|
Body Identification
Body identification is a subfield of forensic science that uses a variety of scientific and non-scientific methods to identify a body. Forensic purposes are served by rigorous scientific forensic identification techniques, but these are generally preceded by formal identification. This involves requesting a family member or friend of the victim to visually identify the body. If a body is not badly decomposed or damaged, one or more persons who knew the deceased well can visually confirm their identity. Authorities will also compare supportive documents such as a driver's license, passport, or other authoritative photo ID before accepting a personal identification. Any formal investigation should be used to support additional scientific evidence, allowing forensic scientists to either reinforce or question the supposed identity of the victim. Scientific methods are also used in cases where these introductory approaches are not possible. These scientific identification techniques, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forensic Science
Forensic science, also known as criminalistics, is the application of science to criminal and civil laws, mainly—on the criminal side—during criminal investigation, as governed by the legal standards of admissible evidence and criminal procedure. Forensic science is a broad field that includes; DNA analysis, fingerprint analysis, blood stain pattern analysis, firearms examination and ballistics, tool mark analysis, serology, toxicology, hair and fiber analysis, entomology, questioned documents, anthropology, odontology, pathology, epidemiology, footwear and tire tread analysis, drug chemistry, paint and glass analysis, digital audio video and photo analysis. Forensic scientists collect, preserve, and analyze scientific evidence during the course of an investigation. While some forensic scientists travel to the scene of the crime to collect the evidence themselves, others occupy a laboratory role, performing analysis on objects brought to them by other individuals. Still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fingerprint
A fingerprint is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. The recovery of partial fingerprints from a crime scene is an important method of forensic science. Moisture and grease on a finger result in fingerprints on surfaces such as glass or metal. Deliberate impressions of entire fingerprints can be obtained by ink or other substances transferred from the peaks of friction ridges on the skin to a smooth surface such as paper. Fingerprint records normally contain impressions from the pad on the last joint of fingers and thumbs, though fingerprint cards also typically record portions of lower joint areas of the fingers. Human fingerprints are detailed, nearly unique, difficult to alter, and durable over the life of an individual, making them suitable as long-term markers of human identity. They may be employed by police or other authorities to identify individuals who wish to conceal their identity, or to identify people who are incapacitated or deceased and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MicroRNA
MicroRNA (miRNA) are small, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules containing 21 to 23 nucleotides. Found in plants, animals and some viruses, miRNAs are involved in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. miRNAs base-pair to complementary sequences in mRNA molecules, then gene silence said mRNA molecules by one or more of the following processes: (1) cleavage of mRNA strand into two pieces, (2) destabilization of mRNA by shortening its poly(A) tail, or (3) translation of mRNA into proteins. This last method of gene silencing is the least efficient of the three, and requires the aid of ribosomes. miRNAs resemble the small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) of the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway, except miRNAs derive from regions of RNA transcripts that fold back on themselves to form short hairpins, whereas siRNAs derive from longer regions of double-stranded RNA. The human genome may encode over 1900 miRNAs, although more recent analysis suggests that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Fingerprinting
DNA profiling (also called DNA fingerprinting) is the process of determining an individual's DNA characteristics. DNA analysis intended to identify a species, rather than an individual, is called DNA barcoding. DNA profiling is a forensic technique in criminal investigations, comparing criminal suspects' profiles to DNA evidence so as to assess the likelihood of their involvement in the crime. It is also used in paternity testing, to establish immigration eligibility, and in genealogical and medical research. DNA profiling has also been used in the study of animal and plant populations in the fields of zoology, botany, and agriculture. Background Starting in the 1980s, scientific advances allowed the use of DNA as a material for the identification of an individual. The first patent covering the direct use of DNA variation for forensicsUS5593832A was filed by Jeffrey Glassberg in 1983, based upon work he had done while at Rockefeller University in the United States in 1981. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alec Jeffreys -2008
Alec or Aleck is a Scottish form of the given name Alex. It may be a diminutive of the name Alexander or a given name in its own right. Notable people with the name include: People *Alec Aalto (1942–2018), Finnish diplomat *Alec Acton (1938–1994), English footballer *Alec Albiston (1917–1998), Australian rules footballer *Alec Alston (1937–2009), English footballer *Alec and Peter Graham (1881–1957), New Zealand mountaineers, guides, and hotel operators *Alec Anderson (1894–1953), American NFL player *Alec Asher (born 1991), American MLB player *Alec Ashworth (1939–1995), English professional footballer *Alec Astle (born 1949), New Zealand former cricketer *Alec Atkinson (1919–2015), British Royal Air Force officer and civil servant * Alec B. Francis (1867–1934), English silent-film actor *Alec Bagot (1893–1968), South Australian adventurer, polemicist, and politician *Alec Baillie (died 2020), American bassist *Alec Baldwin (born 1958), American actor *Alec Ban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthopedic Plate
An orthopedic plate is a form of internal fixation used in orthopaedic surgery to hold fractures in place to allow bone healing. Most modern plates include bone screws to help the orthopedic plate stay in place. Historic overview Prior to the invention of the orthopedic plate, metal wiring was used to solve the issue of bone fractures until about 1850. It was debated when the first use of this technique was actually made. Supposedly, the first use of this metal wiring was by the ancient Greeks. The first recorded use of metal wiring was is 1755 in a French journal. It was not until 1870, a Frenchman by the name of Laurent Berenger-Feraud began writing a book on internal fixation and bone fractures called "''Traité de l'immobilisation directe des fragments osseux dans les fractures"'' (a book on direct immobilization of bone fragments of fractures). All the information proved to be beneficial in medical procedures, however one thing lacked, the antiseptic treatments needed to prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiographs
Radiography is an imaging technology, imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnostic" and "therapeutic") and industrial radiography. Similar techniques are used in airport security (where "body scanners" generally use backscatter X-ray). To create an image in conventional radiography, a beam of X-rays is produced by an X-ray generator and is projected toward the object. A certain amount of the X-rays or other radiation is absorbed by the object, dependent on the object's density and structural composition. The X-rays that pass through the object are captured behind the object by a X-ray detector, detector (either photographic film or a digital detector). The generation of flat two dimensional images by this technique is called projectional radiography. In computed tomography (CT scanning) an X-ray source and its associa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OPG W56J -
{{disambig ...
OPG may refer to: *Osteoprotegerin *Office of the Public Guardian (other) *Office of HM Paymaster General *Online Policy Group *Ontario Power Generation * Open Government Partnership * Optical parametric generator *Orthopantomograph, a panoramic radiograph * Orthopantogram or Panoramic radiograph A panoramic radiograph is a panoramic scanning dental X-ray of the upper and lower jaw. It shows a two-dimensional view of a half-circle from ear to ear. Panoramic radiography is a form of focal plane tomography; thus, images of multiple pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
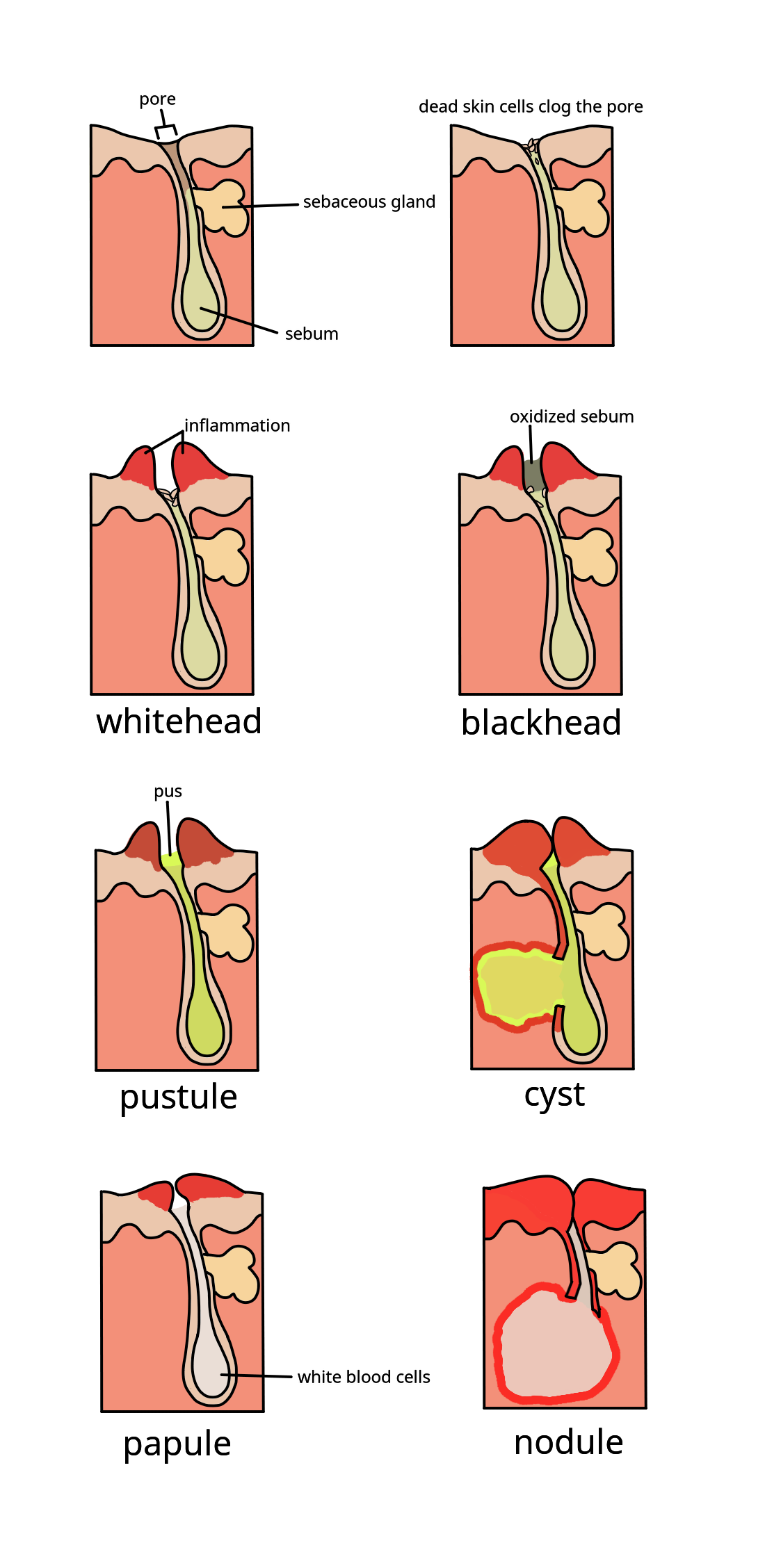
Acne
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term Cutaneous condition, skin condition that occurs when Keratinocyte, dead skin cells and Sebum, oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include comedo, blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and possible scarring. It primarily affects skin with a relatively high number of sebaceous gland, oil glands, including the face, upper part of the chest, and back. The resulting appearance can lead to anxiety (mood), anxiety, reduced self-esteem, and, in extreme cases, clinical depression, depression or suicidal ideations, thoughts of suicide. Susceptibility to acne is primarily genetic in 80% of cases. The roles of diet and cigarette smoking in the condition are unclear, and neither hygiene, cleanliness nor exposure to sunlight appear to play a part. In both sexes, hormones called androgens appear to be part of the underlying mechanism, by causing increased production of sebum. Another common fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanocytic Nevus
A melanocytic nevus (also known as nevocytic nevus, nevus-cell nevus and commonly as a mole) is a type of melanocytic tumor that contains nevus cells. Some sources equate the term mole with "melanocytic nevus", but there are also sources that equate the term mole with any nevus form. The majority of moles appear during the first two decades of a person's life, with about one in every 100 babies being born with moles. Acquired moles are a form of benign neoplasm, while congenital moles, or congenital nevi, are considered a minor malformation or hamartoma and may be at a higher risk for melanoma. A mole can be either subdermal (under the skin) or a pigmented growth on the skin, formed mostly of a type of cell known as a melanocyte. The high concentration of the body's pigmenting agent, melanin, is responsible for their dark color. Moles are a member of the family of skin lesions known as nevi and can occur in all mammalian species, but have been documented most extensively in humans, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tattoo
A tattoo is a form of body modification made by inserting tattoo ink, dyes, and/or pigments, either indelible or temporary, into the dermis layer of the skin to form a design. Tattoo artists create these designs using several Process of tattooing, tattooing processes and techniques, including hand-tapped traditional tattoos and modern tattoo machines. The history of tattooing goes back to Neolithic times, practiced across the globe by many cultures, and the symbolism and impact of tattoos varies in different places and cultures. Tattoos may be decorative (with no specific meaning), symbolic (with a specific meaning to the wearer), or pictorial (a depiction of a specific person or item). Many tattoos serve as Rite of passage, rites of passage, marks of status and rank, symbols of religious and spiritual devotion, decorations for bravery, marks of fertility, pledges of love, amulets and talismans, protection, and as punishment, like the marks of outcasts, slaves and convicts. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birthmark
A birthmark is a congenital, benign irregularity on the skin which is present at birth or appears shortly after birth—usually in the first month. They can occur anywhere on the skin. Birthmarks are caused by overgrowth of blood vessels, melanocytes, smooth muscle, fat, fibroblasts, or keratinocytes. Dermatologists divide birthmarks into two types: pigmented birthmarks and vascular birthmarks. Pigmented birthmarks caused by excess skin pigment cells include: moles, café au lait spots, and Mongolian spots. Vascular birthmarks, also called red birthmarks, are caused by increased blood vessels and include macular stains (salmon patches), hemangiomas, and port-wine stains. A little over 1 in 10 babies have a vascular birthmark present by age 1. Several birthmark types are part of the group of skin lesions known as nevi or naevi, which is Latin for "birthmarks". Birthmarks occur as a result of a localized imbalance in factors controlling the development and migration of skin ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |