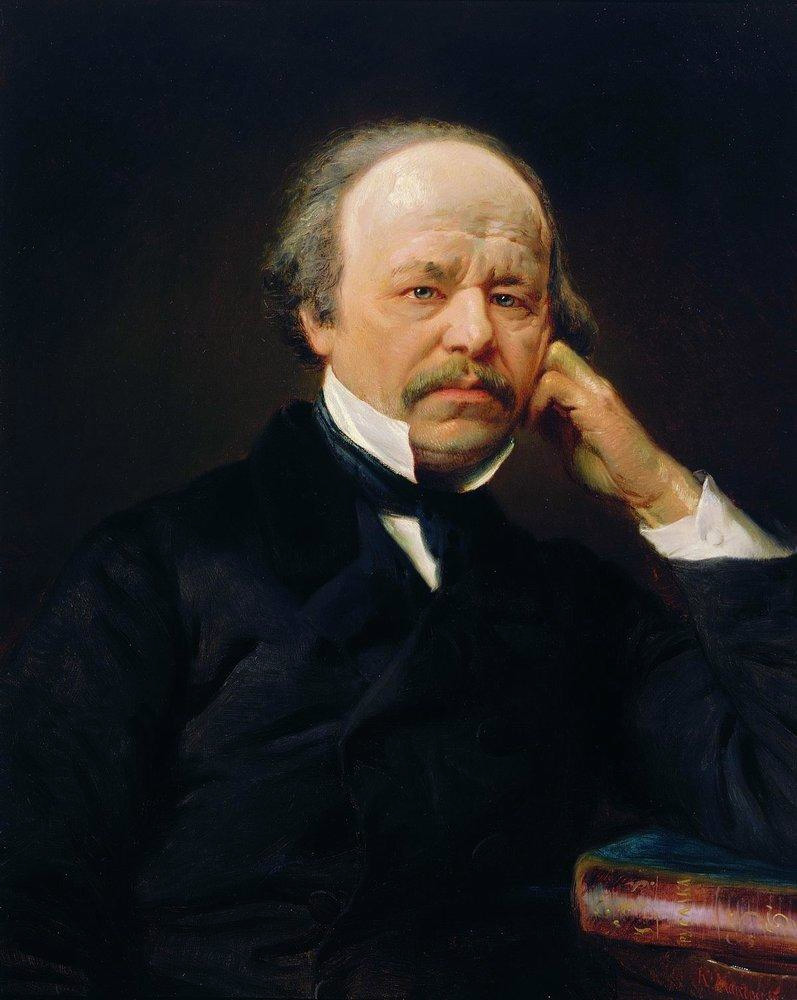|
Boris Khaykin
Boris Emmanuilovich Khaikin (russian: Борис Эммануилович Хайкин; be, Барыс Эмануілавіч Хайкін; – 10 May 1978) was a Soviet and Russian conductor who was named a People's Artist of the USSR in 1972. Biography Khaikin was born in Minsk, then part of the Russian Empire. He studied at the Moscow Conservatory under Nicolai Malko and Konstantin Saradzhev. He was artistic director of the Little Leningrad Opera Theatre in 1936-43 and the principal conductor at the Kirov Theatre in 1944-53, where he conducted the première of Sergei Prokofiev's '' Betrothal in a Monastery'' on 3 November 1946. He moved to the Bolshoi Theatre in 1954. He died in Moscow, and was buried in the Donskoye Cemetery. Discography Khaikin is noted for his two critically acclaimed recordings of ''Khovanshchina'': a 1946 edition with Mark Reizen, and a 1972 version with Irina Arkhipova. His record of Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov's little known early first symphony ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conducting
Conducting is the art of directing a musical performance, such as an orchestral or choral concert. It has been defined as "the art of directing the simultaneous performance of several players or singers by the use of gesture." The primary duties of the conductor are to interpret the score in a way which reflects the specific indications in that score, set the tempo, ensure correct entries by ensemble members, and "shape" the phrasing where appropriate. Conductors communicate with their musicians primarily through hand gestures, usually with the aid of a baton, and may use other gestures or signals such as eye contact. A conductor usually supplements their direction with verbal instructions to their musicians in rehearsal. The conductor typically stands on a raised podium with a large music stand for the full score, which contains the musical notation for all the instruments or voices. Since the mid-19th century, most conductors have not played an instrument when conducting, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symphony No
A symphony is an extended musical composition in Western classical music, most often for orchestra. Although the term has had many meanings from its origins in the ancient Greek era, by the late 18th century the word had taken on the meaning common today: a work usually consisting of multiple distinct sections or movements, often four, with the first movement in sonata form. Symphonies are almost always scored for an orchestra consisting of a string section (violin, viola, cello, and double bass), brass, woodwind, and percussion instruments which altogether number about 30 to 100 musicians. Symphonies are notated in a musical score, which contains all the instrument parts. Orchestral musicians play from parts which contain just the notated music for their own instrument. Some symphonies also contain vocal parts (e.g., Beethoven's Ninth Symphony). Etymology and origins The word ''symphony'' is derived from the Greek word (), meaning "agreement or concord of sound", "concert of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Unknown Soldier (opera)
Unknown Soldier may refer to: Places * Tomb of the Unknown Soldier, a type of memorial site in many nations * The British grave of The Unknown Warrior in Westminster Abbey * Tomb of the Unknown Soldier (Arlington), United States memorial Literature * ''The Unknown Soldier'' (novel), a 1954 novel by Väinö Linna * "Unknown Soldier" (short story), a short story by Kurt Vonnegut Film * ''The Unknown Soldier'' (1926 film) * ''The Unknown Soldier'' (1955 film), a Finnish film based on the novel by Väinö Linna * ''Unknown Soldier'' (1968 film), a film by Donald Shebib * ''The Unknown Soldier'' (1985 film), a Finnish film based on the novel by Väinö Linna * ''The Unknown Soldier'' (1998 miniseries), a British miniseries featuring Aislín McGuckin * ''The Unknown Soldier'' (2006 film), a German documentary film by Michael Verhoeven about the * ''The Unknown Soldier'' (2017 film), a Finnish film based on the novel by Väinö Linna Music * Unknown Soldier (Fela Kuti al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirill Molchanov
Kirill Vladimirovich Molchanov (russian: Кирилл Владимирович Молчанов; 7 September 1922 – 14 March 1982) was a Russian and Soviet composer. He was appointed director of the Bolshoi, at the time political disfavour had fallen on the lead soprano Galina Vishnevskaya. His works are in the Social Realist romantic tradition and were not warmly received when performed abroad.World affairs report 1975 "The Bolshoi Opera performed "The Dawns Are Quiet Here," by Kiril Molchanov at Lincoln Center's Metropolitan Opera House (NYT, 7/14). It is a piece of socialist realism about the heroism of women in an anti-aircraft company during World War II. It was panned by Harold C. Schonberg, who suggested the only reason it was performed was because Molchanov is director general of the Bolshoi Opera." Works Operas Taken from: * ''The Stone Flower'' (Каменный цветок) inspired by Pavel Bazhov's story of the same name, Moscow, 1950 * ''Dawn'' (Заря) on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Demon (opera)
''Demon'' (russian: Демон) is an opera in three acts (six scenes) by Russian composer Anton Rubinstein. The work was composed in 1871. The libretto was by Pavel Viskovatov, based on the poem of the same name by Mikhail Lermontov. Background Lermontov's poem was banned as sacrilegious until 1860. Its popularity and its lurid story made it an excellent candidate for an opera libretto, and Rubinstein himself worked out the scenario from which Viskovatov produced the final text. The opera was premiered at the Mariinsky Theatre, St. Petersburg, on , conducted by Eduard Nápravník. The stage design was by Mikhayil Bocharov, Matvey Shishkov, and Lagorio. The Moscow premiere was in 1879 at the Bolshoi Theatre, conducted by Enrico Bevignani. The opera was published by V. Bessel and Co., St. Petersburg, in 1876. A further edition was in 1968 by Muzgiz, Moscow. Critical reception Rubinstein invited several musicians of the group known as '' The Five'', including César Cui, Mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anton Rubinstein
Anton Grigoryevich Rubinstein ( rus, Антон Григорьевич Рубинштейн, r=Anton Grigor'evič Rubinštejn; ) was a Russian pianist, composer and conductor who became a pivotal figure in Russian culture when he founded the Saint Petersburg Conservatory. He was the elder brother of Nikolai Rubinstein, who founded the Moscow Conservatory. As a pianist, Rubinstein ranks among the great 19th-century keyboard virtuosos. He became most famous for his series of historical recitals—seven enormous, consecutive concerts covering the history of piano music. Rubinstein played this series throughout Russia and Eastern Europe and in the United States when he toured there. Although best remembered as a pianist and educator (most notably in the latter as the composition teacher of Tchaikovsky), Rubinstein was also a prolific composer throughout much of his life. He wrote 20 operas, the best known of which is '' The Demon''. He composed many other works, including five pian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tchaikovsky Symphony Orchestra
The Tchaikovsky Symphony Orchestra is a Russian classical music radio orchestra established in 1930. It was founded as the Moscow Radio Symphony Orchestra, and served as the official symphony for the Soviet All-Union Radio network. History Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, the orchestra was renamed in 1993 by the Russian Ministry of Culture in recognition of the central role the music of Tchaikovsky plays in its repertoire. The current music director is Vladimir Fedoseyev, who has been in that position since 1974. During Soviet times, the orchestra was sometimes known as the USSR State Radio and Television Symphony Orchestra, the USSR State Radio Symphony Orchestra, or the USSR All-Union National Radio and Central Television Symphony Orchestra. Music Directors *Vladimir Fedoseyev (1974–) *Gennady Rozhdestvensky (1961–1974) *Alexander Gauk (1953–1961) *Nikolai Golovanov (1937–1953) * Alexander Orlov (1930–1937) Selected discogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Stone Guest (Dargomyzhsky)
''The Stone Guest'' (''Каменный гость'' in Cyrillic script, Cyrillic, ''Kamennyj gost' '' in transliteration) is an opera in three acts by Alexander Dargomyzhsky from a libretto taken almost verbatim from Alexander Pushkin's 1830 The Stone Guest (play), play of the same name which had been written in blank verse and which forms part of his collection ''Little Tragedies''. It was first performed at the Mariinsky Theatre, Saint Petersburg, 16 February 1872 (Old Style and New Style dates, Old Style). According to the composer's wishes, the last few lines of tableau 1 were composed by César Cui, and the whole was orchestrated by Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov. Many years later, Rimsky-Korsakov revised his own orchestration of the opera, rewrote a few of Dargomyzhsky's own original passages, and added an orchestral prelude. This version, completed in 1903 and first performed in 1907 at the Bolshoi Theatre, is now considered the standard version. Performance History The Austrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Dargomyzhsky
Alexander Sergeyevich Dargomyzhsky ( rus, link=no, Александр Сергеевич Даргомыжский, Aleksandr Sergeyevich Dargomyzhskiy., ɐlʲɪkˈsandr sʲɪrˈɡʲe(j)ɪvʲɪdʑ dərɡɐˈmɨʂskʲɪj, Ru-Aleksandr-Sergeevich-Dargomyzhsky.ogg; ) was a 19th-century Russian composer. He bridged the gap in Russian opera composition between Mikhail Glinka and the later generation of The Five and Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky. Biography Dargomyzhsky was born in village Troitskoye, Belyov uyezd, Tula Governorate (now Arsenyevsky District, Tula Oblast), and educated in Saint Petersburg. He was already known as a talented musical amateur when in 1833 he met Mikhail Glinka and was encouraged to devote himself to composition. His opera '' Esmeralda'' (libretto by composer, based on Victor Hugo's ''The Hunchback of Notre Dame'') was composed in 1839 (performed 1847), and his '' Rusalka'' was performed in 1856; but he had little success or recognition either at home or abro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Life For The Tsar
''A Life for the Tsar'' ( rus, "Жизнь за царя", italic=yes, Zhizn za tsarya ) is a "patriotic-heroic tragic opera" in four acts with an epilogue by Mikhail Glinka. During the Soviet era the opera was known under the name ''Ivan Susanin'' (russian: Иван Сусанин ). The original Russian libretto, based on historical events, was written by Nestor Kukolnik, Egor Fyodorovich (von) Rozen, Vladimir Sollogub and Vasily Zhukovsky. It premiered on 27 November 1836 OS (9 December NS) at the Bolshoi Kamenny Theatre in St. Petersburg. The historical basis of the plot involves Ivan Susanin, a patriotic hero of the early 17th century who died in the expulsion of the invading Polish army for the newly elected Tsar Michael of Russia, the first of the Romanov dynasty, elected in 1613.Osborne (2007) p. 143 History Composition history The plot of ''A Life for the Tsar'' had been used earlier in 1815, when Catterino Cavos, an Italian-Russian composer, had written a two-act si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Glinka
Mikhail Ivanovich Glinka ( rus, link=no, Михаил Иванович Глинка, Mikhail Ivanovich Glinka., mʲɪxɐˈil ɪˈvanəvʲɪdʑ ˈɡlʲinkə, Ru-Mikhail-Ivanovich-Glinka.ogg; ) was the first Russian composer to gain wide recognition within his own country and is often regarded as the fountainhead of Russian classical music. His compositions were an important influence on Russian composers, notably the members of The Five (composers), The Five, who produced a distinctive Russian style of music. Early life and education Glinka was born in the village of Novospasskoye, not far from the Desna River in the Smolensk Governorate of the Russian Empire (now in the Yelninsky District of the Smolensk Oblast). His wealthy father had retired as an army captain, and the family had a strong tradition of loyalty and service to the tsars, and several members of his extended family had lively cultural interests. His great-great-grandfather was a Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergei Lemeshev
Sergei Yakovlevich Lemeshev (russian: Серге́й Я́ковлевич Ле́мешев; – 27 June 1977) was a Soviet and Russian opera singer and director. People's Artist of the USSR (1950). Biography Early life and career Lemeshev was born into a peasant family, and his father wanted him to become a cobbler. In 1914, he left a parish school and was sent to be trained to make shoes in Saint Petersburg. In 1917, he graduated from school in Tver, where he received vocal training. He began first at a local workers' club and later moved to Moscow. Between 1921 and 1925, he studied at the Moscow Conservatory with Nazari Raisky. In 1924, he sang in the opera studio of Konstantin Stanislavski. From 1926 and 1931, he sang in the theatres of Sverdlovsk, Harbin, and Tbilisi. In 1931 Lemeshev was invited to the Bolshoi Theatre, made his debut and eventually became the theatre's soloist. His lyrical tenor of an unusually soft and light timbre almost at once brought him love and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |