|
Bombardier Beetle
Bombardier beetles are ground beetles (Carabidae) in the tribes Brachinini, Paussini, Ozaenini, or Metriini—more than 500 species altogether—which are most notable for the defense mechanism that gives them their name: when disturbed, they eject a hot noxious chemical spray from the tip of the abdomen with a popping sound. The spray is produced from a reaction between two hypergolic chemical compounds, hydroquinone and hydrogen peroxide, which are stored in two reservoirs in the beetle's abdomen. When the aqueous solution of hydroquinones and hydrogen peroxide reaches the " vestibule" ( Eisner's word), catalysts facilitate the decomposition of the hydrogen peroxide and the oxidation of the hydroquinone. Heat from the reaction brings the mixture to near the boiling point of water and produces gas that drives the ejection. The damage caused can be fatal to attacking insects. Some bombardier beetles can direct the spray in a wide range of directions. The beetle's unusual defe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animalia
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1 million are insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a bilaterally symmetric body plan. The Bilateria include the protostomes, containing animals such as nematodes, arthropods, flatworms, annelids and molluscs, and the deuterostomes, containing the echinode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aqueous Solution
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, or sodium chloride (NaCl), in water would be represented as . The word ''aqueous'' (which comes from ''aqua'') means pertaining to, related to, similar to, or dissolved in, water. As water is an excellent solvent and is also naturally abundant, it is a ubiquitous solvent in chemistry. Since water is frequently used as the solvent in experiments, the word solution refers to an aqueous solution, unless the solvent is specified. A ''non-aqueous solution'' is a solution in which the solvent is a liquid, but is not water. (See also Solvent and Inorganic nonaqueous solvent.) Characteristics Substances that are ''hydrophobic'' ('water-fearing') do not dissolve well in water, whereas those that are ''hydrophilic'' ('water-friendly') do. An example of a hydrophilic substance is sodium chlo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
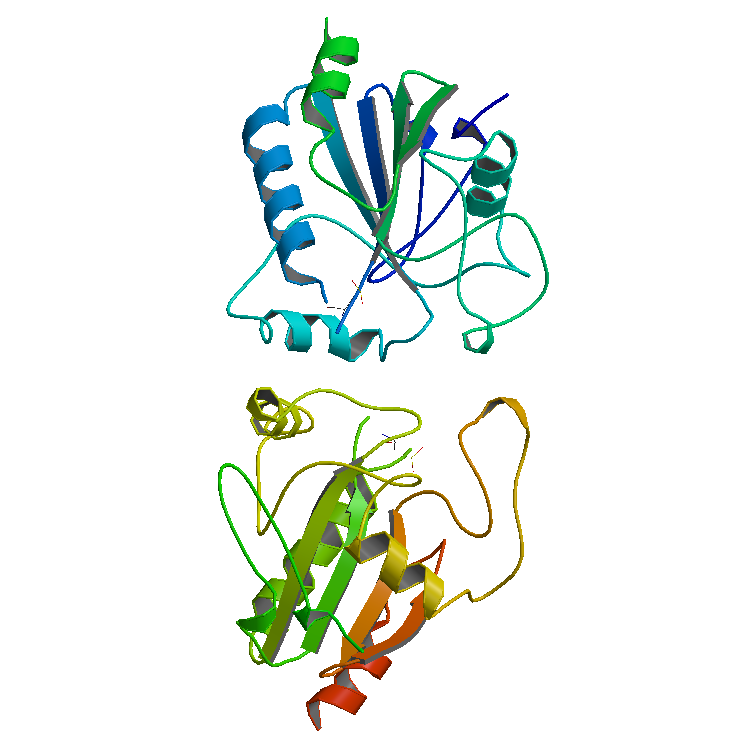
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peroxidase
Peroxidases or peroxide reductases ( EC numberbr>1.11.1.x are a large group of enzymes which play a role in various biological processes. They are named after the fact that they commonly break up peroxides. Functionality Peroxidases typically catalyze a reaction of the form: :ROOR' + \overset + 2H+ -> ce + R'OH Optimal substrates For many of these enzymes the optimal substrate is hydrogen peroxide, but others are more active with organic hydroperoxides such as lipid peroxides. Peroxidases can contain a heme cofactor in their active sites, or alternately redox-active cysteine or selenocysteine residues. The nature of the electron donor is very dependent on the structure of the enzyme. * For example, horseradish peroxidase can use a variety of organic compounds as electron donors and acceptors. Horseradish peroxidase has an accessible active site, and many compounds can reach the site of the reaction. * On the other hand, for an enzyme such as cytochrome c peroxidase, the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalase
Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen (such as bacteria, plants, and animals) which catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. It is a very important enzyme in protecting the cell from oxidative damage by reactive oxygen species (ROS). Catalase has one of the highest turnover numbers of all enzymes; one catalase molecule can convert millions of hydrogen peroxide molecules to water and oxygen each second. Catalase is a tetramer of four polypeptide chains, each over 500 amino acids long. It contains four iron-containing heme groups that allow the enzyme to react with hydrogen peroxide. The optimum pH for human catalase is approximately 7, and has a fairly broad maximum: the rate of reaction does not change appreciably between pH 6.8 and 7.5. The pH optimum for other catalases varies between 4 and 11 depending on the species. The optimum temperature also varies by species. Structure Human catalase forms a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnivorous
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose food and energy requirements derive from animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other soft tissues) whether through hunting or scavenging. Nomenclature Mammal order The technical term for mammals in the order Carnivora is ''carnivoran'', and they are so-named because most member species in the group have a carnivorous diet, but the similarity of the name of the order and the name of the diet causes confusion. Many but not all carnivorans are meat eaters; a few, such as the large and small cats (felidae) are ''obligate'' carnivores (see below). Other classes of carnivore are highly variable. The Ursids, for example: While the Arctic polar bear eats meat almost exclusively (more than 90% of its diet is meat), almost all other bear species are omnivorous, and one species, the giant panda, is nearly exclusively herbivorous. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pheropsophus Verticalis 01 Pengo
''Pheropsophus'' is a genus of beetles in the family Carabidae, containing the following 138 species: * '' Pheropsophus abbreviatus'' Arrow, 1901 * ''Pheropsophus abyssinicus'' Alluaud, 1916 * ''Pheropsophus acutecostatus'' Fairmaire, 1892 * ''Pheropsophus adrianae'' Giachino, 2005 * '' Pheropsophus aequinoctialis'' (Linnaeus, 1763) * ''Pheropsophus africanus'' (Dejean, 1825) * ''Pheropsophus akhaensis'' Kirschenhofer, 2010 * '' Pheropsophus alexandrae'' Giachino, 2003 * ''Pheropsophus amnicola'' Darlington, 1968 * '' Pheropsophus andrewesi'' Jedlicka, 1964 * '' Pheropsophus androyanus'' Alluaud, 1932 * ''Pheropsophus angolensis'' (Erichson, 1843) * ''Pheropsophus aptinoides'' Chaudoir, 1876 * ''Pheropsophus aptinomorphus'' Heller, 1910 * ''Pheropsophus arcanus'' (Erichson, 1843) * ''Pheropsophus assimilis'' Chaudoir, 1876 * ''Pheropsophus baehri'' Giachino, 2005 * ''Pheropsophus baliothorax'' Heller, 1910 * ''Pheropsophus balkei'' Giachino, 2005 * ''Pheropsophus basiguttatus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irreducible Complexity
Irreducible complexity (IC) is the argument that certain biological systems with multiple interacting parts would not function if one of the parts was removed, so supposedly could not have evolved by successive small modifications from earlier less complex systems through natural selection, which would need all intermediate precursor systems to have been fully functional. Irreducible complexity has become central to the creationist concept of intelligent design, but the concept of irreducible complexity has been rejected by the scientific community,"We therefore find that Professor Behe's claim for irreducible complexity has been refuted in peer-reviewed research papers and has been rejected by the scientific community at large." 4:Whether ID Is Science, in E. Application of the Endorsement Test to the ID Policy, Ruling, Judge John E. Jones III, ''Kitzmiller v. Dover Area School District'' which regards intelligent design as pseudoscience. Irreducible complexity is one of two mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creationism
Creationism is the religious belief that nature, and aspects such as the universe, Earth, life, and humans, originated with supernatural acts of divine creation. Gunn 2004, p. 9, "The ''Concise Oxford Dictionary'' says that creationism is 'the belief that the universe and living organisms originated from specific acts of divine creation.'" In its broadest sense, creationism includes a continuum of religious views, Haarsma 2010, p. 168, "Some Christians, often called 'Young Earth creationists,' reject evolution in order to maintain a semi-literal interpretation of certain biblical passages. Other Christians, called 'progressive creationists,' accept the scientific evidence for some evolution over a long history of the earth, but also insist that God must have performed some miracles during that history to create new life-forms. Intelligent design, as it is promoted in North America is a form of progressive creation. Still other Christians, called theistic evolutionists' or 'ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boiling Point
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor. The boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding environmental pressure. A liquid in a partial vacuum has a lower boiling point than when that liquid is at atmospheric pressure. A liquid at low pressure has a lower boiling point than when that liquid is at atmospheric pressure. Because of this, water boils at under standard pressure at sea level, but at at altitude. For a given pressure, different liquids will boiling, boil at different temperatures. The normal boiling point (also called the atmospheric boiling point or the atmospheric pressure boiling point) of a liquid is the special case in which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the defined atmospheric pressure at sea level, one Atmosphere (unit), atmosphere. At that temperature, the vapor pressure of the liquid becomes suffici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. There are two classes of redox reactions: * ''Electron-transfer'' – Only one (usually) electron flows from the reducing agent to the oxidant. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * ''Atom transfer'' – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides, other chemical species can serve the same function. In hydrogenation, C=C (and other) bonds ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |