|
Bridgeport, Chicago
Bridgeport is one of the 77 community areas in Chicago, on the city's South Side, bounded on the north by the South Branch of the Chicago River, on the west by Bubbly Creek, on the south by Pershing Road, and on the east by the Union Pacific railroad tracks. Neighboring communities are Pilsen across the river to the north, McKinley Park to the west, Canaryville to the south, and Armour Square to the east. Bridgeport has been the home of five Chicago mayors. Once known for its racial intolerance, Bridgeport today ranks as one of the city's most diverse neighborhoods. History Bridgeport was initially called the " Portage de Checagou" (or Portage des Chenes), and Fr. Jacques Marquette and trader Louis Joliet traveled through in 1673. It technically remained under French control until 1763, then British control until 1783 or 1795 (since British traders based out of Detroit or Canada used it). A settler named Charles Lee or Leigh came from Virginia and settled along the sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawrence County, Illinois
Lawrence County is the easternmost county in the U.S. state of Illinois. At the 2020 census, the population was 15,280. Its county seat is Lawrenceville. History Lawrence County was formed in 1821 out of Crawford and Edwards counties. It was named for Capt. James Lawrence, who was killed in action during the War of 1812 while commanding the frigate . Mortally wounded, he gave his men the famous last order, "Don't give up the ship." File:Lawrence County Illinois 1821.png, Lawrence County from its creation in 1821 to 1824 File:Lawrence_County_Illinois_1824.png, Lawrence County between 1824 and 1841 File:Lawrence County Illinois 1841.png, Lawrence County in 1841, when the creation of Richland County reduced Lawrence to its current size Geography According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of , of which is land and (0.5%) is water. Climate and weather In recent years, average temperatures in the county seat of Lawrenceville have ranged from a low of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armour Square, Chicago
Armour Square is a Chicago neighborhood on the city's South Side, as well as a larger, officially defined community area, which also includes Chinatown and the CHA Wentworth Gardens housing project. Armour Square is bordered by Bridgeport to the west, Pilsen to the northwest, Douglas and Grand Boulevard to the east and southeast, and with the Near South Side bordering the area to the north, and Fuller Park bordering its southernmost boundary, along Pershing Road. Armour Square neighborhood Bounded by 18th Street to the north, Pershing Road to the south, the Union Pacific railroad tracks on the west and the Dan Ryan Expressway to the east, Armour Square has historically been a predominantly white, working-class neighborhood with a particularly significant population of both Italian-Americans and Croatian-Americans. With its location being immediately south of Chinatown, today the neighborhood also has a large Asian population as well. Armour Square's most recognizable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Baptiste Beaubien
Jean Baptiste Beaubien (September 5, 1787 - January 5, 1864), a multi-lingual fur-trader born in Detroit, Michigan, became an early resident of what became Chicago, Illinois, as well as an early civic and militia leader in Cook County, Illinois during the Black Hawk War, before moving to Du Page County, Illinois in his final years. Early and family life Jean Baptiste Beaubien was born in Detroit to the former Marie-Josephette Douaire De Bondy, and her husband, Joseph Cuillerier Beaubien, of a prominent local French-Canadian family. The couple had 10 children, and his father also had 15 children from a prior marriage. His younger brother Mark Beaubien (1800-1881) would also move to Chicago in 1826 and achieve some prominence for his Sauganash Hotel. Unlike his friend and competitor, John Kinzie, Beaubien does not appear to have owned slaves, but he did employ free persons of color in 1830. Jean Beaubien married four times, beginning in 1804. He survived three wives and possibly s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Robinson (chief)
Alexander Robinson (1789 – April 22, 1872) (also known as ''Che-che-pin-quay'' or ''The Squinter''), was a British-Ottawa chief born on Mackinac Island who became a fur trader and ultimately settled near what later became Chicago. Multilingual in Odawa, Potawatomi, Ojibwa (or Chippewa), English and French, Robinson also helped evacuate survivors of the Fort Dearborn Massacre in 1812. In 1816, Robinson was a translator for native peoples during the Treaty of St. Louis. He became a Potawatomi chief in 1829 and in that year and in 1833, he and fellow Metis Billy Caldwell negotiated treaties on behalf of the United Nations of Ottawa, Chippewa, and Potawatomi with the United States. Although Robinson helped lead Native Americans across the Mississippi River in 1835, unlike Caldwell, Robinson returned to the Chicago area by 1840 and lived as a respected citizen in western Cook County until his death decades later. Early and family life Born to an Ottawa mother and a Scots-Irish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Métis In The United States
The Métis ( ; Canadian ) are Indigenous peoples who inhabit Canada's three Prairie Provinces, as well as parts of British Columbia, the Northwest Territories, and the Northern United States. They have a shared history and culture which derives from specific mixed European (primarily French) and Indigenous ancestry which became a distinct culture through ethnogenesis by the mid-18th century, during the early years of the North American fur trade. In Canada, the Métis, with a population of 624,220 as of 2021, are one of three major groups of Indigenous peoples that were legally recognized in the Constitution Act of 1982, the other two groups being the First Nations and Inuit. Smaller communities who self-identify as Métis exist in Canada and the United States, such as the Little Shell Tribe of Chippewa Indians of Montana. The United States recognizes the Little Shell Tribe as an Ojibwe Native American tribe. Alberta is the only Canadian province with a recognized Métis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackhawk War
The Black Hawk War was a conflict between the United States and Native Americans led by Black Hawk, a Sauk leader. The war erupted after Black Hawk and a group of Sauks, Meskwakis (Fox), and Kickapoos, known as the "British Band", crossed the Mississippi River, into the U.S. state of Illinois, from Iowa Indian Territory in April 1832. Black Hawk's motives were ambiguous, but he was apparently hoping to reclaim land sold to the United States in the disputed 1804 Treaty of St. Louis. U.S. officials, convinced that the British Band was hostile, mobilized a frontier militia and opened fire on a delegation from the Native Americans on May 14, 1832. Black Hawk responded by successfully attacking the militia at the Battle of Stillman's Run. He led his band to a secure location in what is now southern Wisconsin and was pursued by U.S. forces. Meanwhile, other Native Americans conducted raids against forts and colonies largely unprotected with the absence of the militia. Some Ho- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Dearborn Massacre
The Battle of Fort Dearborn (sometimes called the Fort Dearborn Massacre) was an engagement between United States troops and Potawatomi Native Americans that occurred on August 15, 1812, near Fort Dearborn in what is now Chicago, Illinois (at that time, wilderness in the Illinois Territory). The battle, which occurred during the War of 1812, followed the evacuation of the fort as ordered by the commander of the United States Army of the Northwest, William Hull. The battle lasted about 15 minutes and resulted in a complete victory for the Native Americans. After the battle, Fort Dearborn was burned down. Some of the soldiers and settlers who had been taken captive were later ransomed. Following the battle, the federal government became convinced that all Indians had to be removed from the territory and the vicinity of any settlements, as settlers continued to migrate to the area. The fort was rebuilt in 1816. Background Fort Dearborn was constructed by United States troops under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ho-Chunk
The Ho-Chunk, also known as Hoocągra or Winnebago (referred to as ''Hotúŋe'' in the neighboring indigenous Iowa-Otoe language), are a Siouan-speaking Native American people whose historic territory includes parts of Wisconsin, Minnesota, Iowa, and Illinois. Today, Ho-Chunk people are enrolled in two federally recognized tribes, the Ho-Chunk Nation of Wisconsin and the Winnebago Tribe of Nebraska. The Winnebago Tribe of Nebraska have an Indian reservation in Nebraska. While related, the two tribes are distinct federally recognized sovereign nations and peoples, each having its own constitutionally formed government and completely separate governing and business interests. Since the late 20th century, both tribal councils have authorized the development of casinos. The Ho-Chunk Nation is working on language restoration and has developed a Hoocąk-language iOS app. Since 1988, it has pursued a claim to the Badger Army Ammunition Plant as traditional territory; the area has si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
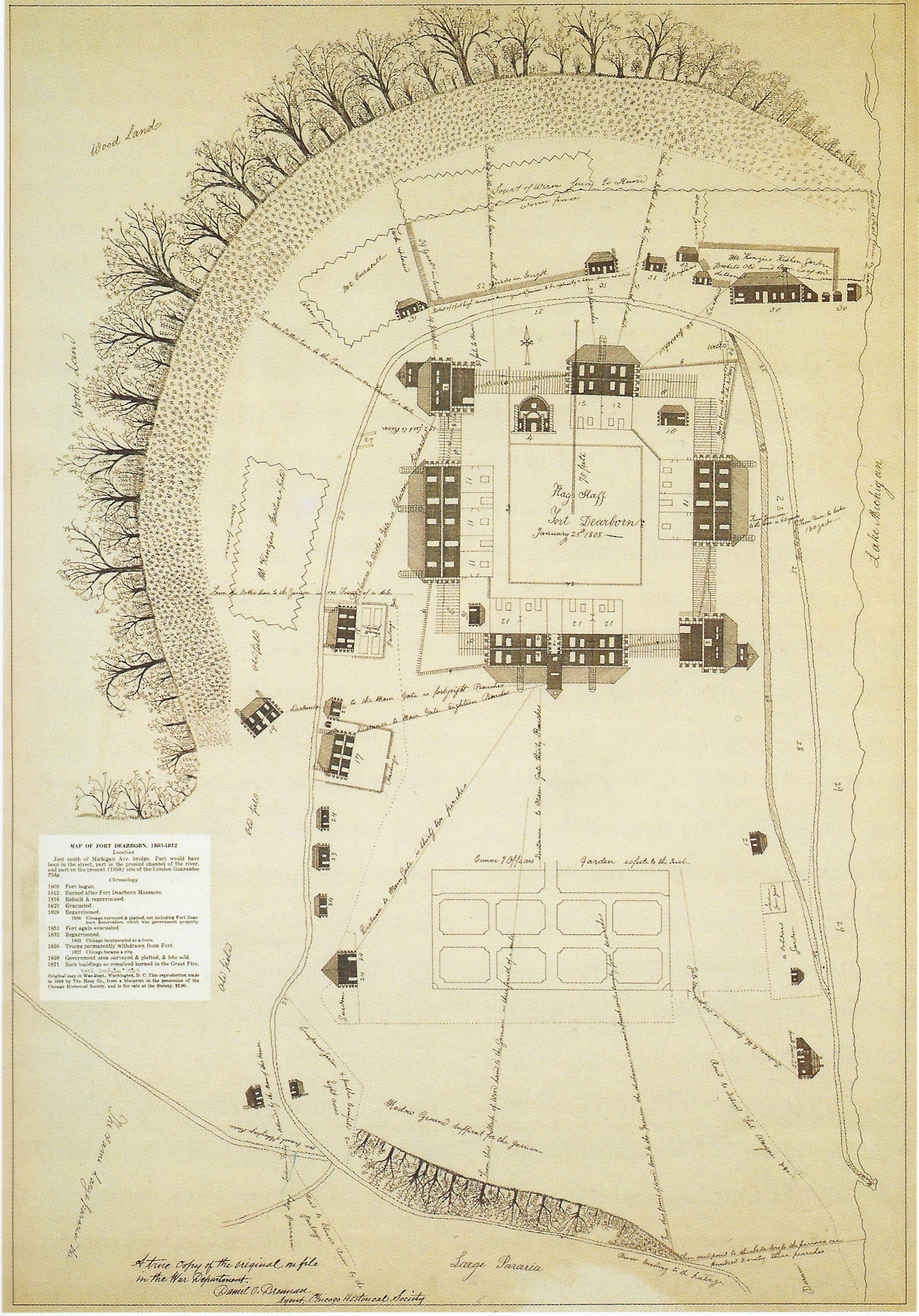
Fort Dearborn
Fort Dearborn was a United States fort built in 1803 beside the Chicago River, in what is now Chicago, Illinois. It was constructed by troops under Captain John Whistler and named in honor of Henry Dearborn, then United States Secretary of War. The original fort was destroyed following the Battle of Fort Dearborn during the War of 1812, and a second fort was constructed on the same site in 1816. By 1837, the fort had been de-commissioned. Parts of the fort were lost to the widening of the Chicago River in 1855, and a fire in 1857. The last vestiges of Fort Dearborn were destroyed in the Great Chicago Fire of 1871. The site of the fort is now a Chicago Landmark, located in the Michigan–Wacker Historic District. Background Historic events The history of human activity in the Chicago area prior to the arrival of European explorers is mostly unknown. In 1673, an expedition headed by Louis Jolliet and Jacques Marquette was the first recorded to have crossed the Chicago Portage a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Michigan
Lake Michigan is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume () and the third-largest by surface area (), after Lake Superior and Lake Huron. To the east, its basin is conjoined with that of Lake Huron through the wide, deep, Straits of Mackinac, giving it the same surface elevation as its easterly counterpart; the two are technically a single lake. Lake Michigan is the world's largest lake by area in one country. Located in the United States, it is shared, from west to east, by the states of Wisconsin, Illinois, Indiana, and Michigan. Ports along its shores include Milwaukee and the City of Green Bay in Wisconsin; Chicago in Illinois; Gary in Indiana; and Muskegon in Michigan. Green Bay is a large bay in its northwest, and Grand Traverse Bay is in the northeast. The word "Michigan" is believed to come from the Ojibwe word (''michi-gami'' or ''mishigami'') meaning "great water". History Some of most studied ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Joliet
Louis Jolliet (September 21, 1645after May 1700) was a French-Canadian explorer known for his discoveries in North America. In 1673, Jolliet and Jacques Marquette, a Jesuit Catholic priest and missionary, were the first non-Natives to explore and map the Upper Mississippi River. Early life Jolliet was born in 1645 in Beaupré, a French settlement near Quebec City, to Jean Jolliet and Marie D'Abancourt. When he was six years old, his father died; his mother then married a successful merchant, Geoffroy Guillot dit Lavalle, until his death in 1665. Shortly after the passing of his mother's second husband, she was married to Martin Prevost until her death in 1678. Jolliet's stepfather owned land on the Ile d'Orleans, an island in the Saint Lawrence River in Quebec that was home to First Nations in Canada, First Nations. Jolliet spent much time on Ile d'Orleans, so it was likely that he began speaking Indigenous languages of the Americas at a young age. Besides French language, French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Marquette
Jacques Marquette S.J. (June 1, 1637 – May 18, 1675), sometimes known as Père Marquette or James Marquette, was a French Jesuit missionary who founded Michigan's first European settlement, Sault Sainte Marie, and later founded Saint Ignace. In 1673, Marquette, with Louis Jolliet, an explorer born near Quebec City, was the first European to explore and map the northern portion of the Mississippi River Valley. Early life Jacques Marquette was born in Laon, France, on June 1, 1637. He came of an ancient family distinguished for its civic and military services. Marquette joined the Society of Jesus at age 17. He studied and taught in France for several years, then the Jesuits assigned him to New France in 1666 as a missionary to the indigenous peoples of the Americas. When he arrived in Quebec, he was assigned to Trois-Rivières on the Saint Lawrence River, where he assisted Gabriel Druillettes and, as preliminary to further work, devoted himself to the study of the local lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |