|
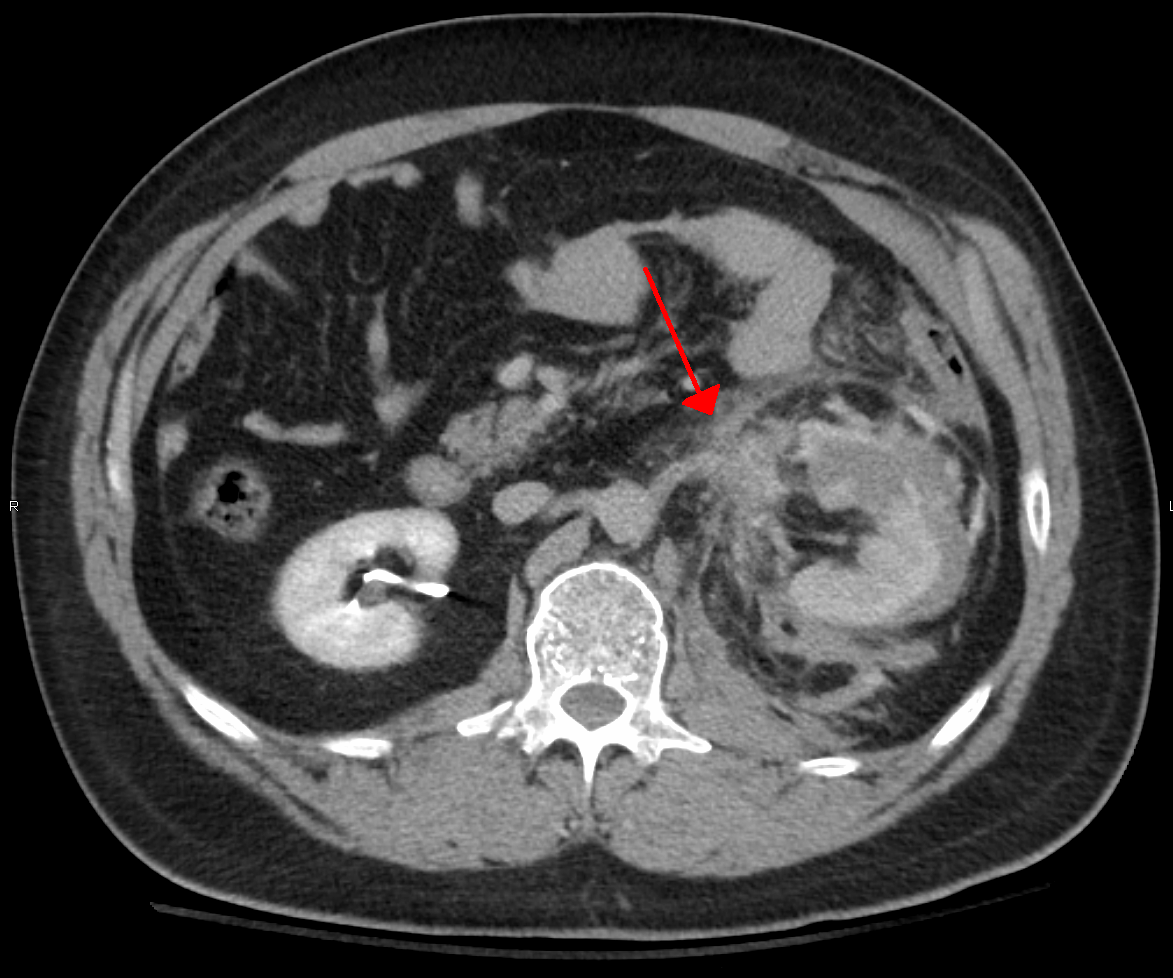
Blunt Kidney Trauma
The kidney is injured in approximately 10 percent of all significant blunt abdominal trauma. Of those, 13 percent are sports-related when the kidney, followed by testicle, is most frequently involved. However, the most frequent cause by far is traffic collisions, followed by falls. The consequences are usually less severe than injuries involving other internal organs. Sports related injury Blunt injuries to the kidney from helmets, shoulder pads, and knees are described in football, and in soccer, martial arts, and all-terrain vehicle crashes. A literature review of peer-reviewed articles in May 2009 demonstrated that urogenital injuries are uncommon in team and individual sports, and that most of them are low-grade injuries, cycling being the most commonly associated, followed by winter sports, horse riding and contact/collision sports. A special situation has existed in the athletic participant with a single kidney. Formerly, the American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Spo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, acid–base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hydrogen, ammonium, potassium and uric acid. The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. Each adult human kidney contains around 1 million nephrons, while a mouse kidney contains on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blunt Trauma
Blunt trauma, also known as blunt force trauma or non-penetrating trauma, is physical traumas, and particularly in the elderly who fall. It is contrasted with penetrating trauma which occurs when an object pierces the skin and enters a tissue of the body, creating an open wound and bruise. Blunt trauma can result in contusions, abrasions, lacerations, internal hemorrhages, bone fractures, as well as death. Blunt trauma represents a significant cause of disability and death in people under the age of 35 years worldwide. Classification Blunt abdominal trauma Blunt abdominal trauma (BAT) represents 75% of all blunt trauma and is the most common example of this injury. 75% of BAT occurs in motor vehicle crashes, in which rapid deceleration may propel the driver into the steering wheel, dashboard, or seatbelt, causing contusions in less serious cases, or rupture of internal organs from briefly increased intraluminal pressure in the more serious, depending on the force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urogenital
The genitourinary system, or urogenital system, are the organs of the reproductive system and the urinary system. These are grouped together because of their proximity to each other, their common embryological origin and the use of common pathways, like the male urethra. Also, because of their proximity, the systems are sometimes imaged together. The term "apparatus urogenitalis" was used in ''Nomina Anatomica'' (under Splanchnologia) but is not used in the current ''Terminologia Anatomica''. Development The urinary and reproductive organs are developed from the intermediate mesoderm. The permanent organs of the adult are preceded by a set of structures that are purely embryonic and that, with the exception of the ducts, disappear almost entirely before the end of fetal life. These embryonic structures are on either side: the pronephros, the mesonephros and the metanephros of the kidney, and the Wolffian and Müllerian ducts of the sex organ. The pronephros disappears very ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
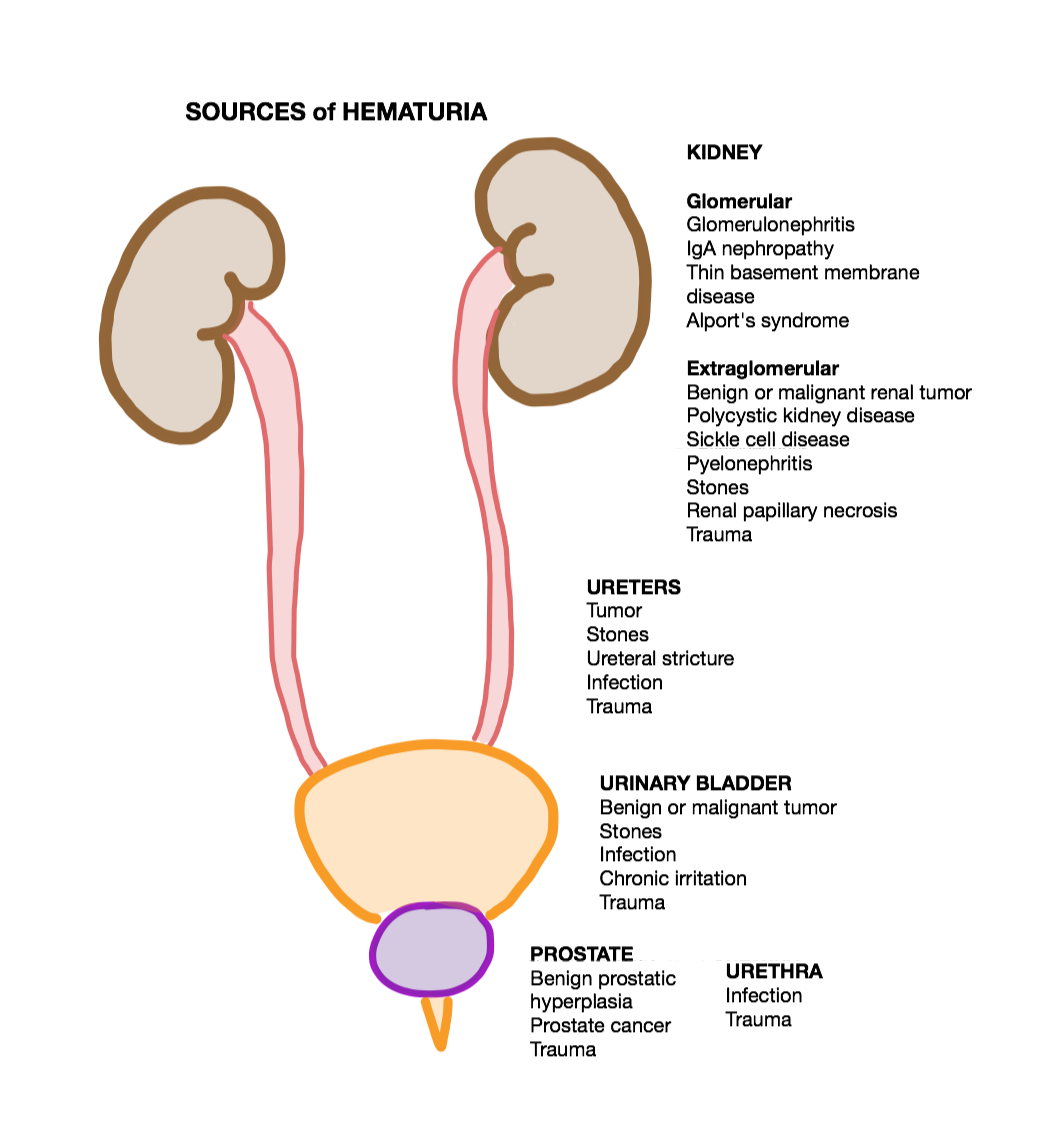
Hematuria
Hematuria or haematuria is defined as the presence of blood or red blood cells in the urine. “Gross hematuria” occurs when urine appears red, brown, or tea-colored due to the presence of blood. Hematuria may also be subtle and only detectable with a microscope or laboratory test. Blood that enters and mixes with the urine can come from any location within the urinary system, including the kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra, and in men, the prostate. Common causes of hematuria include urinary tract infection (UTI), kidney stones, viral illness, trauma, bladder cancer, and exercise. These causes are grouped into glomerular and non-glomerular causes, depending on the involvement of the glomerulus of the kidney. But not all red urine is hematuria. Other substances such as certain medications and foods (e.g. blackberries, beets, food dyes) can cause urine to appear red. Menstruation in women may also cause the appearance of hematuria and may result in a positive urine dipstick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shock (circulatory)
Shock is the state of insufficient blood flow to the tissues of the body as a result of problems with the circulatory system. Initial symptoms of shock may include weakness, fast heart rate, fast breathing, sweating, anxiety, and increased thirst. This may be followed by confusion, unconsciousness, or cardiac arrest, as complications worsen. Shock is divided into four main types based on the underlying cause: low volume, cardiogenic, obstructive, and distributive shock. Low volume shock, also known as hypovolemic shock, may be from bleeding, diarrhea, or vomiting. Cardiogenic shock may be due to a heart attack or cardiac contusion. Obstructive shock may be due to cardiac tamponade or a tension pneumothorax. Distributive shock may be due to sepsis, anaphylaxis, injury to the upper spinal cord, or certain overdoses. The diagnosis is generally based on a combination of symptoms, physical examination, and laboratory tests. A decreased pulse pressure (systolic blood pressure m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomography
Tomography is imaging by sections or sectioning that uses any kind of penetrating wave. The method is used in radiology, archaeology, biology, atmospheric science, geophysics, oceanography, plasma physics, materials science, astrophysics, quantum information, and other areas of science. The word ''tomography'' is derived from Ancient Greek τόμος ''tomos'', "slice, section" and γράφω ''graphō'', "to write" or, in this context as well, "to describe." A device used in tomography is called a tomograph, while the image produced is a tomogram. In many cases, the production of these images is based on the mathematical procedure tomographic reconstruction, such as X-ray computed tomography technically being produced from multiple projectional radiographs. Many different reconstruction algorithms exist. Most algorithms fall into one of two categories: filtered back projection (FBP) and iterative reconstruction (IR). These procedures give inexact results: they represent a compr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focused Assessment With Sonography For Trauma
Focused assessment with sonography in trauma (commonly abbreviated as FAST) is a rapid bedside ultrasound examination performed by surgeons, emergency physicians, and paramedics as a screening test for blood around the heart (pericardial effusion) or abdominal organs (hemoperitoneum) after trauma. There is also the extended FAST (eFAST) which includes some additional ultrasound views to assess for pneumothorax. The four classic areas that are examined for free fluid are the perihepatic space (including Morison's pouch or the hepatorenal recess), perisplenic space, pericardium, and the pelvis. With this technique it is possible to identify the presence of intraperitoneal or pericardial free fluid. In the context of traumatic injury, this fluid will usually be due to bleeding. Indications Reasons a FAST or eFAST would be performed would be: #Blunt abdominal trauma #Penetrating abdominal trauma #Blunt thoracic trauma #Penetrating thoracic trauma #Undifferentiated shock (low blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parenchyma
Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ or structure such as a tumour. In zoology it is the name for the tissue that fills the interior of flatworms. Etymology The term ''parenchyma'' is New Latin from the word παρέγχυμα ''parenchyma'' meaning 'visceral flesh', and from παρεγχεῖν ''parenchyma'' meaning 'to pour in' from παρα- ''para-'' 'beside' + ἐν ''en-'' 'in' + χεῖν ''chyma'' 'to pour'. Originally, Erasistratus and other anatomists used it to refer to certain human tissues. Later, it was also applied to plant tissues by Nehemiah Grew. Structure The parenchyma is the ''functional'' parts of an organ (anatomy), organ, or of a structure such as a tumour in the body. This is in contrast to the Stroma (animal tissue), stroma, which refers to the ''structural'' tissue of organs or of structures, namely, the connective tissues. Brain The brain parenchyma refers to the functional tissue in the brain that is made up of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |