|
Brefeldin A
Brefeldin A is a lactone antiviral produced by the fungus '' Penicillium brefeldianum''. Brefeldin A inhibits protein transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the golgi complex indirectly by preventing association of COP-I coat to the Golgi membrane. Brefeldin A was initially isolated with hopes to become an antiviral drug but is now primarily used in research to study protein transport. History The compound gets its name from a species of anamorph fungus of the ''Penicillium'' genus known as ''Eupenicillium brefeldianum'', though it is found in a variety of species that span several genera. It was first isolated from ''Penicillium decumbens'' in 1958 by V.L. Singleton who initially called it Decumbin. It was later identified as a metabolite by H.P. Siggs who then went on to identify the chemical structure of the compound in 1971. Since then several successful total synthesis methods have been described. Interest in researching brefeldin A was initially lacking due to poo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
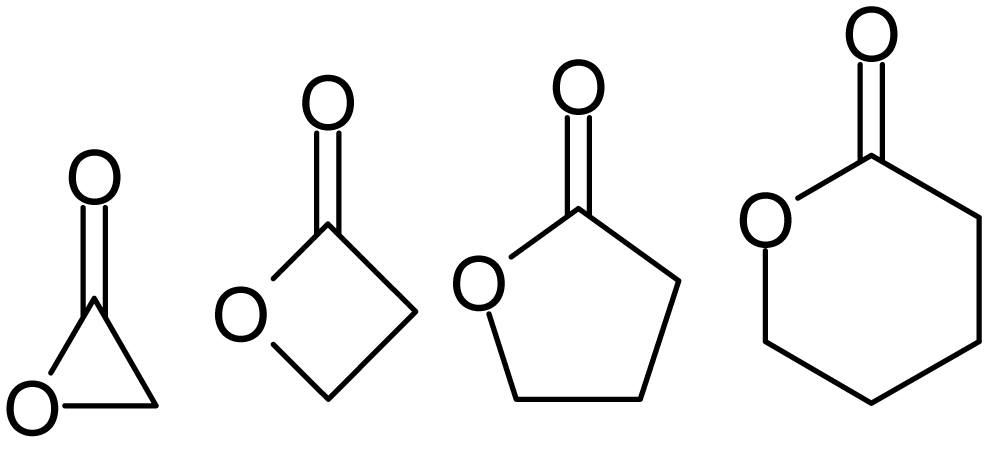
Lactone
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters, containing a 1-oxacycloalkan-2-one structure (), or analogues having unsaturation or heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring. Lactones are formed by intramolecular esterification of the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids, which takes place spontaneously when the ring that is formed is five- or six-membered. Lactones with three- or four-membered rings (α-lactones and β-lactones) are very reactive, making their isolation difficult. Special methods are normally required for the laboratory synthesis of small-ring lactones as well as those that contain rings larger than six-membered. Nomenclature Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (''aceto'' = 2 carbon atoms, ''propio'' = 3, ''butyro'' = 4, ''valero'' = 5, ''capro'' = 6, etc.), with a ''-lactone'' suffix and a Greek letter prefix that specifies the number of carbon atoms in the heterocycle — that is, the distance between the relevant -OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethyl Sulfoxide
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is an organosulfur compound with the formula ( CH3)2. This colorless liquid is the sulfoxide most widely used commercially. It is an important polar aprotic solvent that dissolves both polar and nonpolar compounds and is miscible in a wide range of organic solvents as well as water. It has a relatively high boiling point. DMSO has the unusual property that many individuals perceive a garlic-like taste in the mouth after DMSO makes contact with their skin. In terms of chemical structure, the molecule has idealized Cs symmetry. It has a trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry consistent with other three-coordinate S(IV) compounds, with a nonbonded electron pair on the approximately tetrahedral sulfur atom. Synthesis and production Dimethyl sulfoxide was first synthesized in 1866 by the Russian scientist Alexander Zaytsev, who reported his findings in 1867. Dimethyl sulfoxide is produced industrially from dimethyl sulfide, a by-product of the Kraf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SNARE (protein)
SNARE proteins – " SNAP REceptor" – are a large protein family consisting of at least 24 members in yeasts, more than 60 members in mammalian cells, and some numbers in plants. The primary role of SNARE proteins is to mediate vesicle fusion – the fusion of vesicles with the target membrane; this notably mediates exocytosis, but can also mediate the fusion of vesicles with membrane-bound compartments (such as a lysosome). The best studied SNAREs are those that mediate the neurotransmitter release of synaptic vesicles in neurons. These neuronal SNAREs are the targets of the neurotoxins responsible for botulism and tetanus produced by certain bacteria. Types SNAREs can be divided into two categories: ''vesicle'' or ''v-SNAREs'', which are incorporated into the membranes of transport vesicles during budding, and ''target'' or ''t-SNAREs'', which are associated with nerve terminal membranes. Evidence suggests that t-SNAREs form stable subcomplexes which serve as guides f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncompetitive Inhibitor
Uncompetitive inhibition, also known as anti-competitive inhibition, takes place when an enzyme inhibitor binds only to the complex formed between the enzyme and the substrate (the E-S complex). Uncompetitive inhibition typically occurs in reactions with two or more substrates or products. While uncompetitive inhibition requires that an enzyme-substrate complex must be formed, non-competitive inhibition can occur with or without the substrate present. Uncompetitive inhibition is distinguished from competitive inhibition by two observations: first uncompetitive inhibition cannot be reversed by increasing and second, as shown, the Lineweaver–Burk plot yields parallel rather than intersecting lines. This behavior is found in the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by tertiary amines (R3N). Such compounds bind to the enzyme in its various forms, but the acyl-intermediate-amine complex cannot break down into enzyme plus product. Mechanism As inhibitor binds, the amount of ES comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GTPase
GTPases are a large family of hydrolase enzymes that bind to the nucleotide guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and hydrolyze it to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). The GTP binding and hydrolysis takes place in the highly conserved P-loop "G domain", a protein domain common to many GTPases. Functions GTPases function as molecular switches or timers in many fundamental cellular processes. Examples of these roles include: * Signal transduction in response to activation of cell surface receptors, including transmembrane receptors such as those mediating taste, smell and vision. * Protein biosynthesis (a.k.a. translation) at the ribosome. * Regulation of cell differentiation, proliferation, division and movement. * Translocation of proteins through membranes. * Transport of vesicles within the cell, and vesicle-mediated secretion and uptake, through GTPase control of vesicle coat assembly. GTPases are active when bound to GTP and inactive when bound to GDP. In the generalized recepto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARF Protein
ADP ribosylation factors (ARFs) are members of the ARF family of GTP-binding proteins of the Ras superfamily. ARF family proteins are ubiquitous in eukaryotic cells, and six highly conserved members of the family have been identified in mammalian cells. Although ARFs are soluble, they generally associate with membranes because of N-terminus myristoylation. They function as regulators of vesicular traffic and actin remodelling. The small ADP ribosylation factor (Arf) GTP-binding proteins are major regulators of vesicle biogenesis in intracellular traffic. They are the founding members of a growing family that includes Arl (Arf-like), Arp (Arf-related proteins) and the remotely related Sar (Secretion-associated and Ras-related) proteins. Arf proteins cycle between inactive GDP-bound and active GTP-bound forms that bind selectively to effectors. The classical structural GDP/GTP switch is characterised by conformational changes at the so-called switch 1 and switch 2 regions, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GBF1
Golgi-specific brefeldin A-resistance guanine nucleotide exchange factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GBF1'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-10-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor
Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) are proteins or protein domains that activate monomeric GTPases by stimulating the release of guanosine diphosphate (GDP) to allow binding of guanosine triphosphate (GTP). A variety of unrelated structural domains have been shown to exhibit guanine nucleotide exchange activity. Some GEFs can activate multiple GTPases while others are specific to a single GTPase. Function Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) are proteins or protein domains involved in the activation of small GTPases. Small GTPases act as molecular switches in intracellular signaling pathways and have many downstream targets. The most well-known GTPases comprise the Ras superfamily and are involved in essential cell processes such as cell differentiation and proliferation, cytoskeletal organization, vesicle trafficking, and nuclear transport. GTPases are active when bound to GTP and inactive when bound to GDP, allowing their activity to be regulated by GEFs and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species. Yeasts are unicellular organisms that evolved from multicellular ancestors, with some species having the ability to develop multicellular characteristics by forming strings of connected budding cells known as pseudohyphae or false hyphae. Yeast sizes vary greatly, depending on species and environment, typically measuring 3–4 µm in diameter, although some yeasts can grow to 40 µm in size. Most yeasts reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by the asymmetric division process known as budding. With their single-celled growth habit, yeasts can be contrasted with molds, which grow hyphae. Fungal species that can take both forms (depending on temperature or other conditions) are ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammalian
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class (biology), class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in Female#Mammalian female, females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three ossicles, middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they Genetic divergence, diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant taxon, extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 Order (biology), orders. The largest Order (biology), orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, Mole (animal), moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla (cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, pinniped, seals, and others). In terms of cladistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidizing Agent
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or "Electron acceptor, accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ). In other words, an oxidizer is any substance that oxidizes another substance. The oxidation state, which describes the degree of loss of electrons, of the oxidizer decreases while that of the reductant increases; this is expressed by saying that oxidizers "undergo reduction" and "are reduced" while reducers "undergo oxidation" and "are oxidized". Common oxidizing agents are oxygen, hydrogen peroxide and the halogens. In one sense, an oxidizing agent is a chemical species that undergoes a chemical reaction in which it gains one or more electrons. In that sense, it is one component in an Redox, oxidation–reduction (redox) reaction. In the second sense, an oxidizing agent is a chemical species that transfers electronegative atoms, usually oxygen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |