|
Boreham Wood F.C. Players
Boreham is a village and civil parish, in Essex, England. The parish is in the City of Chelmsford and Chelmsford Parliament constituency. The village is approximately northeast from the county town of Chelmsford. History Boreham is listed in the Domesday Book of 1086 as ''Borham'', thought to mean 'village on a hill'. Local legend holds that highwayman Dick Turpin rode down the route than now forms part of the A12 on his famous ride from London to York, although historians now believe the ride never occurred. In the 1930s Boreham House and its surrounding land of was bought by car magnate Henry Ford. In addition to using the house as a school for training Ford tractor mechanics, the company's British chairman, Lord Perry, established Fordson Estates Limited there, and founded the Henry Ford Institute of Agricultural Engineering, an agricultural college. The house also served as the temporary home for the National College of Agricultural Engineering in 1962. This moved to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Village Sign
In many parts of England, an ornamental village sign is erected to announce the village name to those entering the village. They are typically placed on the principal road entrance or in a prominent location such as a village green. The design often depicts a particularly characteristic feature of the village or a scene from its history, heritage, or culture. They are typically made of wood or metal or a combination of both, the designs are often made by the local community. Ornamental timber and iron signs were common historically to identify buildings of importance such as inns or town halls. However, the tradition of village signs is believed to have started in Norfolk early in the 20th century when Edward VII suggested that village signs would aid motorists and give a feature of interest on the Sandringham Estate. The spread of interest beyond Norfolk can be attributed to Prince Albert, Duke of York (later George VI) who gave a speech to the Royal Academy in 1920 promoting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National College Of Agricultural Engineering
The National College of Agricultural Engineering was opened in 1962. It was closed as a separate entity at the end of 2007 and the land sold for housing. Foundation In February 1959, the Ministry of Education (United Kingdom), Minister of Education of the United Kingdom announced to the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons that a new ''National College'' devoted to agriculture was to be established to provide a national centre for the agricultural engineering industry which would also attract overseas students. The National College of Agricultural Engineering as it was initially known began at Silsoe in Bedfordshire, England. In September 1962, the first cohort of 20 undergraduate students began their studies at Boreham House near Chelmsford in Essex. The move to the more permanent home at Silsoe was in 1963. In 1964 the first 15 postgraduate students joined from nine countries. Merger The Department of Education and Science and the Department for Educatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugar Beet
A sugar beet is a plant whose root contains a high concentration of sucrose and which is grown commercially for sugar production. In plant breeding, it is known as the Altissima cultivar group of the common beet (''Beta vulgaris''). Together with other beet cultivars, such as beetroot and chard, it belongs to the subspecies ''Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''vulgaris.'' Its closest wild relative is the sea beet (''Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''maritima''). Sugar beets are grown in climates that are too cold for sugar cane. The low sugar content of the beets makes growing them a marginal proposition unless prices are relatively high. In 2020, Russia, the United States, Germany, France and Turkey were the world's five largest sugar beet producers. In 2010–2011, Europe, and North America except Arctic territories failed to supply the overall domestic demand for sugar and were all net importers of sugar. The US harvested of sugar beets in 2008. In 2009, sugar beets accounted for 20% of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
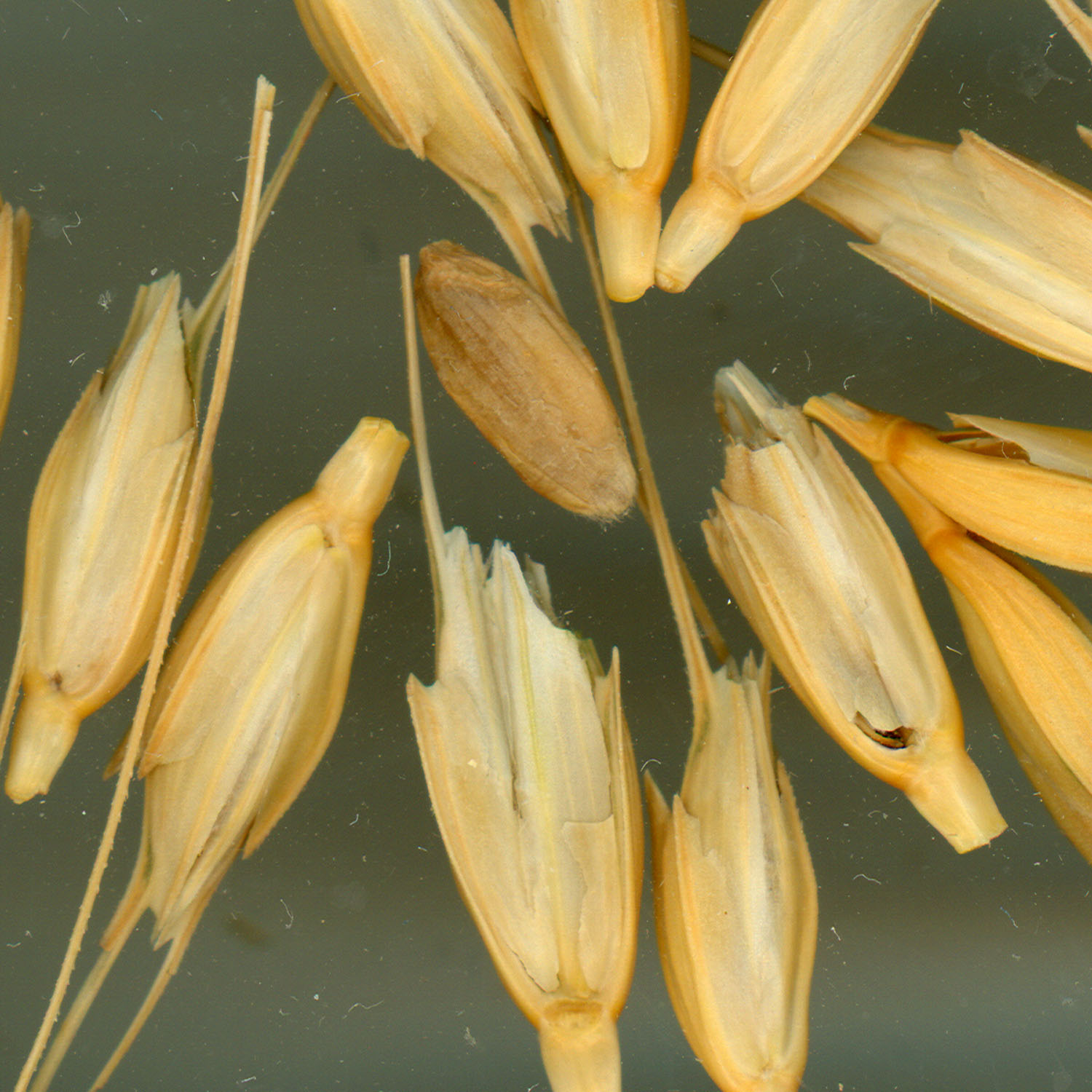
Wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeological record suggests that wheat was first cultivated in the regions of the Fertile Crescent around 9600 BCE. Botanically, the wheat kernel is a type of fruit called a caryopsis. Wheat is grown on more land area than any other food crop (, 2014). World trade in wheat is greater than for all other crops combined. In 2020, world production of wheat was , making it the second most-produced cereal after maize. Since 1960, world production of wheat and other grain crops has tripled and is expected to grow further through the middle of the 21st century. Global demand for wheat is increasing due to the unique viscoelastic and adhesive properties of gluten proteins, which facilitate the production of processed foods, whose consumption is inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Architecture
The term Norman architecture is used to categorise styles of Romanesque architecture developed by the Normans in the various lands under their dominion or influence in the 11th and 12th centuries. In particular the term is traditionally used for English Romanesque architecture. The Normans introduced large numbers of castles and fortifications including Norman keeps, and at the same time monasteries, abbeys, churches and cathedrals, in a style characterised by the usual Romanesque rounded arches (particularly over windows and doorways) and especially massive proportions compared to other regional variations of the style. Origins These Romanesque styles originated in Normandy and became widespread in northwestern Europe, particularly in England, which contributed considerable development and where the largest number of examples survived. At about the same time, a Norman dynasty that ruled in Sicily produced a distinctive variation–incorporating Byzantine and Saracen influen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A12 Road (Great Britain)
The A12 is a major road in Eastern England. It runs north-east/south-west between London and the coastal town of Lowestoft in the north-eastern corner of Suffolk, following a similar route to the Great Eastern Main Line until Ipswich. A section of the road between Lowestoft and Great Yarmouth became part of the A47 in 2017. Between the junctions with the M25 and the A14, the A12 forms part of the unsigned Euroroute E30 (prior to 1985, it was the E8). Unlike most A roads, this section of the A12, together with the A14 and the A55, has junction numbers as if it were a motorway. The section of the A12 through Essex has sections of dual two lanes and dual three lanes, with eight changes in width between the M25 to Ipswich. It was named as Britain's worst road because of "potholes and regular closures due to roadworks" in a 2007 survey by Cornhill Insurance. The A12 is covered by Highways England's A12 and A120 Route Management Strategy. Starting just north of the Blackwall Tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
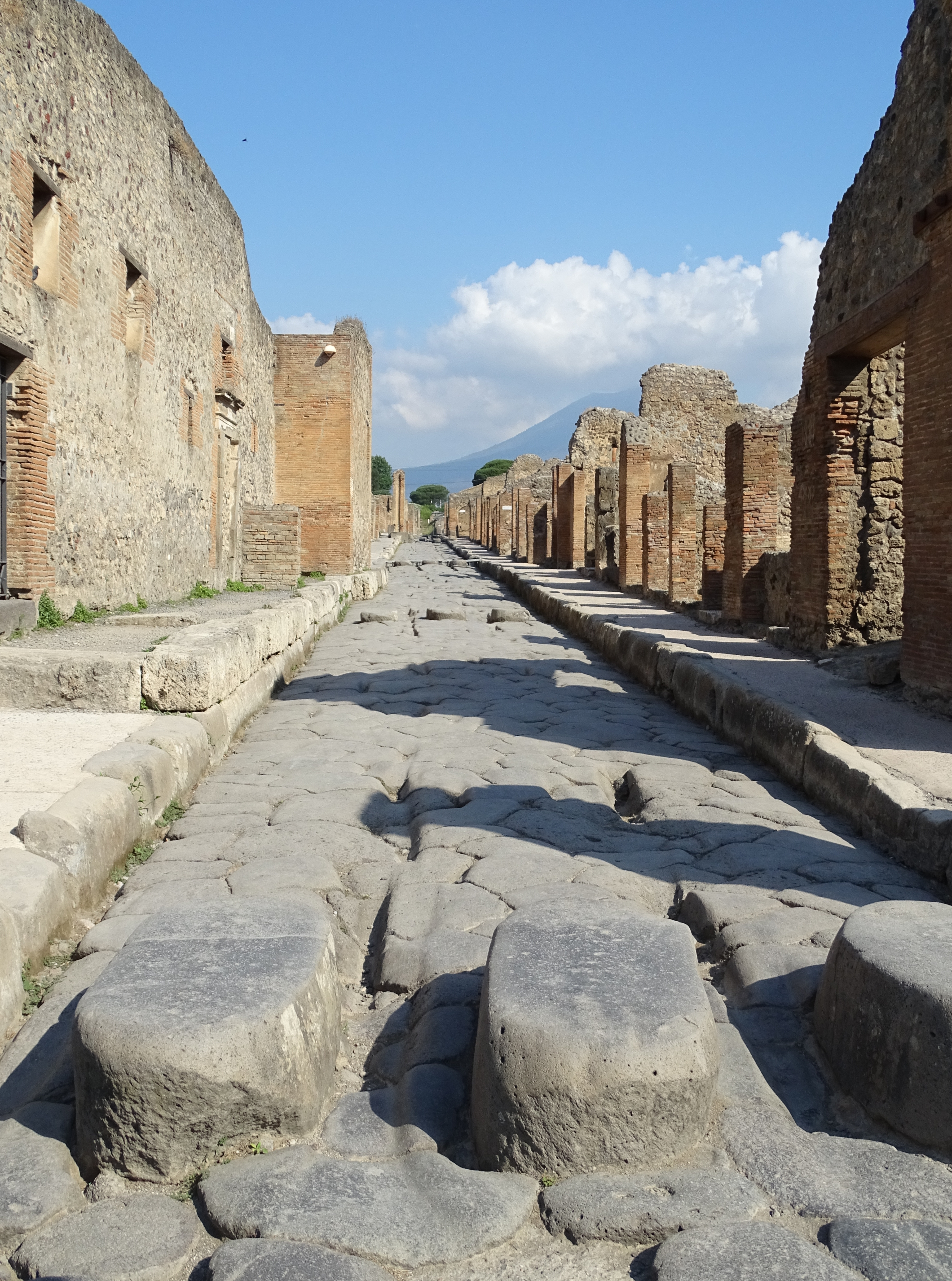
Roman Road
Roman roads ( la, viae Romanae ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, and were built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. They provided efficient means for the overland movement of armies, officials, civilians, inland carriage of official communications, and trade goods. Roman roads were of several kinds, ranging from small local roads to broad, long-distance highways built to connect cities, major towns and military bases. These major roads were often stone-paved and metaled, cambered for drainage, and were flanked by footpaths, bridleways and drainage ditches. They were laid along accurately surveyed courses, and some were cut through hills, or conducted over rivers and ravines on bridgework. Sections could be supported over marshy ground on rafted or piled foundations.Corbishley, Mike: "The Roman World", page 50. Warwick Press, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Chelmer
The River Chelmer is a river that flows entirely through the county of Essex, England, running from the northwest of the county through Chelmsford to the River Blackwater near Maldon. Course The source of the river is in the parish of Debden in north west Essex. The two primary source streams run to the north and to the west of the hamlet of Debden Green. The longer of the sources rises iRowney Wood on the hill to the west of Debden Green, only a few hundred metres to the south east of the source of the River Cam that heads north through Cambridge eventually emptying into The Wash.Ordnance Survey of Great Britain The River Chelmer flows past Thaxted, south through the district of Uttlesford around the northeast of Great Dunmow. It continues flowing south-southeast into the borough of Chelmsford and on into the city of Chelmsford where the River Can flows into it. It then flows east through the borough and into the district of Maldon until it meets the River Blackwater east o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parish Councils In England
Parish councils are civil local authorities found in England which are the lowest tier of local government. They are elected corporate bodies, with variable tax raising powers, and they carry out beneficial public activities in geographical areas known as civil parishes. There are about 9,000 parish and town councils in England, and over 16 million people live in communities served by them. Parish councils may be known by different styles, they may resolve to call themselves a town council, village council, community council, neighbourhood council, or if the parish has city status, it may call itself a city council. However their powers and duties are the same whatever name they carry.Local Government and Public Involvement in Health Act 2007 Parish councils receive the majority of their funding by levying a precept upon the council tax paid by the residents of the parish (or parishes) covered by the council. In 2021-22 the amount raised by precept was £616 million. Other fund ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunsmiths
A gunsmith is a person who repairs, modifies, designs, or builds guns. The occupation differs from an armorer, who usually replaces only worn parts in standard firearms. Gunsmiths do modifications and changes to a firearm that may require a very high level of craftsmanship, requiring the skills of a top-level machinist, a very skilled woodworker, and even an engineer. Gunsmiths perform factory-level repairs and renovations to restore a well-used or deteriorated firearms to new condition. They may make alterations to adapt sporting guns to better fit the individual shooter that may require extensive modifications to the firearm's stocks and metal parts. Repairs and redesigns may require fabrication and fitting of unavailable parts and assemblies constructed by smiths themselves. Gunsmiths may also renew metal finishes or apply decorative carvings or engravings to guns. Many gun shops offer gunsmithing service on the premises. Overview Gunsmiths may be employed in: *factories by fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Boreham
HMS ''Boreham'' was one of 93 ships of the of inshore minesweepers. Their names were all chosen from villages ending in ''-ham''. The minesweeper was named after Boreham in Essex Essex () is a county in the East of England. One of the home counties, it borders Suffolk and Cambridgeshire to the north, the North Sea to the east, Hertfordshire to the west, Kent across the estuary of the River Thames to the south, and G .... References * Ham-class minesweepers Ships built in Lowestoft 1952 ships Cold War minesweepers of the United Kingdom Royal Navy ship names Ham-class minesweepers of the Royal Malaysian Navy {{malaysia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ham Class Minesweeper
The Ham class was a class of inshore minesweepers (IMS), known as the Type 1, of the British Royal Navy. The class was designed to operate in the shallow water of rivers and estuaries. All of the ships in the class are named for British place names that end with -"ham". The parent firm that was responsible for supervising construction was Samuel White of Cowes, Isle of Wight. Unlike traditional minesweepers, they were not equipped for sweeping moored or magnetic mines. Their work was to locate individual mines and neutralise them. This was a then-new role, and the class was configured for working in the shallow water of rivers, estuaries and shipping channels. The class consisted of 93 ships, launched between 1954 and 1959. was the first. They were built in three slightly different sub-groups, the first sub-group, the 26-group, is distinguished by pennant numbers 26xx, and the second and third sub-groups, the 27-group, are distinguished by pennant numbers 27xx. The 26-group wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)