|
Bodyguard Of Lies
''Bodyguard of Lies'' is a 1975 non-fiction book written by Anthony Cave Brown, his first major historical work. Named for a wartime quote of Winston Churchill, it is a narrative account of Allied military deception operations during the Second World War. The British and American governments resisted Brown's attempts to research the book. Many of the topics were still classified and he was denied access to British war records. The material in the book is predominantly based on oral testimony as well as some American records, declassified toward the end of Brown's research. Critical reception has been mixed, but generally negative. Contemporary historians, such as Charles B. MacDonald, praised the work – although some did comment on its length. Modern reviewers have identified inconsistencies or errors in the material, based on later declassified records. Also, some of Brown's personal conclusions have been questioned. Background ''Bodyguard of Lies'' was Brown's firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthony Cave Brown
Anthony Cave Brown (21 March 1929 – 14 July 2006) was a British journalist, espionage non-fiction writer, and historian. Early years Brown. was born in Bath, and moved to London as a boy, stuffing propaganda leaflets into bombs meant for Nazi Germany towards the end of World War II. He was educated at Luton Grammar School, and joined the Royal Air Force for his national service, working as a photographer. Journalist Brown began his reporting career in Luton and Bristol before moving to Fleet Street in the mid-1950s where he joined the ''Daily Mail''. During the late 1950s he covered the Hungarian uprising (in 1956) and the Algerian War of Independence. In 1958 he was awarded Reporter of the Year. Brown secured the first Western interview with Egyptian president, Gamel Abdel Nasser, and was a frequent drinking companion of Kim Philby in the Middle East prior to the latter's 1963 defection to the Soviet Union. He also interviewed the dissident Soviet writer Boris Pasternak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freedom Of Information
Freedom of information is freedom of a person or people to publish and consume information. Access to information is the ability for an individual to seek, receive and impart information effectively. This sometimes includes "scientific, indigenous, and traditional knowledge; freedom of information, building of open knowledge resources, including open Internet and open standards, and open access and availability of data; preservation of digital heritage; respect for cultural and linguistic diversity, such as fostering access to local content in accessible languages; quality education for all, including lifelong and e-learning; diffusion of new media and information literacy and skills, and social inclusion online, including addressing inequalities based on skills, education, gender, age, race, ethnicity, and accessibility by those with disabilities; and the development of connectivity and affordable ICTs, including mobile, the Internet, and broadband infrastructures". Public ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Mincemeat
Operation Mincemeat was a successful British deception operation of the Second World War to disguise the 1943 Allied invasion of Sicily. Two members of British intelligence obtained the body of Glyndwr Michael, a tramp who died from eating rat poison, dressed him as an officer of the Royal Marines and placed personal items on him identifying him as the fictitious Captain (Acting Major) William Martin. Correspondence between two British generals that suggested that the Allies planned to invade Greece and Sardinia, with Sicily as merely the target of a feint, was also placed on the body. Part of the wider Operation Barclay, Mincemeat was based on the 1939 Trout memo, written by Rear Admiral John Godfrey, the Director of the Naval Intelligence Division, and his personal assistant, Lieutenant Commander Ian Fleming. With the approval of the British Prime Minister, Winston Churchill, and the military commander in the Mediterranean, General Dwight D. Eisenhower, the plan began by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
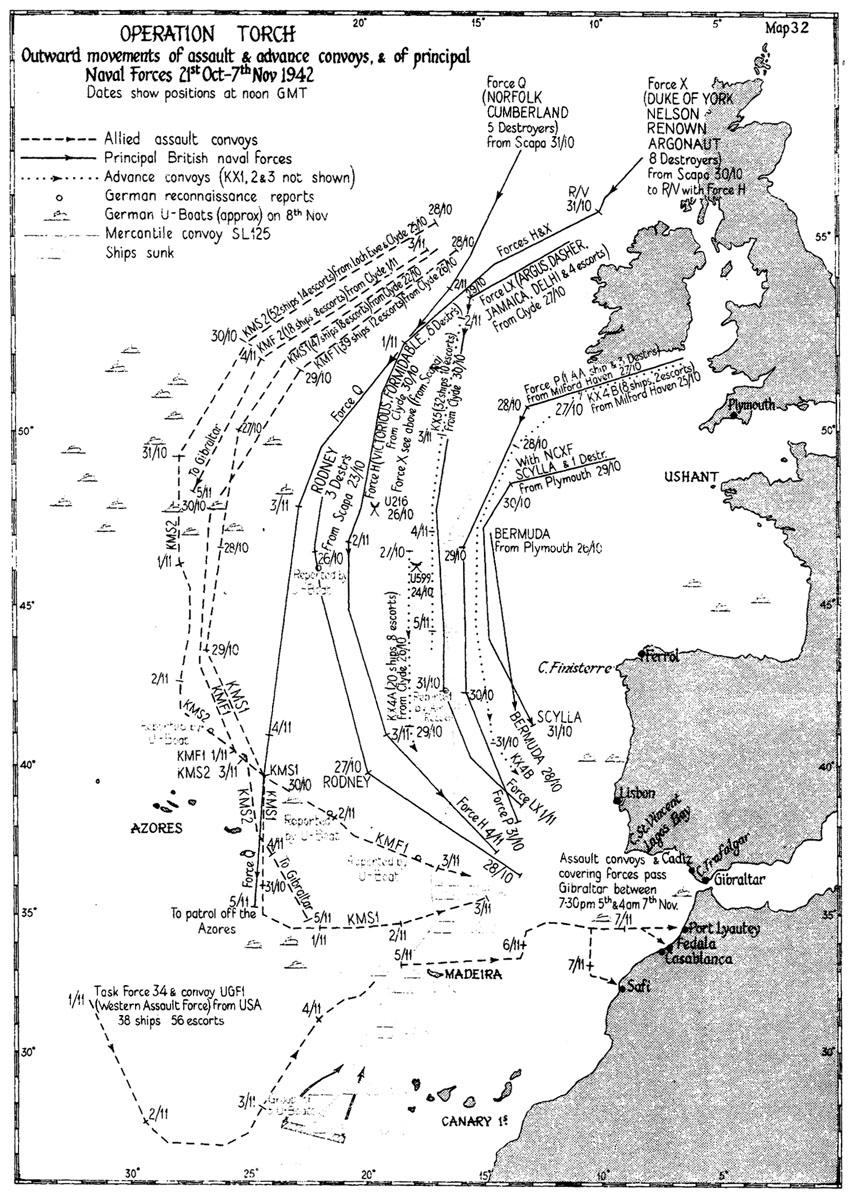
Operation Torch
Operation Torch (8 November 1942 – Run for Tunis, 16 November 1942) was an Allies of World War II, Allied invasion of French North Africa during the Second World War. Torch was a compromise operation that met the British objective of securing victory in North Africa while allowing American armed forces the opportunity to engage in the fight against Nazi Germany on a limited scale. It was the first mass involvement of US troops in the Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II, European–North African Theatre, and saw the first major airborne assault carried out by the United States. While the French colonies were formally aligned with Germany via Vichy France, the loyalties of the population were mixed. Reports indicated that they might support the Allies. American General Dwight D. Eisenhower, supreme commander of the Allied forces in Mediterranean Theater of Operations, planned a three-pronged attack on Casablanca (Western), Oran (Center) and Algiers (Easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abwehr
The ''Abwehr'' (German for ''resistance'' or ''defence'', but the word usually means ''counterintelligence'' in a military context; ) was the German military-intelligence service for the ''Reichswehr'' and the ''Wehrmacht'' from 1920 to 1944. Although the 1919 Treaty of Versailles prohibited the Weimar Republic from establishing an intelligence organization of their own, they formed an espionage group in 1920 within the Ministry of Defence, calling it the ''Abwehr''. The initial purpose of the ''Abwehr'' was defence against foreign espionage: an organizational role which later evolved considerably. Under General Kurt von Schleicher (prominent in running the ''Reichswehr'' from 1926 onwards) the individual military services' intelligence units were combined and, in 1929, centralized under Schleicher's ''Ministeramt'' within the Ministry of Defence, forming the foundation for the more commonly understood manifestation of the ''Abwehr''. Each ''Abwehr'' station throughout German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admiral Canaris
Wilhelm Franz Canaris (1 January 1887 – 9 April 1945) was a German admiral and the chief of the ''Abwehr'' (the German military-intelligence service) from 1935 to 1944. Canaris was initially a supporter of Adolf Hitler, and the Nazi regime. However, following the German invasion of Poland in 1939, Canaris turned against Hitler and committed acts of both passive and active resistance during the war. Being the head of Nazi Germany's military-intelligence agency, he was in a key position to participate in resistance. As the war turned against Germany, Canaris and other military officers expanded their clandestine opposition to the leadership of Nazi Germany. By 1945, his acts of resistance and sabotage against the Nazi regime came to light and Canaris was executed in Flossenbürg concentration camp for high treason as the Allied forces advanced through Southern Germany. Early life Canaris was born on 1 January 1887 in Aplerbeck (now a part of Dortmund) in Westphalia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Agent
In the field of counterintelligence, a double agent is an employee of a secret intelligence service for one country, whose primary purpose is to spy on a target organization of another country, but who is now spying on their own country's organization for the target organization. Double agentry may be practised by spies of the target organization who infiltrate the controlling organization or may result from the ''turning'' (switching sides) of previously loyal agents of the controlling organization by the target. The threat of execution is the most common method of turning a captured agent (working for an intelligence service) into a double agent (working for a foreign intelligence service) or a double agent into a ''re-doubled agent''. It is unlike a defector, who is not considered an agent as agents are in place to function for an intelligence service and defectors are not, but some consider that defectors in place are agents until they have defected. Double agents are ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double-Cross System
The Double-Cross System or XX System was a World War II counter-espionage and deception operation of the British Security Service (a civilian organisation usually referred to by its cover title MI5). Nazi agents in Britain – real and false – were captured, turned themselves in or simply announced themselves, and were then used by the British to broadcast mainly disinformation to their Nazi controllers. Its operations were overseen by the Twenty Committee under the chairmanship of John Cecil Masterman; the name of the committee comes from the number 20 in Roman numerals: "XX" (i.e. a double cross). The policy of MI5 during the war was initially to use the system for counter-espionage Counterintelligence is an activity aimed at protecting an agency's intelligence program from an opposition's intelligence service. It includes gathering information and conducting activities to prevent espionage, sabotage, assassinations or ot .... It was only later that its potential for dece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Bevan (British Army Officer)
Colonel (United Kingdom), Colonel John Henry "Johnny" Bevan (5 April 1894 – 3 December 1978) was a British Army officer who, during the Second World War, made an important contribution to military deception, culminating in Operation Bodyguard, the plan to conceal the D-Day landings in Normandy. In civilian life he was a respected stockbroker in his father's firm. Bevan had an upper-class upbringing, including an education at Eton College, Eton and University of Oxford, Oxford. During the First World War he fought with the Hertfordshire Regiment in France and later became involved with intelligence analysis. His latter work came to the attention of wartime leaders, including Winston Churchill. Bevan stayed in the army for a while following the end of the war, and then took up a career in stock brokerage. He joined his father's firm, got married, and built up his profile as an honest businessman. At the outbreak of the Second World War, Bevan was recalled to his Territorial Arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dudley Clarke
Brigadier Dudley Wrangel Clarke, ( – ) was an officer in the British Army, known as a pioneer of military deception operations during the Second World War. His ideas for combining fictional orders of battle, visual deception and double agents helped define Allied deception strategy during the war, for which he has been referred to as "the greatest British deceiver of WW2". Clarke was also instrumental in the founding of three famous military units, namely the British Commandos, the Special Air Service and the US Rangers. Born in Johannesburg and brought up near London, Clarke joined the Royal Artillery as an officer in 1916 but transferred to the Royal Flying Corps after finding he was too young to fight in France. He spent the First World War learning to fly, first in Reading and then Egypt. Clarke returned to the Royal Artillery in 1919 and had a varied career doing intelligence work in the Middle East. In 1936 he was posted to Palestine, where he helped organise the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Controlling Section
The London Controlling Section (LCS) was a British secret department established in September 1941, under Oliver Stanley, with a mandate to coordinate Allied strategic military deception during World War II. The LCS was formed within the Joint Planning Staff at the offices of the War Cabinet, which was presided over by Winston Churchill as Prime Minister. At first the department struggled to have any impact, and Stanley spent time away from the office due to his wife's terminal illness. In June his post of Controlling Officer was handed over to Colonel John Bevan, who managed the LCS until the end of the war. The organisation was publicly revealed by Sir Ronald Wingate in 1969. Early deception Following the onset of the Second World War, the Allied nations began to recognise deception as a useful strategy. In early 1941 Lieutenant-Colonel Dudley Clarke's 'A' Force department, based in Cairo, undertook deception operations for the North African campaign. As their work came to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)