|
Blorenge
Blorenge, also called The Blorenge (; cy, Blorens), is a prominent hill overlooking the valley of the River Usk near Abergavenny, Monmouthshire, southeast Wales. It is situated in the southeastern corner of the Brecon Beacons National Park. The summit plateau reaches a height of . Geography Blorenge overlooks the market town of Abergavenny and the villages of Llanfoist and Govilon in the Usk Valley to the north. At the foot of the hill lies the Monmouthshire & Brecon Canal. It drops away steeply to the northwest into Cwm Llanwenarth. To the south, gentler slopes fall away to Blaenavon at the head of the Lwyd valley. Prominent peaks seen from the Blorenge include the Skirrid to the east of Abergavenny and the Sugar Loaf to the north. The high moorland ridge continues to the south of the minor road at Foxhunter car park and assumes the name Mynydd y Garn-fawr. The cairn referenced in the title of this southerly shoulder of Blorenge may be that now known as Carn y Defaid whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abergavenny
Abergavenny (; cy, Y Fenni , archaically ''Abergafenni'' meaning "mouth of the River Gavenny") is a market town and community in Monmouthshire, Wales. Abergavenny is promoted as a ''Gateway to Wales''; it is approximately from the border with England and is located where the A40 trunk road and the A465 Heads of the Valleys road meet. Originally the site of a Roman fort, Gobannium, it became a medieval walled town within the Welsh Marches. The town contains the remains of a medieval stone castle built soon after the Norman conquest of Wales. Abergavenny is situated at the confluence of the River Usk and a tributary stream, the Gavenny. It is almost entirely surrounded by mountains and hills: the Blorenge (), the Sugar Loaf (), Ysgyryd Fawr (Great Skirrid), Ysgyryd Fach (Little Skirrid), Deri, Rholben and Mynydd Llanwenarth, known locally as " Llanwenarth Breast". Abergavenny provides access to the nearby Black Mountains and the Brecon Beacons National Park. The M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blaenavon Industrial Landscape
Blaenavon Industrial Landscape, in and around Blaenavon, Torfaen, Wales, was inscribed a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 2000. The Blaenavon Ironworks, now a museum, was a major centre of iron production using locally mined or quarried iron ore, coal and limestone. Raw materials and products were transported via horse-drawn tramroads, canals and steam railways. The Landscape includes protected or listed monuments of the industrial processes, transport infrastructure, workers' housing and other aspects of early industrialisation in South Wales. Location The Industrial Revolution in Britain was based on iron and coal, the main products of the South Wales valleys. Production of pig iron in the region grew from 39,600 tons in 1796 to 666,000 tons in 1852, and the iron was used to build railways, factories and engines around the world. Blaenavon was an important centre of coal mining and iron making in South Wales during the late 18th and early 19th centuries. The Blaenavon Ironwo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Llanfoist
Llanfoist ( cy, Llan-ffwyst) is both a village near Abergavenny, in Monmouthshire, Wales, and the community of Llanfoist Fawr. Llanfoist derives from ''Ffwyst'', an early Christian Welsh saint, although the anglicised version of the church patron is ''Saint Faith''. The population was 1,228 in 2011. The Church of St Faith 1901 Kelly's Directory of Monmouthshire describes the parish church of St Faith's: The church holds records for baptisms from 1736–1975, for marriages from 1736–1971, for banns from 1824–47 and 1890–1933, and for burials from 1736-1945. There are also Bishops Transcripts for 1725-32, 1734–51, 1753-4, 1756–75, 1777–1806, 1808–10, 1813, 1815–16, 1820–37, 1841–58, 1862–1865, 1869 and 1880. The parish of Llanelen has historically been held with Llanfoist, although since the retirement of the last resident Rector, the Reverend Thomas Arthur Foster (1923-2010) in 1992 the parishes have been served from Govilon ( Llanwenarth Ultra). At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Usk
The River Usk (; cy, Afon Wysg) rises on the northern slopes of the Black Mountain (''y Mynydd Du''), Wales, in the westernmost part of the Brecon Beacons National Park. Initially forming the boundary between Carmarthenshire and Powys, it flows north into Usk Reservoir, then east by Sennybridge to Brecon before turning southeast to flow by Talybont-on-Usk, Crickhowell and Abergavenny after which it takes a more southerly course. Beyond the eponymous town of Usk it passes the Roman legionary fortress of Caerleon to flow through the heart of the city of Newport and into the Severn Estuary at Uskmouth beyond Newport near the Newport Wetlands. The river is about long. The Monmouthshire and Brecon Canal follows the Usk for most of the length of the canal. Etymology The name of the river derives from a Common Brittonic word meaning "abounding in fish" (or possibly "water"), this root also appears in other British river names such as Exe, Axe, Esk and other variants. The nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skirrid
Ysgyryd Fawr ( en, Skirrid) is an easterly outlier of the Black Mountains in Wales, and forms the easternmost part of the Brecon Beacons National Park. The hill is often referred to locally as just The Skirrid. The smaller hill of Ysgyryd Fach or "Little Skirrid" (270m) lies about 4.5 km / 2.5 mi to the south. It is 486 m or 1594 feet high and lies just to the north-east of Abergavenny, Monmouthshire, about 10 miles from the English border. The Beacons Way passes along the ridge. Geology The distinctive shape of this Old Red Sandstone hill comprises a long ridge oriented nearly north–south, with a jagged western side resulting from ice age landslips . The upper slopes of the hill are composed of Devonian age sandstones assigned to the Senni Formation (formerly known as the "Senni Beds"). These overlie weaker mudstones of the St Maughans Formation - a situation which has contributed to the instability of the hill's steep flanks, resulting in a ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonian Period
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant adaptive radiation of life on dry land occurred during the Devonian. Free-sporing vascular plants began to spread across dry land, forming extensive forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants appeared. The arthropod groups of myriapods, arachnids and hexapods also became well-established early in this period, after starting their expansion to land at least from the Ordovician period. Fish reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The placoderms began dominating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Red Sandstone
The Old Red Sandstone is an assemblage of rocks in the North Atlantic region largely of Devonian age. It extends in the east across Great Britain, Ireland and Norway, and in the west along the northeastern seaboard of North America. It also extends northwards into Greenland and Svalbard. These areas were a part of the ancient continent of Euramerica, Euramerica/Laurussia. In Britain it is a lithostratigraphy, lithostratigraphic unit (a sequence of rock strata) to which Stratigraphy, stratigraphers accord Geological unit#Lithostratigraphic units, supergroup status and which is of considerable importance to early paleontology. For convenience the short version of the term, ORS is often used in literature on the subject. The term was coined to distinguish the sequence from the younger New Red Sandstone which also occurs widely throughout Britain. Sedimentology The Old Red Sandstone describes a suite of sedimentary rocks deposited in a variety of environments during the Devonian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carboniferous'' means "coal-bearing", from the Latin '' carbō'' ("coal") and '' ferō'' ("bear, carry"), and refers to the many coal beds formed globally during that time. The first of the modern 'system' names, it was coined by geologists William Conybeare and William Phillips in 1822, based on a study of the British rock succession. The Carboniferous is often treated in North America as two geological periods, the earlier Mississippian and the later Pennsylvanian. Terrestrial animal life was well established by the Carboniferous Period. Tetrapods (four limbed vertebrates), which had originated from lobe-finned fish during the preceding Devonian, became pentadactylous in and diversified during the Carboniferous, including early amphibian line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coity Mountain
Coity Mountain (also spelled ''Coety Mountain'', Welsh: ''Mynydd Coety'') is a flat-topped mountain in the South Wales Valleys, between Blaenavon and Abertillery. The highest points of both Torfaen and Blaenau Gwent unitary authorities are at the summit of Coity Mountain. The summit is also known as Twyn Ffynhonnau Goerion. Some to the southeast lies a major subsidiary top of the hill, Mynydd Varteg Fawr (549m) at the southeastern end of whose broad ridge is a trig point at 544m. A few hundred metres to the southeast of this summit is a memorial known as the "Dog Stone" which commemorates ''Carlo the Red Setter'', a dog shot accidentally by his master while hunting on the 12 August 1864. Co-ordinates for the Dog Stone 51.45'15.58N 3.05'08.81W. Other notable tops include those of Mulfran (524m) (Welsh Welsh may refer to: Related to Wales * Welsh, referring or related to Wales * Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales * Welsh people People * Welsh (surname) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal Measures
In lithostratigraphy, the coal measures are the coal-bearing part of the Upper Carboniferous System. In the United Kingdom, the Coal Measures Group consists of the Upper Coal Measures Formation, the Middle Coal Measures Formation and the Lower Coal Measures Formation. The group records the deposition of fluvio-deltaic sediments which consists mainly of clastic rocks (claystones, shales, siltstones, sandstones, conglomerates) interstratified with the beds of coal. In most places, the coal measures are underlain by coarser clastic sequences known as Millstone Grit, of Namurian age. The top of the coal measures may be marked by an unconformity, the overlying rocks being Permian or later in age. In some parts of Britain, however, the coal measures grade up into mainly coal-barren red beds of late Westphalian and possibly Stephanian age. Within the Pennine Basin these barren measures are now referred to as the Warwickshire Group, from the district where they achieve their thickest d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
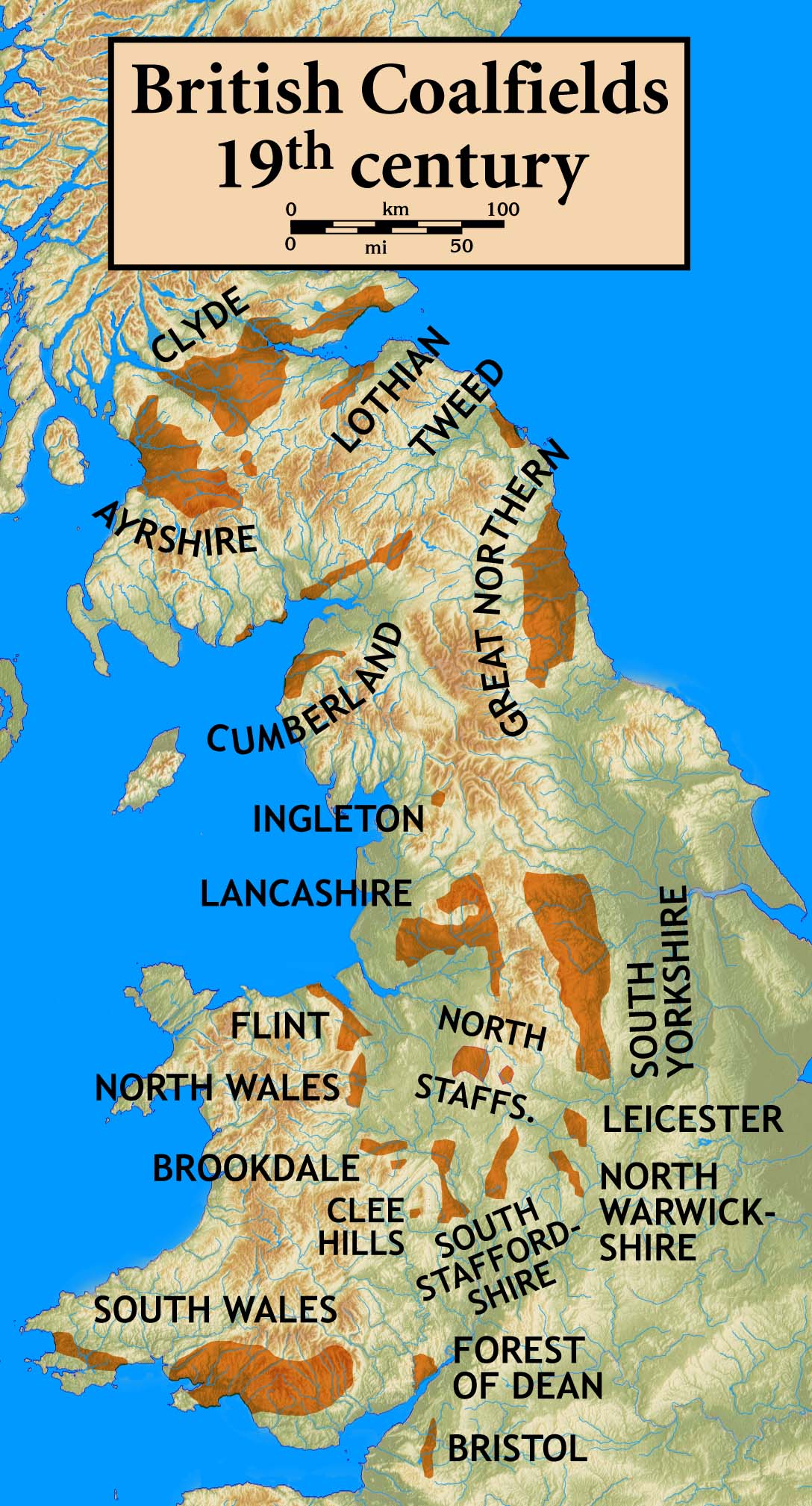
South Wales Coalfield
The South Wales Coalfield ( cy, Maes glo De Cymru) extends across Pembrokeshire, Carmarthenshire, Swansea, Neath Port Talbot, Bridgend, Rhondda Cynon Taf, Merthyr Tydfil, Caerphilly, Blaenau Gwent and Torfaen. It is rich in coal deposits, especially in the South Wales Valleys. Description It comprises a fully exposed synclinorium with a varying thickness of coal measures (Upper Carboniferous/Pennsylvanian) with thick, workable seams in the lower parts and generally thinner and sparser seams in the upper parts, together with a development of sandstones (Pennant Sandstone). These sandstones have been much used in building construction (including the characteristic terraces of former miners' houses) and give rise to bleak uplands rising 300–600 metres above sea level between the steep-sided valleys in which most deep mines were developed. The coal generally increases in grade or "rank" from east to west, with bituminous coals in the east, and anthracite in the west, mostly to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)