|
Blue Dwarf (other)
The term blue dwarf refers to various types of stars having a peak emission in blue or ultraviolet. Those can be: Astronomical objects * A blue compact dwarf galaxy * An early-type main-sequence star ** B-type main-sequence star ** O-type main sequence star ** OB star * Blue dwarf (red-dwarf stage), a hypothetical stage in red dwarf interstellar evolution * O-type subdwarf * B-type subdwarf A B-type subdwarf (sdB) is a kind of subdwarf star with spectral type B. They differ from the typical subdwarf by being much hotter and brighter. They are situated at the "extreme horizontal branch" of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram. Masses o ... See also * Blue star (other) * Blue giant (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Compact Dwarf Galaxy
A dwarf galaxy is a small galaxy composed of about 1000 up to several billion stars, as compared to the Milky Way's 200–400 billion stars. The Large Magellanic Cloud, which closely orbits the Milky Way and contains over 30 billion stars, is sometimes classified as a dwarf galaxy; others consider it a full-fledged galaxy. Dwarf galaxies' formation and activity are thought to be heavily influenced by interactions with larger galaxies. Astronomers identify numerous types of dwarf galaxies, based on their shape and composition. Formation One theory states that most galaxies, including dwarf galaxies, form in association with dark matter, or from gas that contains metals. However, NASA's Galaxy Evolution Explorer space probe identified new dwarf galaxies forming out of gases with low metallicity. These galaxies were located in the Leo Ring, a cloud of hydrogen and helium around two massive galaxies in the constellation Leo. Because of their small size, dwarf galaxies have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main-sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell. Stars on this band are known as main-sequence stars or dwarf stars. These are the most numerous true stars in the universe and include the Sun. After condensation and ignition of a star, it generates thermal energy in its dense core region through nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium. During this stage of the star's lifetime, it is located on the main sequence at a position determined primarily by its mass but also based on its chemical composition and age. The cores of main-sequence stars are in hydrostatic equilibrium, where outward thermal pressure from the hot core is balanced by the inward pressure of gravitational collapse from the overlying layers. The strong dependence of the rate of energy gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-type Main-sequence Star
A B-type main-sequence star (B V) is a main-sequence (hydrogen-burning) star of spectral type B and luminosity class V. These stars have from 2 to 16 times the mass of the Sun and surface temperatures between 10,000 and 30,000 K. B-type stars are extremely luminous and blue. Their spectra have neutral helium, which are most prominent at the B2 subclass, and moderate hydrogen lines. Examples include Regulus and Algol A. This class of stars was introduced with the Harvard sequence of stellar spectra and published in the ''Revised Harvard photometry'' catalogue. The definition of type B-type stars was the presence of non-ionized helium lines with the absence of singly ionized helium in the blue-violet portion of the spectrum. All of the spectral classes, including the B type, were subdivided with a numerical suffix that indicated the degree to which they approached the next classification. Thus B2 is 1/5 of the way from type B (or B0) to type A. Later, however, more refined s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
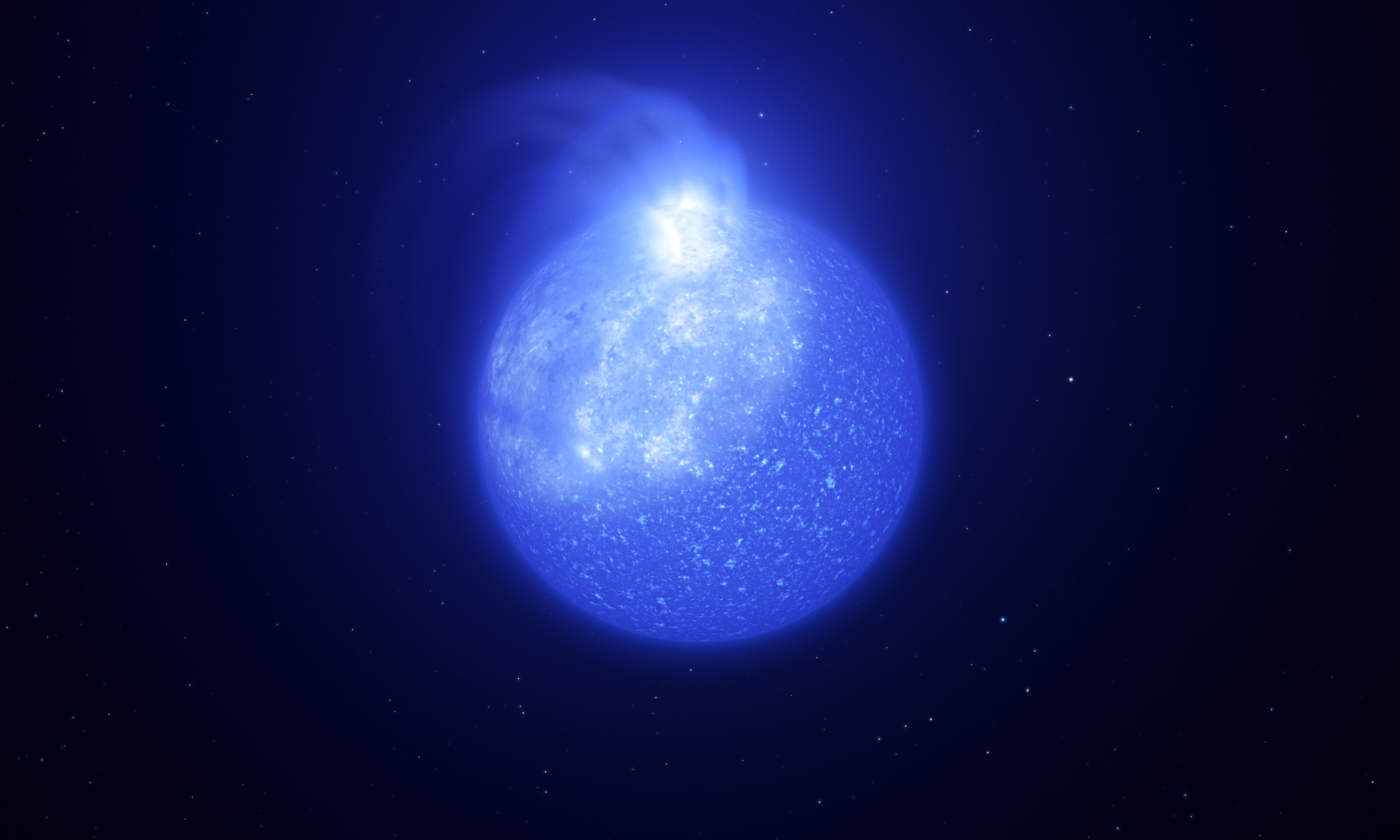
O-type Main Sequence Star
An O-type main-sequence star (O V) is a main-sequence (core hydrogen-burning) star of spectral type O and luminosity class V. These stars have between 15 and 90 times the mass of the Sun and surface temperatures between 30,000 and 50,000 K. They are between 40,000 and 1,000,000 times as luminous as the Sun. Spectral standard stars The "anchor" standards which define the MK classification grid for O-type main-sequence stars, i.e. those standards which have not changed since the early 20th century, are (O7 V) and (O9 V). The Morgan–Keenan–Kellerman (MKK) "Yerkes" atlas from 1943 listed O-type standards between O5 and O9, but only split luminosity classes for the O9s. The two MKK O9 V standards were Iota Orionis and . The revised Yerkes standards ("MK") presented listed in Johnson & Morgan (1953) presented no changes to the O5 to O8 types, and listed 5 O9 V standards (, , , , 10 Lacertae) and 3 O9.5 V standards (, Sigma Orionis, Zeta Oph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OB Star
OB stars are hot, massive stars of spectral types O or early-type B that form in loosely organized groups called OB associations. They are short lived, and thus do not move very far from where they formed within their life. During their lifetime, they will emit much ultraviolet radiation. This radiation rapidly ionizes the surrounding interstellar gas of the giant molecular cloud, forming an H II region or Strömgren sphere. In lists of spectra the ''"spectrum of OB"'' refers to ''"unknown, but belonging to an OB association so thus of early type"''. See also * O-type main-sequence star * B-type main-sequence star * Stellar kinematics In astronomy, stellar kinematics is the observational study or measurement of the kinematics or motions of stars through space. Stellar kinematics encompasses the measurement of stellar velocities in the Milky Way and its satellites as well as ... References * * External links * Bouy, Hervé and Alves, JoãoCosmography of OB Stars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Dwarf (red-dwarf Stage)
A blue dwarf is a predicted class of star that develops from a red dwarf after it has exhausted much of its hydrogen fuel supply. Because red dwarfs fuse their hydrogen slowly and are fully convective (allowing their entire hydrogen supply to be fused, instead of merely that in the core), they are predicted to have lifespans of trillions of years; the Universe is currently not old enough for any blue dwarfs to have formed yet, but their future existence is predicted based on theoretical models. Hypothetical scenario Stars increase in luminosity as they age, and a more luminous star needs to radiate energy more quickly to maintain equilibrium. Stars larger than red dwarfs do this by increasing their size and becoming red giants with larger surface areas. Rather than expanding, however, red dwarfs with less than 0.25 solar masses are predicted to increase their radiative rate by increasing their surface temperatures and becoming "bluer". This is because the surface layers of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
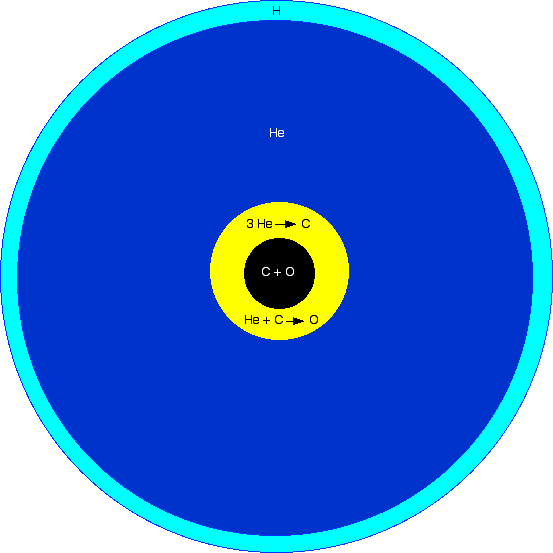
O-type Subdwarf
A subdwarf O star (sdO) is a type of hot, but low-mass star. O-type subdwarfs are much dimmer than regular O-type main-sequence stars, but with a brightness about 10 to 100 times that of the Sun, and have a mass approximately half that of the Sun. Their temperature ranges from 40,000 to 100,000 K. Ionized helium is prominent in their spectra. Gravity acceleration is expressed by log ''g'' between 4.0 and 6.5. Many sdO stars are moving at high velocity through the Milky Way and are found at high galactic latitudes. Structure The structure of a subdwarf O star is believed to be a carbon and oxygen core surrounded by a helium burning shell. The spectrum shows that the content is from 50 to 100% helium. History In the early 1970s Greenstein and Sargent measured temperatures and gravity strengths and were able to plot their correct position on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. The Palomar-Green survey, Hamburg surveys, Sloan Digital Sky Survey and Supernova Ia Progenitor Survey (ESO-SPY ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-type Subdwarf
A B-type subdwarf (sdB) is a kind of subdwarf star with spectral type B. They differ from the typical subdwarf by being much hotter and brighter. They are situated at the "extreme horizontal branch" of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram. Masses of these stars are around 0.5 solar masses, and they contain only about 1% hydrogen, with the rest being helium. Their radius is from 0.15 to 0.25 solar radii, and their temperature is from 20,000 to 40,000K. These stars represent a late stage in the evolution of some stars, caused when a red giant star loses its outer hydrogen layers before the core begins to fuse helium. The reasons why this premature mass loss occurs are unclear, but the interaction of stars in a binary star system is thought to be one of the main mechanisms. Single subdwarfs may be the result of a merger of two white dwarfs. The sdB stars are expected to become white dwarfs without going through any more giant stages. Subdwarf B stars, being more luminous than white ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Star (other)
Blue star or bluestar may refer to: * O-type star (a.k.a. blue star), a stellar classification Animals * ''Linckia laevigata'', a sea star from the Indian and West Pacific Oceans * '' Phataria unifascialis'', a sea star from the East Pacific Businesses * Blue Star (company), an Indian Air conditioning company * Blue Star Ferries, a Greek ferry company * Blue Star Infotech, Indian company * Blue Star Line, a former British shipping company * Blue Star Productions, a publishing imprint and a division of Book World, Inc * Bluestar (bus company), based in Southampton, England * Bluestar Company, a predecessor of ChemChina Military * Operation Blue Star, a 1984 Indian military operation * Blue stars used on service flags denote a United States service member fighting in a war ** Blue Star Memorial Highway, a system of highway markers honoring veterans ** Blue Star Mothers Club, a non-profit military support group Music * "Blue Star" (song), first recorded 1955 * ''Blue Star'' (al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |