|
Boreopterus
''Boreopterus'' is a genus of boreopterid pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Barremian-Aptian-age Lower Cretaceous Yixian Formation of Dalian, Liaoning, China. Etymology ''Boreopterus'' was named in 2005 by Lü Junchang and Ji Qiang. The type species is ''Boreopterus cuiae''. The genus name is derived from Greek ''boreios'', "northern" and ''pteron'', "wing". The specific epithet honors Cui Xu. Description ''Boreopterus'' is based on holotype JZMP-04-07-3, a nearly complete but crushed skeleton and skull. The skull is 235 millimeters long (9.25 inches), low and elongated with a rounded tip. Its wingspan is estimated to have been around 1.45 meters (4.76 feet). Its teeth, especially the anterior nine pairs, are quite large, forming a mesh of sharp teeth at the front of the mouth; the third and fourth teeth from the front are the largest. There are at least 27 teeth in each side of both the upper and lower jaws, which is a large amount. Classification Lü and Ji ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhenyuanopterus
''Zhenyuanopterus'' is a genus of boreopterid pterosaur which is known from Lower Cretaceous (early Aptian stage) Yixian Formation of Liaoning, China. It contains one species, ''Zhenyuanopterus longirostris'', which was first described and named by Lü Junchang. Discovery and naming ''Zhenyuanopterus longirostris'' was named by paleontologist Lü Junchang in 2005. The genus is named after Sun Zhenyuan, who gave Lü Junchang the fossils along with Zi Fan. The specific name ("long-snouted") refers to the long snout of the pterosaur. One specimen is known; a complete skeleton, it was found in the Huangbanjigou locality of the Yixian Formation, and it is catalogued as GLGMV 0001 in the Guilin Longshan Geological Museum in Guangxi, China. A second, larger partial specimen, consisting of the rear half of the body, was found at the same locality and catalogued as XHPM1088 at the Dalian Xinghai Paleontological Museum. In 2014, Teng Fangfang and colleagues described it. Description T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
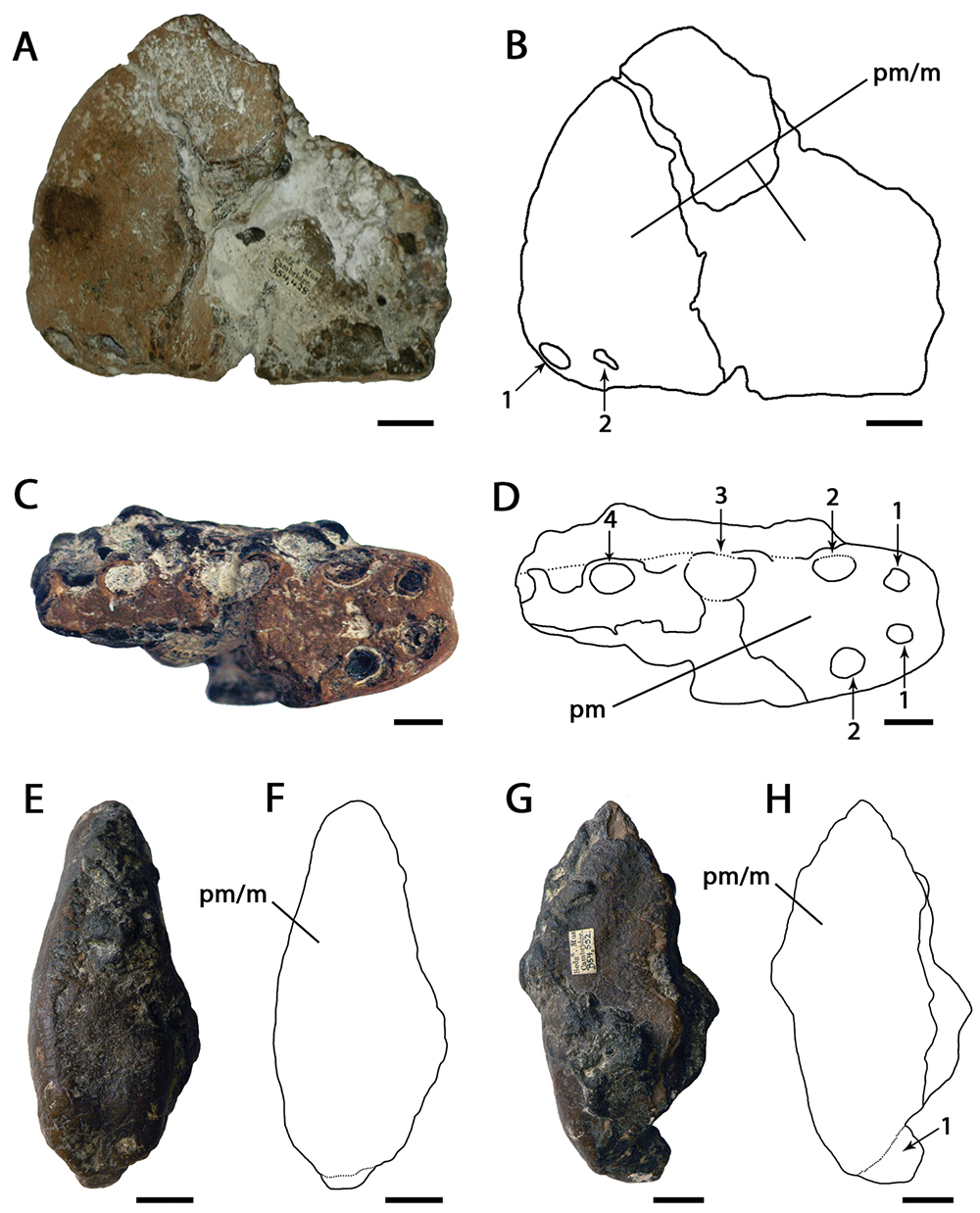
Boreopterid
Boreopteridae (meaning "northern wings") is a group of pterodactyloid pterosaurs from the Aptian-age Lower Cretaceous Yixian Formation of Liaoning, China. Classification In 2006, Lü Junchang and colleagues named the clade Boreopteridae for the clade containing the common ancestor of ''Boreopterus'' and ''Feilongus'' and all its descendants, which the authors reclassified as close relatives of the ornithocheirids. (''Feilongus'' had originally been considered a gallodactylid). Many possible boreopterids were subsequently described, one possible example being ''Aetodactylus'', which has been claimed to be similar to ''Boreopterus''. Originally considered close relatives of the ornithocheirids, many of these supposed boreopterids have been found to belong to other groups of the pterodactyloid lineage. In 2012, a phylogenetic analysis by Lü ''et al.'' divided the Boreopteridae into two subfamilies: Boreopterinae, comprising ''Boreopterus'' and ''Zhenyuanopterus'', and Moganopterina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boreopteridae
Boreopteridae (meaning "northern wings") is a group of pterodactyloid pterosaurs from the Aptian-age Lower Cretaceous Yixian Formation of Liaoning, China. Classification In 2006, Lü Junchang and colleagues named the clade Boreopteridae for the clade containing the common ancestor of ''Boreopterus'' and ''Feilongus'' and all its descendants, which the authors reclassified as close relatives of the ornithocheirids. (''Feilongus'' had originally been considered a gallodactylid). Many possible boreopterids were subsequently described, one possible example being ''Aetodactylus'', which has been claimed to be similar to ''Boreopterus''. Originally considered close relatives of the ornithocheirids, many of these supposed boreopterids have been found to belong to other groups of the pterodactyloid lineage. In 2012, a phylogenetic analysis by Lü ''et al.'' divided the Boreopteridae into two subfamilies: Boreopterinae, comprising ''Boreopterus'' and ''Zhenyuanopterus'', and Moganopterina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallodactylidae
Gallodactylidae is a group of pterosaurs within the suborder Pterodactyloidea. Gallodactylids differed from other related pterosaurs in several distinct features, including fewer than 50 teeth present only in the jaw tips, and rounded crests present on the rear portion of the skull and jaws but not near the ends of their snouts. At least some species possessed jaw flanges, possibly used to bissect hard-shelled prey. History Gallodactylidae was named to contain ''Gallodactylus'' (now usually considered a synonym of ''Cycnorhamphus'') and its closest relatives. Many subsequent studies, however, showed that ''Gallodactylus'' did not form a clade with any non-synonymous pterosaurs that were not themselves part of a different family, and so the name was often ignored. The name returned to common use with the discovery of ''Gladocephaloideus'', a Chinese pterosaur species that shared many similarities with ''Cycnorhamphus''. Among other features, the Gallodactylidae was distinguished by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornithocheiridae
Ornithocheiridae (or ornithocheirids, meaning "bird hands") is a group of pterosaurs within the suborder Pterodactyloidea. These pterosaurs were among the last to possess teeth. Members that belong to this group lived from the Early to Late Cretaceous periods (Valanginian to Turonian stages), around 140 to 90 million years ago. Ornithocheirids are generally infamous for having an enormously controversial and very confusing taxonomy. Although agreements that these animals were related, and therefore similar to istiodactylids and pteranodontians, there is still no virtual consensus over the exact content and interrelationships of this group. Ornithocheirids were the most successful pterosaurs during their reign, they were also the largest pterosaurs before the appearance of the azhdarchids such as ''Quetzalcoatlus''. Ornithocheirids were excellent fish hunters, they used various flight techniques to catch their prey, and they are also capable of flying great distances without fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feilongus
''Feilongus'' is an extinct genus of ctenochasmatid pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Barremian–Aptian-age Lower Cretaceous Yixian Formation of Beipiao, Liaoning, China. Discovery and naming The genus was named and described in 2005 by Wang Xiaolin, Alexander Kellner, Zhou Zhonghe and Diogenes de Almeida Campos. The type species is ''Feilongus youngi''. The genus name is derived from ''Feilong'', the "flying dragon". The specific name honors the Chinese paleontologist Yang Zhongjian (C. C. Young). ''Feilongus'' is based on holotype IVPP V-12539, a skull and articulated mandible, with on the same plate the detached posterior braincase, of a subadult individual. The fossil is strongly crushed. In 2014, a second specimen, DNMHM D3068 found at Gonggao, was referred to a ''Feilongus'' sp. It consists of a skull with lower jaws and four neck vertebrae. It was a possible subadult or, despite a smaller size, adult. Description The wingspan of ''Feilongus'' was estimated by Wang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeopterodactyloidea
Archaeopterodactyloidea (meaning "ancient Pterodactyloidea") is an extinct clade of pterodactyloid pterosaurs that lived from the middle Late Jurassic to the latest Early Cretaceous periods (Kimmeridgian to Albian stages) of Africa, Asia, Europe and North America. It was named by Alexander Wilhelm Armin Kellner in 1996 as the group that contains ''Germanodactylus'', ''Pterodactylus'', the Ctenochasmatidae and the Gallodactylidae. In 2003, Kellner defined the clade as a node-based taxon consisting of the last common ancestor of ''Pterodactylus'', ''Ctenochasma'' and ''Gallodactylus'' and all its descendants. Although phylogenetic analyses that based on David Unwin's 2003 analysis do not recover monophyletic Archaeopterodactyloidea, phylogenetic analyses that based on Kellner's analyses, or the analyses of Brian Andres (2008, 2010, 2018) recover monophyletic Archaeopterodactyloidea at the base of the Pterodactyloidea. The Antarctic Campanian specimen MN 7801-V was referred to Archa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycnorhamphus
''Cycnorhamphus'' (meaning "swan beak") is a genus of gallodactylid ctenochasmatoid pterosaur from the Late Jurassic period of France and Germany, about 152 million years ago. It is probably synonymous with the genus ''Gallodactylus''. History In 1855, a fossil in a plate of shale from the Kimmeridgian, found near Nusplingen in Württemberg, holotype GPIT "Orig. Quenstedt 1855, Taf. 1" or GPIT 80, was named ''Pterodactylus Suevicus'' by Friedrich August Quenstedt. The specific name refers to the tribal area of Suevia. Quenstedt had earlier mentioned the find in a letter to Professor Heinrich Georg Bronn, which was published in 1854. In it he used the name ''Pterodactylus Württembergicus''. In 1855 and 1858, Christian Erich Hermann von Meyer adopted this older species name but it would be forgotten afterwards. The publication in 1854 was not meant to be a nomenclatural act. According to Peter Wellnhofer, ''Pterodactylus württembergicus'' should be considered a ''nomen oblitum' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haopterus
''Haopterus'' is a genus of pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Barremian-Aptian-age Lower Cretaceous Yixian Formation of Liaoning, China. Its fossil remains dated back 124.6 million years ago. Discovery and naming It was in 2001 named by Wang Xiaolin and Lü Junchang. The type species is ''Haopterus gracilis''. The genus name honors Professor Hao Yichun and combines her name with a Latinized Greek ''pteron'', "wing". The specific name, "slender-built" in Latin, refers to the condition of the metatarsals. The genus is based on holotype IVPP V11726, a crushed fossil found in 1998 at the Sihetun-locality. The layer it was discovered in, was argon-dated at an age of 124.6 million years. It was the first Chinese pterosaur fossil preserving the skull. It consists of the front half of a subadult, including a skull, lower jaws, pectoral girdle, sternum, wings, cervical and dorsal vertebrae, partial pelvis and metatarsals. Description The skull of ''Haopterus'' is with a length of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal (phylogenetics)
In phylogenetics, basal is the direction of the ''base'' (or root) of a phylogenetic tree#Rooted tree, rooted phylogenetic tree or cladogram. The term may be more strictly applied only to nodes adjacent to the root, or more loosely applied to nodes regarded as being close to the root. Note that extant taxa that lie on branches connecting directly to the root are not more closely related to the root than any other extant taxa. While there must always be two or more equally "basal" clades sprouting from the root of every cladogram, those clades may differ widely in taxonomic rank, Phylogenetic diversity, species diversity, or both. If ''C'' is a basal clade within ''D'' that has the lowest rank of all basal clades within ''D'', ''C'' may be described as ''the'' basal taxon of that rank within ''D''. The concept of a 'key innovation' implies some degree of correlation between evolutionary innovation and cladogenesis, diversification. However, such a correlation does not make a given ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladistic
Cladistics (; ) is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups (" clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is typically shared derived characteristics ( synapomorphies'')'' that are not present in more distant groups and ancestors. However, from an empirical perspective, common ancestors are inferences based on a cladistic hypothesis of relationships of taxa whose character states can be observed. Theoretically, a last common ancestor and all its descendants constitute a (minimal) clade. Importantly, all descendants stay in their overarching ancestral clade. For example, if the terms ''worms'' or ''fishes'' were used within a ''strict'' cladistic framework, these terms would include humans. Many of these terms are normally used paraphyletically, outside of cladistics, e.g. as a 'grade', which are fruitless to precisely delineate, especially when including extinct species. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |