
The Neue Pinakothek (, ''New Pinacotheca'') is an art museum in Munich, Germany. Its focus is European Art of the 18th and 19th centuries, and it is one of the most important museums of art of the nineteenth century in the world. Together with the Alte Pinakothek and the Pinakothek der Moderne, it is part of Munich's "Kunstareal" (the "art area"). The building The museum was founded by King Ludwig I of Bavaria in 1853. The original building constructed by Friedrich von Gärtner and August von Voit was destroyed during World War II. The ruin of the Neue Pinakothek was demolished in 1949. The building was replaced in the late 20th century. Designed by architect , the new postmodern building opened in 1981. Its features include arched windows, keystones, bay windows and stairways. It combines a concrete construction with a stone facade design. History Ludwig began to collect contemporary art already as crown prince in 1809 and his collection was steadily enlarged. When the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alte Pinakothek
The Alte Pinakothek (, ''Old Pinakothek'') is an art museum located in the Kunstareal area in Munich, Germany. It is one of the oldest galleries in the world and houses a significant collection of Old Master paintings. The name Alte (Old) Pinakothek refers to the time period covered by the collection—from the fourteenth to the eighteenth century. The Neue Pinakothek, re-built in 1981, covers nineteenth-century art, and Pinakothek der Moderne, opened in 2002, exhibits modern art. All three galleries are part of the Bavarian State Painting Collections, an organization of the Free state of Bavaria. The building King Ludwig I of Bavaria ordered Leo von Klenze to erect a new building for the gallery for the Wittelsbach collection in 1826. The Alte Pinakothek was the largest museum in the world and structurally and conceptually well advanced through the convenient accommodation of skylights for the cabinets. Even the Neo-Renaissance exterior of the Pinakothek clearly stands ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kunstareal
The Kunstareal (, "art district") is a museum quarter in the city centre of Munich, Germany. Area of arts It consists of the three "Pinakotheken" galleries ( Alte Pinakothek, Neue Pinakothek and Pinakothek der Moderne), the Glyptothek, the Staatliche Antikensammlungen (both museums are specialized in Greek and Roman art), the Lenbachhaus, the Museum Brandhorst (a private collection of modern art) and several galleries. Also the Staatliche Sammlung für Ägyptische Kunst (the state collection of Egypt art) was moved to the Kunstareal in 2013. The history of the museums in this area of Munich began in 1816 with the erection of the Glyptothek at Königsplatz and was completed with the new building for the Egyptian Museum (2012) and the extension of the Lenbachhaus (2013). Close to the Pinakothek der Moderne the neo-classical ''Palais Dürckheim'' (constructed in 1842–1844) served at times as a building dedicated to bringing art closer to the visitors, while the adjoining '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
München - Karolinenplatz 2
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the States of Germany, German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the List of cities in Germany by population, third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and Hamburg, and thus the largest which does not constitute its own state, as well as the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 11th-largest city in the European Union. The Munich Metropolitan Region, city's metropolitan region is home to 6 million people. Straddling the banks of the River Isar (a tributary of the Danube) north of the Northern Limestone Alps, Bavarian Alps, Munich is the seat of the Bavarian Regierungsbezirk, administrative region of Upper Bavaria, while being the population density, most densely populated municipality in Germany (4,500 people per km2). Munich is the second-largest city in the Bavarian dialects, Bavarian dialect area, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Münchner Volkstheater
Münchner Volkstheater, or Munich People’s Theater, is a company based in the Bavarian capital and operated by the cultural office of the city government. Its original performing home opened in 1903. This was rebuilt in 1955, in 1983 and finally in 2021. It now can hold over 800 spectators. Since 2002, Christian Stückl has served as the company’s Intendant. Old building In 1903, the architects Gerstenecker and Tittrich in the Josephspitalstraße in the district Altstadt-Lehel, designed and built a reinforced concrete constructed building. It opened with Schiller's ''Kabale und Liebe'' (''Intrigue and Love''). It had about 1000 seats. Then actress Elise Aulinger received her first theatre engagement here. The first performance took place on 10 November 1903. The manager initially was actor Ernst Schrumpf. Administratively, Wilhelm Braun assisted him. A report in the Munich Ratsch-Kathl from November 16, 1904, it can be seen that the theater had already gained recognition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_-_facade_on_Piazza_dei_signori.jpg)




.jpg)