|
Bosque Andino Patagónico
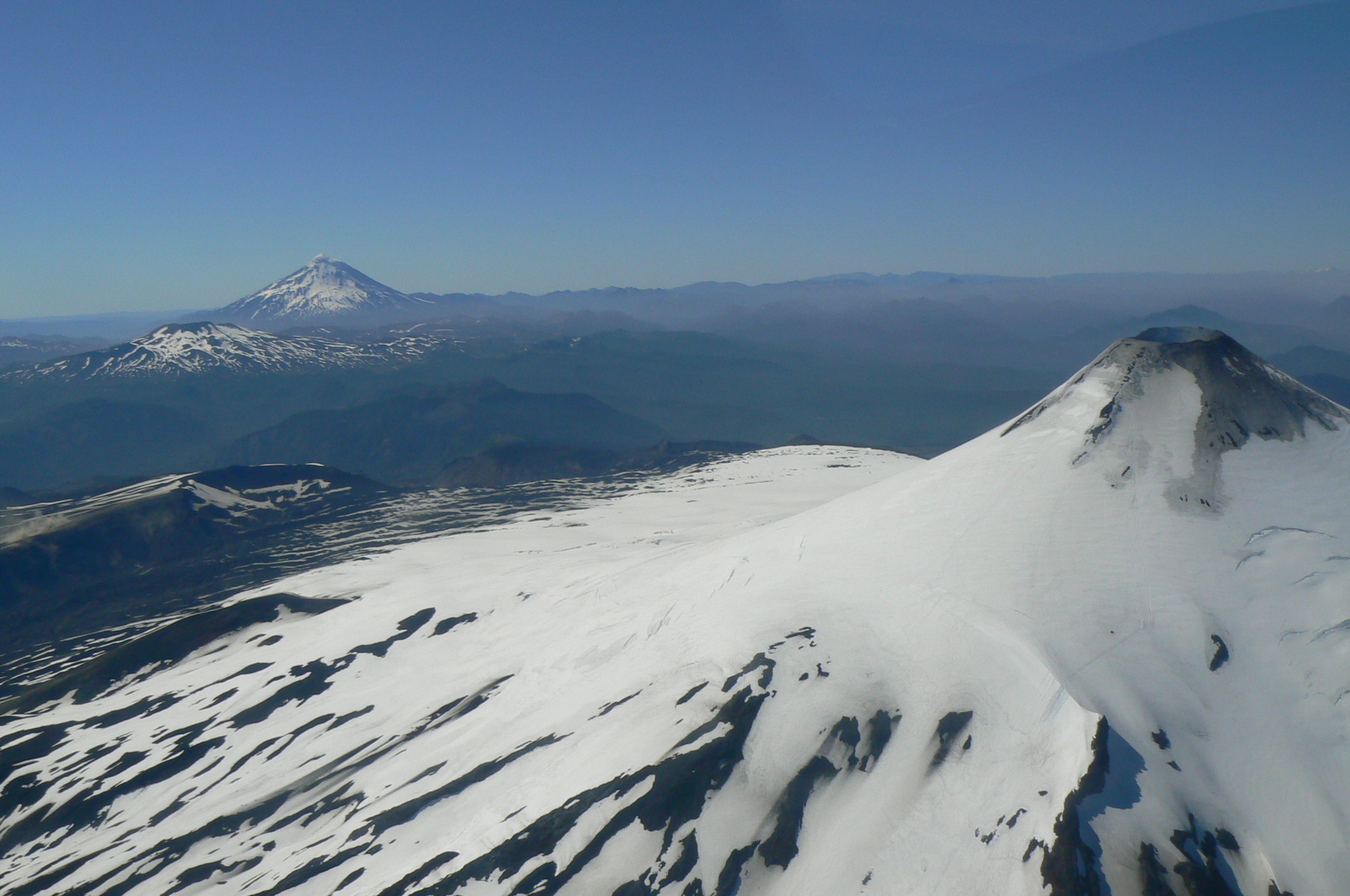
The Bosque Andino Patagónico is a type of temperate to cold forest located in southern Chile and western Patagonia in Argentina at the southern end of South America. The climate here is influenced by humid air masses moving in from the Pacific Ocean which lose most of their moisture as they rise over the Andes. The flora is dominated by trees, usually of the genus ''Nothofagus''. Geography The Bosque Andino Patagónico represents one of the few relatively undisturbed temperate forests that has been little changed by man. It occupies approximately 6.5 million hectares of land. It is culturally significant because of its archaeological and historical value. The Andean Patagonian forest region is located between 37°S and 55°S latitude, and clothes both sides of the Cordillera. The forest extends for about parallel to the Pacific coast, extending from just south of Mendoza in Argentina to the southern end of Santa Cruz Province and to the island portion of the province of Ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zona Sur
Zona Sur (''Southern Zone'') is one of the five natural regions on which CORFO divided continental Chile in 1950. Its northern border is formed by the Bío-Bío River, which separates it from the Central Chile Zone. The Southern Zone borders the Pacific Ocean to the west, and to the east lies the Andean mountains and Argentina. Its southern border is the Chacao Channel, which forms the boundary with the Austral Zone. While the Chiloé Archipelago belongs geographically to the Austral Zone in terms of culture and history, it lies closer to the Southern Zone. Geography Although many lakes can be found in the Andean and coastal regions of central Chile, the south (Sur de Chile) has the country's most lakes. Southern Chile stretches from below the Río Bío-Bío at about 37° south latitude to below Isla de Chiloé at about 43.4° south latitude. In this lake district of Chile, the valley between the Andes and the coastal range is closer to sea level, and the hundreds of river ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Front
A weather front is a boundary separating air masses for which several characteristics differ, such as air density, wind, temperature, and humidity. Disturbed and unstable weather due to these differences often arises along the boundary. For instance, cold fronts can bring bands of thunderstorms and cumulonimbus precipitation or be preceded by squall lines, while warm fronts are usually preceded by stratiform precipitation and fog. In summer, subtler humidity gradients are known as dry lines can trigger severe weather. Some fronts produce no precipitation and little cloudiness, although there is invariably always a wind shift. Cold fronts generally move from west to east, whereas warm fronts move poleward, although any direction is possible. Occluded fronts are a hybrid merge of the two, and stationary fronts are stalled in their motion. Cold fronts and cold occlusions move faster than warm fronts and warm occlusions because the dense air behind them can lift as well as push ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outwash
An outwash plain, also called a sandur (plural: ''sandurs''), sandr or sandar, is a plain formed of glaciofluvial deposits due to meltwater outwash at the terminus of a glacier. As it flows, the glacier grinds the underlying rock surface and carries the debris along. The meltwater at the snout of the glacier deposits its load of sediment over the outwash plain, with larger boulders being deposited near the terminal moraine, and smaller particles travelling further before being deposited. Sandurs are common in Iceland where geothermal activity accelerates the melting of ice flows and the deposition of sediment by meltwater. Formation Sandurs are found in glaciated areas, such as Svalbard, Kerguelen Islands, and Iceland. Glaciers and icecaps contain large amounts of silt and sediment, picked up as they erode the underlying rocks when they move slowly downhill, and at the snout of the glacier, meltwater can carry this sediment away from the glacier and deposit it on a broad plai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ñadi
300px, The archaeological site of Monte Verde is in a zone of ñadi soils. Ñadi is a type of soil and a phytogeographic zone of Southern Chile. Ñadi soils are located in the Chilean Central Valley of Los Lagos Region, specifically between the moraines left by the region's most recent glaciation (the Llanquihue glaciation) and those of the penultimate glaciation (the Santa María glaciation). Ñadis have an impermeable layer, usually called ''fierrillo''. See also *Lahuen Ñadi Natural Monument *Trumao Trumao is the name of a soil of the Andosol order found in southern and central Chile. Trumaos are formed from young volcanic ash, by volcanic ash redeposited by aeolian processes or by volcanic ash mobilized as alluvium. Trumaos are characterized ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Nadi Geography of Chile Soil in Chile Geography of Los Lagos Region Geography of Los Ríos Region Volcanic soils ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andosol
Andosols are soils found in volcanic areas formed in volcanic tephra. In some cases Andosols can also be found outside active volcanic areas. Andosols cover an estimated 1–2% of earth's ice-free land surface. Andosols are a Reference Soil Group of the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB). They are closely related to other types of soils such as Vitrosols, Vitrandosols, Vitrons and Pumice Soils that are used in different soil classification systems. Poorly developed Andosols are often rich in vitreous materials and are therefore also called Vitric Andosols. The name comes from Japanese ( 'dark') and ( 'soil'), synonymous with (). In the USDA soil taxonomy, Andosols are known as Andisols. Andosols are usually defined as soils containing high proportions of glass and amorphous colloidal materials, including allophane, imogolite and ferrihydrite. Because they are generally quite young, Andosols typically are very fertile except in cases where phosphorus is easily fixed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trumao
Trumao is the name of a soil of the Andosol order found in southern and central Chile. Trumaos are formed from young volcanic ash, by volcanic ash redeposited by aeolian processes or by volcanic ash mobilized as alluvium. Trumaos are characterized by containing the following minerals: allophane, imogolite plus a series of paracrystalline and non-crystalline clays. These soils have high porosity and low bulk density. A more dry and a more humid variety of trumaos exists. The dry variety is known simply as trumao while the humid variety is known as trumao húmedo. In terms of latitude trumaos can be found in the Andes from 33° S to 43° S, in the Central Valley from 38° S to 43° S and in the eastern slopes of the Chilean Coast Range from 39° S to 43° S. See also *Andean Volcanic Belt *Ñadi 300px, The archaeological site of Monte Verde is in a zone of ñadi soils. Ñadi is a type of soil and a phytogeographic zone of Southern Chile. Ñadi soils are located in the Chilean Ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulk Density
Bulk density, also called apparent density or volumetric density, is a property of powders, granules, and other "divided" solids, especially used in reference to mineral components (soil, gravel), chemical substances, (pharmaceutical) ingredients, foodstuff, or any other masses of corpuscular or particulate matter (particles). Bulk density is defined as the mass of the many particles of the material divided by the total volume they occupy. The total volume includes particle volume, inter-particle void volume, and internal pore volume. Bulk density is not an intrinsic property of a material; it can change depending on how the material is handled. For example, a powder poured into a cylinder will have a particular bulk density; if the cylinder is disturbed, the powder particles will move and usually settle closer together, resulting in a higher bulk density. For this reason, the bulk density of powders is usually reported both as "freely settled" (or "poured" density) and "tappe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porosity
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure the "accessible void", the total amount of void space accessible from the surface (cf. closed-cell foam). There are many ways to test porosity in a substance or part, such as industrial CT scanning. The term porosity is used in multiple fields including pharmaceutics, ceramics, metallurgy, materials, manufacturing, petrophysics, hydrology, earth sciences, soil mechanics, and engineering. Void fraction in two-phase flow In gas-liquid two-phase flow, the void fraction is defined as the fraction of the flow-channel volume that is occupied by the gas phase or, alternatively, as the fraction of the cross-sectional area of the channel that is occupied by the gas phase. Void fraction usually varies from location to location in the flow ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Ash
Volcanic ash consists of fragments of rock, mineral crystals, and volcanic glass, created during volcano, volcanic eruptions and measuring less than 2 mm (0.079 inches) in diameter. The term volcanic ash is also often loosely used to refer to all explosive eruption products (correctly referred to as ''tephra''), including particles larger than 2 mm. Volcanic ash is formed during explosive volcanic eruptions when dissolved gases in magma expand and escape violently into the atmosphere. The force of the gases shatters the magma and propels it into the atmosphere where it solidifies into fragments of volcanic rock and glass. Ash is also produced when magma comes into contact with water during phreatomagmatic eruptions, causing the water to explosively flash to steam leading to shattering of magma. Once in the air, ash is transported by wind up to thousands of kilometres away. Due to its wide dispersal, ash can have a number of impacts on society, including animal a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allophane
Allophane is an amorphous to poorly crystalline hydrous aluminium silicate clay mineraloid. Its chemical formula is Al2O3·(SiO2)1.3-2·(2.5-3)H2O. Since it has short-range atomic order, it is a mineraloid, rather than a mineral, and can be identified by its distinctive infrared spectrum and its X-ray diffraction pattern. It was first described in 1816 in Gräfenthal, Thuringia, Germany. Allophane is a weathering or hydrothermal alteration product of volcanic glass and feldspars and sometimes has a composition similar to kaolinite but generally has a molar ratio of Al:Si = 2. It typically forms under mildly acidic to neutral pH (5–7). Its structure has been debated, but it is similar to clay minerals and is composed of curved alumina octahedral and silica tetrahedral layers.Smalley, I.J. 1979. A spherical structure for allophane. Nature 281, 339 only Transmission electron micrographs show that it is generally made up of aggregates of hollow spherules ~3–5 nm in diameter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with water, atmospheric gases, and biological organisms. Weathering occurs ''in situ'' (on site, with little or no movement), and so is distinct from erosion, which involves the transport of rocks and minerals by agents such as water, ice, snow, wind, waves and gravity. Weathering processes are divided into ''physical'' and ''chemical weathering''. Physical weathering involves the breakdown of rocks and soils through the mechanical effects of heat, water, ice, or other agents. Chemical weathering involves the chemical reaction of water, atmospheric gases, and biologically produced chemicals with rocks and soils. Water is the principal agent behind both physical and chemical weathering, though atmospheric oxygen and carbon dioxide and the activities of biological organisms are also important. Chemical weathering by biological action is also known as biological wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |