|
Boswell Reid
Prof David Boswell Reid MD FRSE FRCPE (1805 – 5 April 1863) was a British physician, chemist and inventor. Through reports on public hygiene and ventilation projects in public buildings, he made a reputation in the field of sanitation. He has been called the "grandfather of air-conditioning". Early life Reid was born in Edinburgh in June 1805, the second son of Peter Reid (1777–1838) and his wife, Christian Arnot, eldest daughter of Hugo Arnot of Balcormo, and was the elder brother of Hugo Reid. When born the family appear to have lived with Peter Reid Sr., a vintner at Milne's Square (now known as Milne's Court) off the Royal Mile. His father gained his doctorate as a physician c.1810 and in 1815 the family was living independently at 7 Roxburgh Place in Edinburgh's South Side. David was educated at the High School in Edinburgh then studied Medicine at Edinburgh University, obtained his medical diploma on 12 July 1830, and was admitted a fellow of the Royal College of Physi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Boswell Reid
Prof David Boswell Reid MD FRSE FRCPE (1805 – 5 April 1863) was a British physician, chemist and inventor. Through reports on public hygiene and ventilation projects in public buildings, he made a reputation in the field of sanitation. He has been called the "grandfather of air-conditioning". Early life Reid was born in Edinburgh in June 1805, the second son of Peter Reid (1777–1838) and his wife, Christian Arnot, eldest daughter of Hugo Arnot of Balcormo, and was the elder brother of Hugo Reid. When born the family appear to have lived with Peter Reid Sr., a vintner at Milne's Square (now known as Milne's Court) off the Royal Mile. His father gained his doctorate as a physician c.1810 and in 1815 the family was living independently at 7 Roxburgh Place in Edinburgh's South Side. David was educated at the High School in Edinburgh then studied Medicine at Edinburgh University, obtained his medical diploma on 12 July 1830, and was admitted a fellow of the Royal College of Physi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Association For The Advancement Of Science
The British Science Association (BSA) is a charity and learned society founded in 1831 to aid in the promotion and development of science. Until 2009 it was known as the British Association for the Advancement of Science (BA). The current Chief Executive is Katherine Mathieson. The BSA's mission is to get more people engaged in the field of science by coordinating, delivering, and overseeing different projects that are suited to achieve these goals. The BSA "envisions a society in which a diverse group of people can learn and apply the sciences in which they learn." and is managed by a professional staff located at their Head Office in the Wellcome Wolfson Building. The BSA offers a wide variety of activities and events that both recognize and encourage people to be involved in science. These include the British Science Festival, British Science Week, the CREST Awards, Huxley Summit, Media Fellowships Scheme, along with regional and local events. History Foundation The Asso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leeds And Selby Railway
The Leeds and Selby Railway was an early British railway company and first mainline railway within Yorkshire. It was opened in 1834. As built, the line ran west/east between two termini, Marsh Lane station, Leeds and Selby railway station. The company was leased and then acquired by the York and North Midland Railway in 1840 and 1844; the line remained in use through the subsequent NER, LNER, BR and post-privatisation periods. Use of the line was expanded through junction connections to new railways, most built in the late 19th century; a junction with the York and North Midland Railway in 1839; an end on junction at Selby to Hull (Hull and Selby Railway, 1840); a through route into Leeds and westward (Leeds viaduct extension, 1869); a shortened route to York (Micklefield to Church Fenton, 1869); a line to Wetherby (Cross Gates to Wetherby Line, 1876, closed 1964); a line to Castleford (Garforth to Castleford Line, 1878, closed 1969) and a line avoiding Selby for Goole ( Selb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Quality
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different types of air pollutants, such as gases (including ammonia, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrous oxides, methane, carbon dioxide and chlorofluorocarbons), particulates (both organic and inorganic), and biological molecules. Air pollution can cause diseases, allergies, and even death to humans; it can also cause harm to other living organisms such as animals and food crops, and may damage the natural environment (for example, climate change, ozone depletion or habitat degradation) or built environment (for example, acid rain). Air pollution can be caused by both human activities and natural phenomena. Air pollution is a significant risk factor for a number of pollution-related diseases, including respiratory infections, heart disease, COPD, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
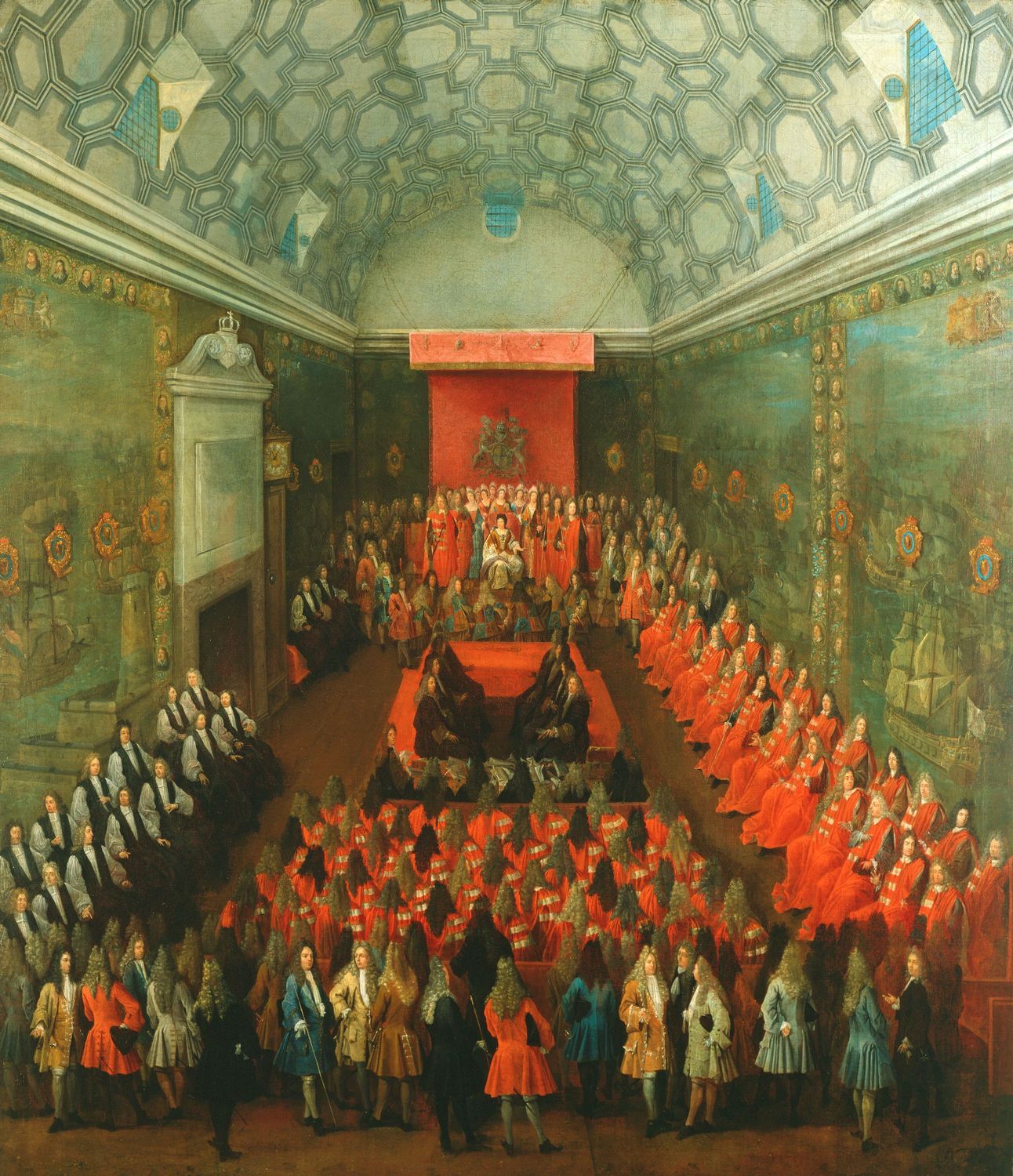
Palace Of Westminster
The Palace of Westminster serves as the meeting place for both the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Informally known as the Houses of Parliament, the Palace lies on the north bank of the River Thames in the City of Westminster, in central London, England. Its name, which derives from the neighbouring Westminster Abbey, may refer to several historic structures but most often: the ''Old Palace'', a England in the Middle Ages, medieval building-complex largely Burning of Parliament, destroyed by fire in 1834, or its replacement, the ''New Palace'' that stands today. The palace is owned by the Crown. Committees appointed by both houses manage the building and report to the Speaker of the House of Commons (United Kingdom), Speaker of the House of Commons and to the Lord Speaker. The first royal palace constructed on the site dated from the 11th century, and Westminster beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Barry
Sir Charles Barry (23 May 1795 – 12 May 1860) was a British architect, best known for his role in the rebuilding of the Palace of Westminster (also known as the Houses of Parliament) in London during the mid-19th century, but also responsible for numerous other buildings and gardens. He is known for his major contribution to the use of Italianate architecture in Britain, especially the use of the Palazzo as basis for the design of country houses, city mansions and public buildings. He also developed the Italian Renaissance garden style for the many gardens he designed around country houses.Bisgrove, p. 179 Background and training Born on 23 May 1795Barry p. 4 in Bridge Street, Westminster (opposite the future site of the Clock Tower of the Palace of Westminster), he was the fourth son of Walter Edward Barry (died 1805), a stationer, and Frances Barry ''née'' Maybank (died 1798). He was baptised at St Margaret's, Westminster, into the Church of England, of which he was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the Bicameralism, upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by Life peer, appointment, Hereditary peer, heredity or Lords Spiritual, official function. Like the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England. The House of Lords scrutinises Bill (law), bills that have been approved by the House of Commons. It regularly reviews and amends bills from the Commons. While it is unable to prevent bills passing into law, except in certain limited circumstances, it can delay bills and force the Commons to reconsider their decisions. In this capacity, the House of Lords acts as a check on the more powerful House of Commons that is independent of the electoral process. While members of the Lords may also take on roles as government ministers, high-ranking officials such as cabinet ministers are usually drawn from the Commons. The House of Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Tower, Palace Of Westminster
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object. Central may also refer to: Directions and generalised locations * Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as Middle Africa * Central America, a region in the centre of America continent * Central Asia, a region in the centre of Eurasian continent * Central Australia, a region of the Australian continent * Central Belt, an area in the centre of Scotland * Central Europe, a region of the European continent * Central London, the centre of London * Central Region (other) * Central United States, a region of the United States of America Specific locations Countries * Central African Republic, a country in Africa States and provinces * Blue Nile (state) or Central, a state in Sudan * Central Department, Paraguay * Central Province (Kenya) * Central Province (Papua New Guinea) * Central Province (Solomon Islands) * Central Province, Sri Lank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Wade Of Chorlton
William Oulton Wade, Baron Wade of Chorlton, (24 December 1932 – 7 June 2018) was a British politician, businessman and agriculturalist. Wade was educated at Birkenhead School and the Queen's University of Belfast. He was an elected member of Cheshire County Council between 1973–77, and then Joint Treasurer of the Conservative Party from 1982–90. Having been awarded a Knighthood in the 1982 Birthday Honours, which was conferred by The Queen on 14 December 1982, Wade was elevated to the House of Lords being created a life peer on 16 May 1990 with the title Baron Wade of Chorlton, of Chester in the County of Cheshire. He sat as a Conservative in the House until his retirement on 1 November 2016. On 9 November 2007, he became an honorary graduand of the University of Chester, where he was presented for admission to the degree of Doctor of Letters, honoris causa. In the Lords, he served as a member of the Science and Technology Select Committee, and later as chairman of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Conservation
Energy conservation is the effort to reduce wasteful energy consumption by using fewer energy services. This can be done by using energy more effectively (using less energy for continuous service) or changing one's behavior to use less service (for example, by driving less). Energy conservation can be achieved through energy efficiency, which has a number of advantages, including a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, a smaller carbon footprint, and cost, water, and energy savings. Energy conservation is an essential factor in building design and construction. It has increased in importance since the 1970s, as 40% of energy use in the U.S. is in buildings. Recently, concern over the effects of climate change and global warming has emphasized the importance of energy conservation. Energy can only be transformed from one form to another, such as when heat energy is converted into vehicle motive power or when water flow's kinetic energy is converted into electricity in hydroelectr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventilation (architecture)
Ventilation is the intentional introduction of outdoor air into a space. Ventilation is mainly used to control indoor air quality by diluting and displacing indoor pollutants; it can also be used to control indoor temperature, humidity, and air motion to benefit thermal comfort, satisfaction with other aspects of indoor environment, or other objectives. The intentional introduction of outdoor air is usually categorized as either mechanical ventilation, natural ventilation, or mixed-mode ventilation (hybrid ventilation). * Mechanical ventilation is the intentional fan driven flow of outdoor air into a building. Mechanical ventilation systems may include supply fans (which push outdoor air into a building), exhaust fans (which draw air out of building and thereby cause equal ventilation flow into a building), or a combination of both. Mechanical ventilation is often provided by equipment that is also used to heat and cool a space. * Natural ventilation is the intentional passive fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westminster
Westminster is an area of Central London, part of the wider City of Westminster. The area, which extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street, has many visitor attractions and historic landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, Buckingham Palace, Westminster Abbey, Westminster Cathedral and much of the West End shopping and entertainment district. The name ( ang, Westmynstre) originated from the informal description of the abbey church and royal peculiar of St Peter's (Westminster Abbey), west of the City of London (until the English Reformation there was also an Eastminster, near the Tower of London, in the East End of London). The abbey's origins date from between the 7th and 10th centuries, but it rose to national prominence when rebuilt by Edward the Confessor in the 11th. Westminster has been the home of England's government since about 1200, and from 1707 the Government of the United Kingdom. In 1539, it became a city. Westminster is often used as a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)