|
Brewster Islands Military Reservation
Brewster Islands Military Reservation was a coastal defense site located on Great Brewster Island and Outer Brewster Island in Boston Harbor, Massachusetts as part of the Harbor Defenses of Boston. History Outer Brewster Island was acquired by the US government in 1913, followed by Great Brewster Island in 1917. In 1920 there was a proposal to build a naval-type turret with two 16-inch guns on Great Brewster Island, but this was not implemented. Calf Island Military Reservation was also considered, but the battery was finally built (without a turret) as Fort Duvall.Parkman, pp. 123-125 The Brewster Islands Military Reservation was built in World War II on these islands. Its mission was to protect Boston Harbor from possible air and naval attack. It never fired its guns, but it did play an important part in the defense of the harbor. Great Brewster Island This island had an observation post and mine casemate for controlling a minefield in the harbor. The island also had an Ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harbor Defenses Of Boston
The Harbor Defenses of Boston was a United States Army Coast Artillery Corps harbor defense command. It coordinated the coast defenses of Boston, Massachusetts from 1895 to 1950, beginning with the Endicott program. These included both coast artillery forts and underwater minefields. The command originated circa 1895 as the Boston Artillery District, was renamed Coast Defenses of Boston in 1913, and again renamed Harbor Defenses of Boston in 1925.Stanton, pp. 455-481Rinaldi, pp. 165-166Berhow, p. 430-434 History Early Boston forts Colonial period Boston Harbor's principal coastal fort of the colonial era was Castle William, whose site was first fortified in 1634 and called "the Castle" until 1692, when it was renamed for William III, the King of England at the time. It is one of the oldest continuously fortified sites in the northeastern United States; however, the site of Fort William and Mary near Portsmouth, New Hampshire was fortified at least two years previously. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calf Island Military Reservation
Calf Island Military Reservation was a World War II coastal defense site located on Calf Island in Hull, Massachusetts. History In 1920 there was a proposal to build a naval-type turret with two 16-inch guns on Great Brewster Island, but this was not implemented. Calf Island was also considered, but the battery was finally built (without a turret) as Fort Duvall. The Calf Island Military Reservation was built in 1941 on state land. It consisted of an early SCR-268 radar, searchlight station, and an observation post. It was returned to the state in 1946. The site today The site today consists of the foundation of the observation tower. See also * Seacoast defense in the United States * United States Army Coast Artillery Corps * List of military installations in Massachusetts References * * * External links List of all US coastal forts and batteriesat the Coast Defense Study Group, Inc. website {{FmrMAForts Hull, Massachusetts Boston Harbor islands Military in B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Boston
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military In Boston
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's mili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Military Installations In Massachusetts
This is a list of current and former military installations in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Current military installations in Massachusetts Joint facilities ;Bases * Joint Base Cape Cod (state designation, not federally recognized)USCG Air Station Cape Cod Official Site ;Centers * David S. Connolly Armed Forces Reserve Center * [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Army Coast Artillery Corps
The U.S. Army Coast Artillery Corps (CAC) was an administrative corps responsible for coastal, harbor, and anti-aircraft defense of the United States and its possessions between 1901 and 1950. The CAC also operated heavy and railway artillery during World War I. History As early as 1882 the need for heavy fixed artillery for seacoast defense was noted in Chester A. Arthur's Second Annual Message to Congress where he noted: In 1885 the Endicott Board was convened under the subsequent Grover Cleveland administration, chaired by Secretary of War William Crowninshield Endicott. This board recommended a large-scale program of harbor defenses at 29 ports, including guns, mortars, and mine fields. Most of their recommendations were implemented and new defenses were constructed by the United States Army Corps of Engineers 1895–1905. As the defenses were constructed, each harbor or river's installations were controlled by Artillery Districts, renamed Coast Defense Commands in 191 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seacoast Defense In The United States
Seacoast defense was a major concern for the United States from its independence until World War II. Before Military aviation, airplanes, many of America's enemies could only reach it from the sea, making coastal forts an economical alternative to Standing army, standing armies or a large navy. After the 1940s, it was recognized that fixed fortifications were obsolete and ineffective against aircraft and missiles. However, in prior eras foreign fleets were a realistic threat, and substantial fortifications were built at key locations, especially protecting major harbors. The defenses heavily depended on fortifications but also included Submarine mines in United States harbor defense, submarine minefields, nets and boom (navigational barrier), booms, ships, and airplanes. Therefore, all of the armed forces participated in seacoast defense, but the United States Army Corps of Engineers, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers played the central role in constructing fixed defenses. Designs evo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coast Artillery Fire Control System
In the U.S. Army Coast Artillery Corps, the term fire control system was used to refer to the personnel, facilities, technology and procedures that were used to observe designated targets, estimate their positions, calculate firing data for guns directed to hit those targets, and assess the effectiveness of such fire, making corrections where necessary. Fire control instruments The Coast Artillery's early fire control instruments supported optical rangefinding and position finding, either horizontal base or vertical base, with both systems usually present for each fort. Early horizontal base rangefinding required two azimuth (a.k.a. bearing or deflection) instruments, preferably widely separated, and a communications system to transmit data to a plotting room and then to the guns. The instruments were often in bunkers called base end stations, as they defined the endpoints of a baseline. A base end station might be a two-story structure with a plotting room or other instrument ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6-inch Gun M1
The 6-inch gun M1897 (152 mm) and its variants the M1900, M1903, M1905, M1908, and M1 (a.k.a. T2) were coastal artillery pieces installed to defend major American seaports between 1897 and 1945. For most of their history they were operated by the United States Army Coast Artillery Corps. They were installed on disappearing carriages or pedestal (a.k.a. barbette) mountings, and during World War II many were remounted on shielded barbette carriages. Most of the weapons not in the Philippines were scrapped within a few years after World War II. History In 1885, William C. Endicott, President Grover Cleveland's Secretary of War, was tasked with creating the Board of Fortifications to review seacoast defenses. The findings of the board illustrated a grim picture of existing defenses in its 1886 report and recommended a massive $127 million construction program of breech-loading cannons, mortars, floating batteries, and submarine mines for some 29 locations on the US coastline. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
37 Mm Gun M1
The 37 mm gun M1 was an anti-aircraft autocannon developed in the United States. It was used by the US Army in World War II. The gun was produced in a towed variant, or mounted along with two M2 machine guns on the M2/ M3 half-track, resulting in the T28/T28E1/M15/M15A1 series of multiple gun motor carriages. In early World War II, each Army Anti-Aircraft Artillery (AAA) Auto-Weapons battalion was authorized a total of thirty-two 37 mm guns in its four firing batteries, plus other weapons. During World War II the 37 mm gun M1 was deployed in coast defense anti- motor torpedo boat batteries (AMTB) alongside 90 mm guns, usually four 90 mm and two 37 mm guns per battery. Some AMTB batteries consisted of four 37 mm guns, but most sources have little information on these batteries. In the later part of the war the 37 mm gun was typically replaced by the 40 mm Bofors gun M1.McGovern and Smith, p. 43 Components Two gun units were coupled to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
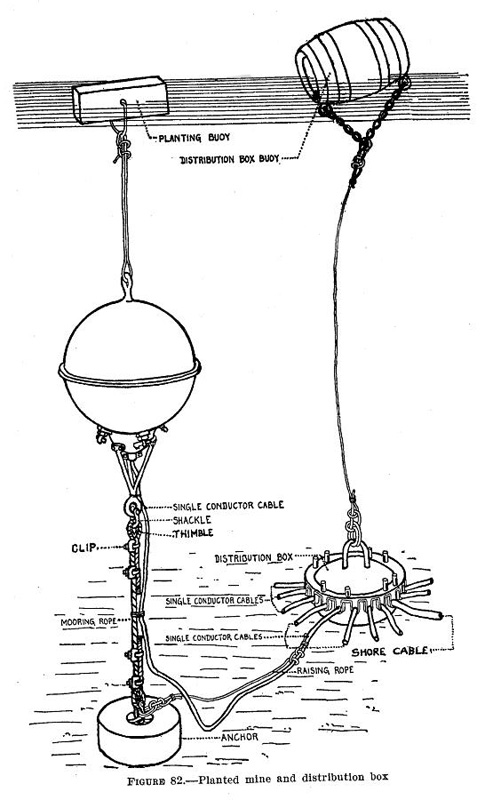
Submarine Mines In United States Harbor Defense
The modern era of defending American harbors with controlled mines or submarine mines (originally referred to as "torpedoes") began in the post-Civil War period, and was a major part of US harbor defenses from circa 1900 to 1947. Brief history In 1866, the United States Army Corps of Engineers established the Engineer School of Application at Willets Point, New York. The first commander of this school, Major Henry Larcom Abbot, was almost single-handedly responsible for designing and supervising the program of research and development that defined the strategy and tactics for the mine defense of American harbors. Abbot experimented with underwater explosives, fuzes, cabling, and electrical equipment for over a decade before publishing the first manuals on the use of mines in coast defense in 1876–77. At least one experimental controlled minefield was emplaced at this time, at Fort Mifflin in Pennsylvania. However, funding of the fortification program of the 1870s was cancell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |