|
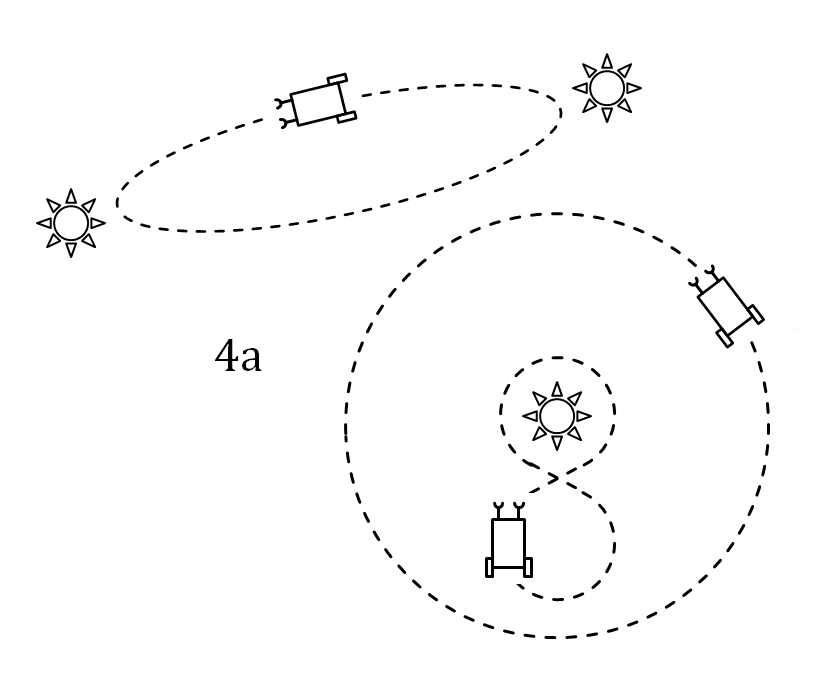
Braitenberg Vehicle
A Braitenberg vehicle is a concept conceived in a thought experiment by the Italian-Austrian cyberneticist Valentino Braitenberg. The book models the animal world in a minimalistic and constructive way, from simple reactive behaviours (like phototaxis) through the simplest vehicles, to the formation of concepts, spatial behaviour, and generation of ideas. For the simplest vehicles, the motion of the vehicle is directly controlled by some sensors (for example photo cells). Yet the resulting behaviour may appear complex or even intelligent. Mechanism A Braitenberg vehicle is an agent that can autonomously move around based on its sensor inputs. It has primitive sensors that measure some stimulus at a point, and wheels (each driven by its own motor) that function as actuators or effectors. In the simplest configuration, a sensor is directly connected to an effector, so that a sensed signal immediately produces a movement of the wheel. Depending on how sensors and wheels are conne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contralateral
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicycle Cart
The term unicycle is often used in robotics and control theory to mean a generalised cart or car moving in a two-dimensional world; these are also often called "unicycle-like" or "unicycle-type" vehicles. This usage is distinct from the literal sense of " one wheeled robot bicycle". These theoretical vehicles are typically shown as having two parallel driven wheels, one mounted on each side of their centre, and (presumably) some sort of offset castor to maintain balance; although in general they could be any vehicle capable of simultaneous arbitrary rotation and translation. An alternative realization uses a single driven wheel with steering, and a pair of idler wheels to give balance and allow a steering torque to be applied. A physically realisable unicycle, in this sense, is a nonholonomic system. This is a system in which a return to the original internal (wheel) configuration does not guarantee return to the original system (unicycle) position. In other words, the system o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
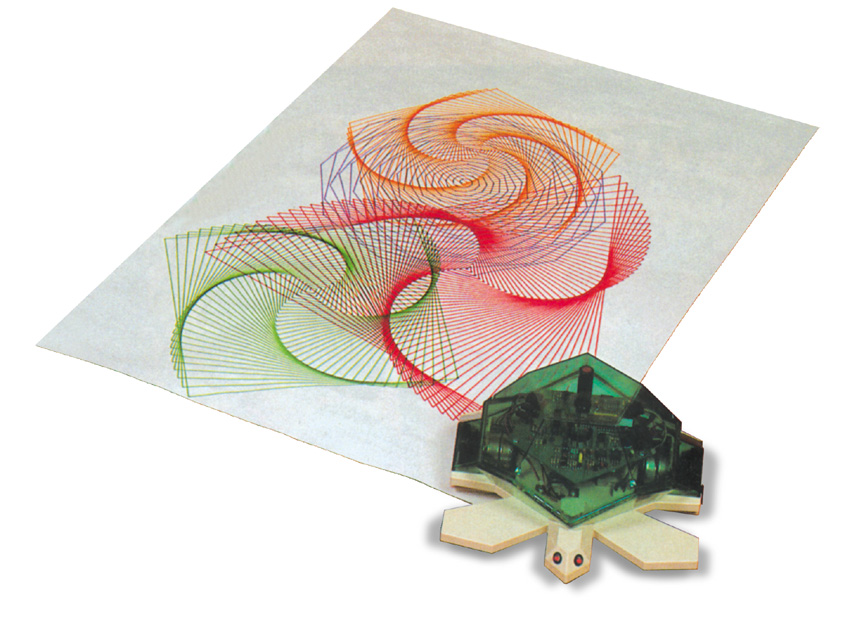
Turtle (robot)
Turtles are a class of educational robots designed originally in the late 1940s (largely under the auspices of researcher William Grey Walter) and used in computer science and mechanical engineering training. These devices are traditionally built low to the ground with a roughly hemispheric (sometimes transparent) shell and a power train capable of a very small turning radius. The robots are often equipped with sensor devices which aid in avoiding obstacles and, if the robot is sufficiently sophisticated, allow it some perception of its environment. Turtle robots are commercially available and are common projects for robotics hobbyists. Turtle robots are closely associated with the work of Seymour Papert and the common use of the Logo programming language in computer education of the 1980s. Turtles specifically designed for use with Logo systems often come with pen mechanisms allowing the programmer to create a design on a large sheet of paper. The original Logo turtle, built by Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BEAM Robotics
BEAM robotics (from biology, electronics, aesthetics and mechanics) is a style of robotics that primarily uses simple analogue circuits, such as comparators, instead of a microprocessor in order to produce an unusually simple design. While not as flexible as microprocessor based robotics, BEAM robotics can be robust and efficient in performing the task for which it was designed. BEAM robots may use a set of the analog circuits, mimicking biological neurons, to facilitate the robot's response to its working environment. Mechanisms and principles The basic BEAM principles focus on a stimulus-response based ability within a machine. The underlying mechanism was invented by Mark W. Tilden where the circuit (or a Nv net of Nv neurons) is used to simulate biological neuron behaviours. Some similar research was previously done by Ed Rietman in 'Experiments In Artificial Neural Networks'. Tilden's circuit is often compared to a shift register, but with several important features makin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Robot
An analog robot is a type of robot which uses analog circuitry to go toward a simple goal such as finding more light or responding to sound. The first real analog robot was invented in the 1940s by William Grey Walter. The name of these robots were ELSIE and ELMER (Electro Mechanical Robot). The original circuitry was developed using two vacuum tubes and a photocell to search and follow a light. Recently a kind of analog robots was developed by Mark Tilden. Some modern analog robots are BEAM robots. Braitenberg Vehicles (described by Valentino Braitenberg) also are frequently analog, consisting of the output of sensors connected to motors without any form of signal processing. See Also * Analog computer An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computer that uses the continuous variation aspect of physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities (''analog signals'') to model the problem being solved. In c ... External links BEAM comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognition
Cognition refers to "the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, intelligence, the formation of knowledge, memory and working memory, judgment and evaluation, reasoning and computation, problem solving and decision making, comprehension and production of language. Imagination is also a cognitive process, it is considered as such because it involves thinking about possibilities. Cognitive processes use existing knowledge and discover new knowledge. Cognitive processes are analyzed from different perspectives within different contexts, notably in the fields of linguistics, musicology, anesthesia, neuroscience, psychiatry, psychology, education, philosophy, anthropology, biology, systemics, logic, and computer science. These and other approaches to the analysis of cognition (such as embodied cognition) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Processing
Information processing is the change (processing) of information in any manner detectable by an observer. As such, it is a process that ''describes'' everything that happens (changes) in the universe, from the falling of a rock (a change in position) to the printing of a text file from a digital computer system. In the latter case, an information processor (the printer) is changing the form of presentation of that text file (from bytes to glyphs). The computers up to this period function on the basis of programs saved in the memory, having no intelligence of their own. In cognitive psychology Within the field of cognitive psychology, information processing is an approach to the goal of understanding human thinking in relation to how they process the same kind of information as computers (Shannon & Weaver, 1963). It arose in the 1940s and 1950s, after World War II (Sternberg & Sternberg, 2012). The approach treats cognition as essentially computational in nature, with ''mind'' b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropotaxis
A taxis (; ) is the movement of an organism in response to a stimulus such as light or the presence of food. Taxes are innate behavioural responses. A taxis differs from a tropism (turning response, often growth towards or away from a stimulus) in that in the case of taxis, the organism has motility and demonstrates guided movement towards or away from the stimulus source. It is sometimes distinguished from a kinesis, a non-directional change in activity in response to a stimulus. Classification Taxes are classified based on the type of stimulus, and on whether the organism's response is to move towards or away from the stimulus. If the organism moves towards the stimulus the taxis are positive, while if it moves away the taxis are negative. For example, flagellate protozoans of the genus ''Euglena'' move towards a light source. This reaction or behavior is called ''positive phototaxis'' since phototaxis refers to a response to light and the organism is moving towards the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ipsilateral
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thought Experiment
A thought experiment is a hypothetical situation in which a hypothesis, theory, or principle is laid out for the purpose of thinking through its consequences. History The ancient Greek ''deiknymi'' (), or thought experiment, "was the most ancient pattern of mathematical proof", and existed before Euclidean mathematics, where the emphasis was on the conceptual, rather than on the experimental part of a thought-experiment. Johann Witt-Hansen established that Hans Christian Ørsted was the first to use the German term ' (lit. thought experiment) circa 1812. Ørsted was also the first to use the equivalent term ' in 1820. By 1883 Ernst Mach used the term ' in a different way, to denote exclusively the conduct of a experiment that would be subsequently performed as a by his students. Physical and mental experimentation could then be contrasted: Mach asked his students to provide him with explanations whenever the results from their subsequent, real, physical experiment differed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |