|
Bombardier MVI
The Mark VI monorail (Mk6) is a monorail train used in the Walt Disney World Monorail System and the Las Vegas Monorail. The Mark VI started replacing the Mark IV monorails at Walt Disney World in 1989, replacing the final Mark IV by 1991. The Mark VI later replaced the two ex-WDW Mark IV monorail sets of the Las Vegas Monorail (then named the MGM Grand-Bally's Monorail) in 2004. The Las Vegas M-VI versions of the trains differ from the Walt Disney World trains in physical appearance and the fact that they are automated, a trait the Walt Disney World monorails lacked until their automation starting in 2014. Train specifications * The trains were built by Bombardier of Canada for a reported cost of over $3.5 million per train. * Each cab car is 40 ft 5 in (12.3 m) long and each intermediate car is 28 ft 2 in (8.6 m) long. The 6-car trains in the Walt Disney World Monorail System total 203 ft 6 in (62 m) in length. * Each car can hold 20 seated passengers and 40 stand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monorail Coral
A monorail (from "wiktionary:mono-, mono", meaning "one", and "Track (rail transport), rail") is a Rail transport, railway in which the track consists of a single rail or a beam. Colloquially, the term "monorail" is often used to describe any form of elevated rail or people mover. More accurately, the term refers to the style of Track (rail transport), track.The term "track" is used here for simplicity. Technically the monorail sits on or is suspended from a guideway containing a singular structure. There is an additional generally accepted rule that the support for the car be narrower than the car. Etymology The term possibly comes from 1897, from German engineer Eugen Langen, who called an elevated railway system with wagons suspended the ''Wuppertal Schwebebahn, Eugen Langen One-railed Suspension Tramway'' (Einschieniges Hängebahnsystem Eugen Langen). Differentiation from other transport systems Monorails have found applications in airport transfer and medium capacity s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Braking
Dynamic braking is the use of an electric traction motor as a generator when slowing a vehicle such as an electric or diesel-electric locomotive. It is termed " rheostatic" if the generated electrical power is dissipated as heat in brake grid resistors, and " regenerative" if the power is returned to the supply line. Dynamic braking reduces wear on friction-based braking components, and regeneration lowers net energy consumption. Dynamic braking may also be used on railcars with multiple units, light rail vehicles, electric trams, trolleybuses, and electric and hybrid electric automobiles. Principle of operation Converting electrical energy to the mechanical energy of a rotating shaft (electric motor) is the inverse of converting the mechanical energy of a rotating shaft to electrical energy (electric generator). Both are accomplished through the interactions of armature windings with a (relatively) moving external magnetic field, with the armature connected to an electrical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monorails
A monorail (from "mono", meaning "one", and "rail") is a railway in which the track consists of a single rail or a beam. Colloquially, the term "monorail" is often used to describe any form of elevated rail or people mover. More accurately, the term refers to the style of track.The term "track" is used here for simplicity. Technically the monorail sits on or is suspended from a guideway containing a singular structure. There is an additional generally accepted rule that the support for the car be narrower than the car. Etymology The term possibly comes from 1897, from German engineer Eugen Langen, who called an elevated railway system with wagons suspended the '' Eugen Langen One-railed Suspension Tramway'' (Einschieniges Hängebahnsystem Eugen Langen). Differentiation from other transport systems Monorails have found applications in airport transfer and medium capacity metros. To differentiate monorails from other transport modes, the Monorail Society defines a monorail a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walt Disney World Transit
Walt is a masculine given name, generally a short form of Walter, and occasionally a surname. Notable people with the name include: People Given name * Walt Arfons (1916-2013), American drag racer and competition land speed record racer * Walt Bellamy (1939-2013), American National Basketball Association player, two-time Basketball Hall of Fame inductee * Walt Bellamy (ice hockey) (1881-1941), Canadian hockey player * Walter Blackman, American member of the Arizona House of Representatives * Walt Bowyer (born 1960), American former National Football League player * Walt Brown (politician) (born 1926), American politician * Walt Clago (1899-1955), American football player * Walt Corey (born 1938), American former National Football League player * Walt Disney (1901-1966), American film producer, director, screenwriter, voice actor, animator, entrepreneur and philanthropist * Walt Dropo (1923-2010), American Major League Baseball and college basketball player * Walt Frazier (born 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Multiple Units Of The United States
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equations. Various common phenomena are related to electricity, including lightning, static electricity, electric heating, electric discharges and many others. The presence of an electric charge, which can be either positive or negative, produces an electric field. The movement of electric charges is an electric current and produces a magnetic field. When a charge is placed in a location with a non-zero electric field, a force will act on it. The magnitude of this force is given by Coulomb's law. If the charge moves, the electric field would be doing work on the electric charge. Thus we can speak of electric potential at a certain point in space, which is equal to the work done by an external agent in carrying a unit of positiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In Walt Disney Parks And Resorts
Rail transport can be found in every theme park resort property owned or licensed by Disney Parks, Experiences and Products, one of the four business segments of the Walt Disney Company. The origins of Disney theme park rail transport can be traced back to Walt Disney himself and his personal fondness for railroads, who insisted that they be included in the first Disney park, the original Disneyland (a key component of the Disneyland Resort) in California in the United States, which opened on July 17, 1955... The Disney tradition of including transport by rail in, and adjacent to, its parks has since been extended to other Disney properties with the opening of Walt Disney World in Florida in the United States, Tokyo Disney Resort in Japan, Disneyland Paris in France, Hong Kong Disneyland Resort in China, and Shanghai Disney Resort in China. The Disney theme park chain is the largest on the planet by annual attendance with over 155 million visitors in 2019, and the rail systems l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bond to form N2, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas. N2 forms about 78% of Earth's atmosphere, making it the most abundant uncombined element. Nitrogen occurs in all organisms, primarily in amino acids (and thus proteins), in the nucleic acids ( DNA and RNA) and in the energy transfer molecule adenosine triphosphate. The human body contains about 3% nitrogen by mass, the fourth most abundant element in the body after oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. The nitrogen cycle describes the movement of the element from the air, into the biosphere and organic compounds, then back into the atmosphere. Many indus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tire Code
Automotive tires are described by an alphanumeric tire code (in North American English) or tyre code (in Commonwealth English), which is generally molded into the sidewall of the tire. This code specifies the dimensions of the tire, and some of its key limitations, such as load-bearing ability, and maximum speed. Sometimes the inner sidewall contains information not included on the outer sidewall, and vice versa. The code has grown in complexity over the years, as is evident from the mix of SI and USC units, and ad-hoc extensions to lettering and numbering schemes. New automotive tires frequently have ratings for traction, treadwear, and temperature resistance, all collectively known as the Uniform Tire Quality Grading. Most tires sizes are given using the ISO metric sizing system. However, some pickup trucks and SUVs use the Light Truck Numeric or Light Truck High Flotation system. National technical standards regulations DOT code The DOT code is an alphanumeric charac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monorail Diagram Tires
A monorail (from "mono", meaning "one", and "rail") is a railway in which the track consists of a single rail or a beam. Colloquially, the term "monorail" is often used to describe any form of elevated rail or people mover. More accurately, the term refers to the style of track.The term "track" is used here for simplicity. Technically the monorail sits on or is suspended from a guideway containing a singular structure. There is an additional generally accepted rule that the support for the car be narrower than the car. Etymology The term possibly comes from 1897, from German engineer Eugen Langen, who called an elevated railway system with wagons suspended the '' Eugen Langen One-railed Suspension Tramway'' (Einschieniges Hängebahnsystem Eugen Langen). Differentiation from other transport systems Monorails have found applications in airport transfer and medium capacity metros. To differentiate monorails from other transport modes, the Monorail Society defines a monorail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governor (device)
A governor, or speed limiter or controller, is a device used to measure and regulate the speed of a machine, such as an engine. A classic example is the centrifugal governor, also known as the Watt or fly-ball governor on a reciprocating steam engine, which uses the effect of inertial force on rotating weights driven by the machine output shaft to regulate its speed by altering the input flow of steam. History Centrifugal governors were used to regulate the distance and pressure between millstones in windmills since the 17th century. Early steam engines employed a purely reciprocating motion, and were used for pumping water – an application that could tolerate variations in the working speed. It was not until the Scottish engineer James Watt introduced the ''rotative'' steam engine, for driving factory machinery, that a constant operating speed became necessary. Between the years 1775 and 1800, Watt, in partnership with industrialist Matthew Boulton, produced some 500 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
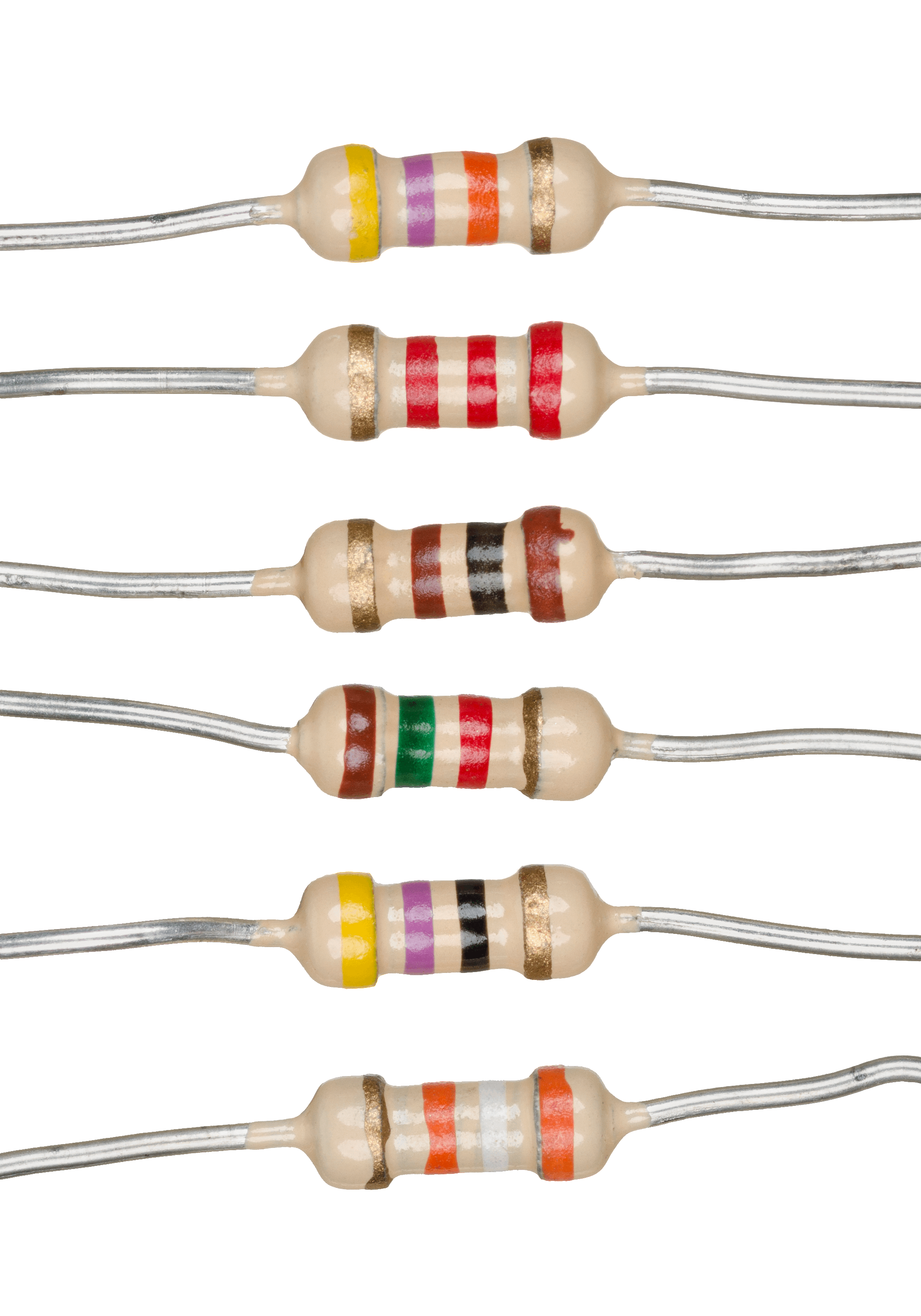
Resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements (such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity. Resistors are common elements of electrical networks and electronic circuits and are ubiquitous in electronic equipment. Practical resistors as discrete components can be composed of various compounds and forms. Resisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilowatt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Watt (1736–1819), an 18th-century Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved the Newcomen engine with his own steam engine in 1776. Watt's invention was fundamental for the Industrial Revolution. Overview When an object's velocity is held constant at one metre per second against a constant opposing force of one newton, the rate at which work is done is one watt. : \mathrm In terms of electromagnetism, one watt is the rate at which electrical work is performed when a current of one ampere (A) flows across an electrical potential difference of one volt (V), meaning the watt is equivalent to the volt-ampere (the latter unit, however, is used for a different quantity from the real power of an electrical circuit). : ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)